A belly button hernia is also known as an umbilical hernia or an epigastric hernia. This is a weakness in the wall of your abdomen that appears as a bulge near the navel. When the abdominal wall muscles are weak, the gut, fluid, Intestine, or fat can push through and protrude in the muscles around the belly button.
An umbilical hernia is a very common disorder, and most people suffer from it in life. It can happen to anyone, at any age, and of any gender. But the incidence in women is more than five times that of men. Pregnancy, obesity, and loose abdominal muscles are the common causes of umbilical hernias.
An umbilical hernia usually happens during pregnancy as the growing baby pushes the abdominal wall, making it weak and prone to hernia. It can also occur due to a weakness in the abdominal wall at birth.
Belly button hernia can be treated at home as well. However, in some cases, it might be recommended to get medical help. This article will discuss everything about belly button hernia, from its causes to its treatment.
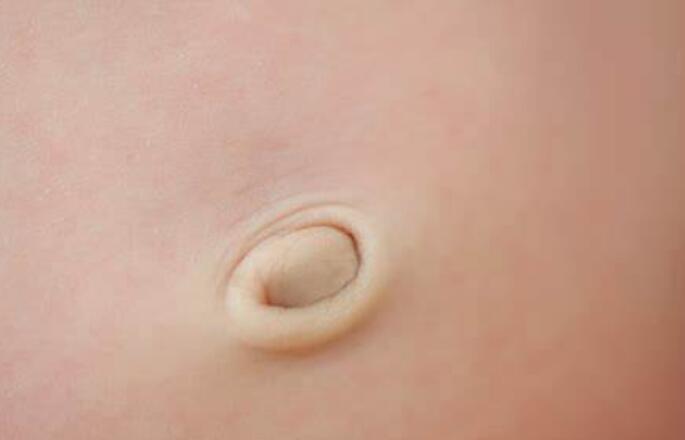
Symptoms of a Belly Button Hernia(umbilical hernia)
The most common symptom of a hernia is a bulge under the skin. If the hernia becomes large, the swelling may become very painful.
Pain – If the hernia becomes large enough, it can become very painful.
Lump – A slight bulge may be felt or seen in the skin near the belly button.
Swelling – Small hernias may not produce any noticeable swelling.
Lump when coughing, sneezing, or lifting – You may feel a lump when coughing, sneezing or lifting heavy products.
Darkening of the skin around the hernia – This discoloration is caused by blood seeping from the wound into the surrounding tissues.
Retraction – A large hernia that protrudes below the skin level may retract into the belly button when coughing, bending, or straining.
Causes of a Belly Button Hernia in adults(umbilical hernia)
There are many causes of a belly button hernia, including:
1. Age: The most common cause of a belly button hernia is age. As a person ages, the walls of the abdominal muscles become weaker and lose their elasticity. This makes it easier for fatty tissue and organs to push through the weakened abdominal wall and form a hernia.
2. Obesity: Obese and overweight individuals are more prone to developing belly button hernias than those with a healthy weight. This is because excess fat can strain the abdominal wall, weakening it and making it more prone to herniation.
3. Genetics: Genetics can play a significant role in determining whether or not someone is more likely to develop a hernia. If a family has a history of hernias, then it is more likely that other family members will develop one as well.
4. Pregnancy: During pregnancy, the uterus grows in size, which puts extra pressure on the abdominal wall. This can weaken the abdominal wall and lead to a hernia in the belly button area.
5. Heavy Lifting: Heavy lifting, such as lifting weights or lifting objects that are too heavy for you, can strain the abdominal wall and lead to a hernia.
6. Chronic Coughing: Chronic coughing can strain the abdominal wall and lead to a hernia. This is because the pressure from the coughing can push organs and fatty tissue through the weakened abdominal wall.
7. Surgery: Surgery on the abdomen, such as appendectomy, can weaken the abdominal wall and increase the risk of a hernia.
8. Straining During Bowel Movements: Straining too much during bowel movements can also strain the abdominal wall, weakening it and making it more likely that a hernia will form.
9. Enlarged Abdominal Organs: An enlarged abdominal organ, such as the stomach, can press against the abdominal wall, putting strain on it and leading to a hernia.
10. Injury: Injury can also cause a belly button hernia. Trauma to the abdominal area can weaken the abdominal muscles and cause the organs or fatty tissue to push through the weakened area.
Who is more prone to suffer from belly button hernia?
Belly button hernia is most commonly seen in adults but can also occur in infants. Both men and women can suffer from belly button hernia, but men are more prone to it than women. This is because men generally have higher rates of obesity, which increases the risk of developing hernias.
Additionally, men typically engage in more strenuous physical activities, which can cause hernias to form. Obesity is a major risk factor for belly button hernias, as excess fat in the abdominal area can put increased pressure on the muscles and soft tissues in the area.
This can weaken the abdominal wall and cause hernias to form. Other risk factors include advancing age, family history, heavy lifting, chronic constipation, and prior surgery.
Infant belly button hernia
An infant belly button hernia is a bulge you can see at your baby’s belly button, where the skin has stretched and gathered. A hernia happens when something comes through the muscle wall, like a piece of the intestine or a blood vessel.
A baby belly button hernia occurs at the umbilical cord’s exit when the skin has been stretched, but no intestine or blood vessel is underneath.
Little red or purple dots can signify a hernia, or you may notice your baby’s navel looks larger than usual or puffier than before, like a strawberry.
How is an umbilical hernia diagnosed?
An umbilical hernia is typically diagnosed during a physical exam. During the exam, the doctor will look for a bulge or lump around the navel. This is usually the first sign of an umbilical hernia.
The doctor may also ask you to cough or strain your abdominal muscles to see if the bulge becomes more pronounced. Additional tests may also be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. This may include an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI.
These tests can help determine the size of the hernia and if any organs are trapped there. Blood tests may also be taken to check for signs of infection or to check your overall health. Sometimes, the doctor may also order an X–ray to look for signs of a hernia.
Is an umbilical hernia dangerous in adults?
An umbilical hernia is a small pocket of tissue that protrudes through the muscle near your belly button. It’s common in adults, especially those who are overweight or have a large belly.
Umbilical hernias don’t cause problems for most people, and they often go away independently as you lose weight. If an umbilical hernia is large and causing problems, such as pain or skin irritation, you may want to surgically repair it.
Home Remedies for umbilical hernia
1. Exercise: Exercise is one of the most effective home remedies for an umbilical hernia. Activities such as walking, swimming, and yoga can help strengthen the abdominal muscles, which can help reduce the pressure on the hernia and prevent it from getting worse.
2. Proper Posture: Maintaining good posture is important for preventing and reducing the symptoms of an umbilical hernia. Make sure to stand up straight and keep your back straight. Avoid bending or stooping too much, and avoid carrying heavy objects.
3. Avoid Heavy Lifting: Heavy lifting can increase the pressure on the hernia and make it worse. To reduce the risk of an umbilical hernia, avoid lifting or carrying heavy objects.
4. Wear a Supportive Binder: Wearing a supportive binder around your abdomen can help reduce the pressure on the hernia and help prevent it from getting worse.
5. Eat a Healthy Diet: Eating a healthy diet is important for maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of an umbilical hernia. Eating a diet high in fiber, low in fat, and rich in fruits and vegetables can help keep your body healthy and reduce the risk of an umbilical hernia.
6. Avoid Tight Clothing: Avoid wearing tight clothing, especially around your abdomen, as this can put extra pressure on the hernia and worsen it.
Medical treatment for umbilical hernia
1. Surgery: Surgery is the most common and effective treatment for umbilical hernias. The procedure involves making a small incision in the abdominal wall, pushing the hernia back into place, and then stitching the area closed. Surgery is the best option for treating umbilical hernias.
2. Hernia Belt: A hernia belt is a type of supportive garment that can be used to treat umbilical hernias. It is worn around the waist and is designed to pressure the hernia, pushing it back into place. This can help reduce the size of the hernia and provide symptom relief.
3. Medications: In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications to treat the symptoms of an umbilical hernia. This may include pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, to reduce discomfort. Antacids may also be prescribed to reduce stomach acid, which can help reduce the pressure in the abdominal area.
How much does umbilical hernia surgery cost?
The cost of Umbilical hernia surgery depends on many factors, including the severity of the hernia and the type of procedure performed.
Generally speaking, the cost of umbilical hernia surgery can range anywhere from $1,000 to $5,000. The type of procedure performed is a major factor in the cost of the surgery.
Laparoscopic umbilical hernia repair is a less invasive technique that allows for quicker recovery and typically costs less than open hernia repair.
The cost of open hernia repair depends on the severity of the hernia and the surgeon’s experience. Anesthesia costs are also a factor when determining the cost of umbilical hernia surgery.
The cost of anesthesia can range from $500 to $2,000 depending on the type of anesthesia used and the amount of time spent in the operating room.
When to see a doctor?
It is important to seek medical attention if you have any of the following symptoms with your umbilical hernia:
- Pain or tenderness around the umbilical area
- Swelling or lump in the umbilical area
- Redness or discoloration around the umbilical area
- Vomiting or difficulty eating
- High Fever
- Inability to pass gas or stool
- Difficulty breathing
- Inability to move the hernia back into the abdomen