Black spots in vision can be a common problem for many people. These spots, which may appear as tiny dots or large patches, can interfere with normal vision and cause discomfort. In this article, we’ll discuss the ten most common causes of black spots in vision and the treatment options available for each.
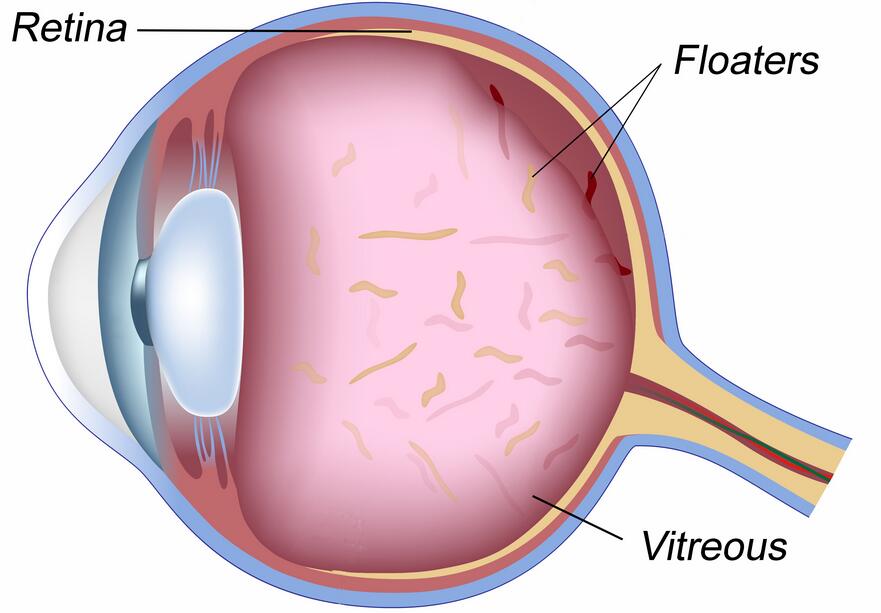
What are Eye floaters?
Before diving into the remedies, let’s better understand what black spots in vision are. Floaters appear as small, shadowy specks or cobweb-like structures that drift across your visual field, often following the movement of your eyes. They are most noticeable when looking at a plain, bright background, such as a clear sky or a white wall.
The primary cause of floaters is age-related changes in the vitreous, the gel-like substance that fills the eye’s interior. As we age, the vitreous begins to liquefy and shrink, causing tiny fibers within it to clump together.
These clumps cast shadows on the retina, resulting in the perception of black spots or floaters. Although most cases of floaters are harmless, there are instances where they can indicate a more serious condition, such as retinal detachment or bleeding within the eye.
Symptoms of Black Spots in Vision
The symptoms of black spots in vision can vary depending on the underlying cause. Some common symptoms include:
- Small, dark spots or specks move around when you move your eyes
- Cobweb-like shapes that float across your vision
- Shadows or spots that move when the eyes move
- Flashes of light
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Loss of vision in the affected eye (in severe cases)
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately.
10 Common Causes of Black Spots in Vision
The following are the common causes of black spots in vision:
1. Vitreous Floaters
Vitreous floaters are a common cause of black spots in vision. These tiny, dark specks or lines appear to float across your field of vision.
They are caused by tiny fibers in the vitreous, a gel-like substance in the eye. The vitreous may shrink and pull away from the retina as we age. This causes the fibers to clump together and cast shadows on the retina, resulting in the appearance of floaters.
While vitreous floaters are usually harmless and don’t require treatment, they can be annoying and interfere with your vision. If you notice a sudden increase in the number of floaters, especially if accompanied by light flashes or a loss of peripheral vision, you should see your eye doctor immediately.
In most cases, vitreous floaters will eventually settle out of your field of vision. But surgery may be an option if they are severe and affecting your vision.
2. Retinal Tear or Detachment
A retinal tear or detachment can cause black spots in your vision. The retina is a layer of tissue at the back of your eye that senses light and sends signals to your brain to create images.
A retinal tear or detachment occurs when the retina is lifted or pulled away from its normal position, which can happen due to several reasons, such as injury, aging, or certain eye conditions.
A retinal tear or detachment can lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated. Treatment options for a retinal tear or detachment depend on the severity and location. This may include laser surgery, cryotherapy, or pneumatic retinopexy. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to reattach the retina and restore vision.
3. Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration is a common eye disease that can cause black spots in your vision. The macula is a small but essential part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. In macular degeneration, the cells in the macula begin to break down, causing vision loss in the center of your visual field.
There are two types of macular degeneration – dry and wet. Dry macular degeneration is the more common type and progresses slowly over time, while wet macular degeneration progresses more quickly and can cause more severe vision loss.
The exact cause of macular degeneration is unknown, but factors such as age, genetics, and smoking may increase your risk of developing the condition.
There is no cure for macular degeneration, but treatment options are available to slow its progression and preserve the remaining vision. These may include medications, laser therapy, photodynamic therapy, or in advanced cases, surgery.
4. Migraines
Migraines can cause black spots or blind spots in your vision, known as a visual aura, before the onset of a headache. These visual disturbances can include flickering lights, zigzag lines, or blind spots, typically lasting for 20-30 minutes. Some people may also experience other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light.
The exact cause of migraines is not fully understood, but they are believed to be related to changes in the brain and the release of certain chemicals. Various factors, such as stress, certain foods or drinks, hormonal changes, or sleep patterns, can trigger migraines.
Treatment for migraines may include medications to relieve pain and manage symptoms and lifestyle modifications to avoid triggers and promote overall wellness. In some cases, preventive medications may be prescribed to reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
5. Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that can cause black spots in your vision and eventually lead to permanent vision loss. Glaucoma occurs when the optic nerve, which carries visual information from the eye to the brain, becomes damaged due to increased pressure inside the eye.
There are several types of glaucoma, but the most common type is primary open-angle glaucoma. This type of glaucoma often has no noticeable symptoms in its early stages. It can cause gradual vision loss over time, starting with the peripheral vision before affecting the central vision.
Treatment for glaucoma typically involves reducing the intraocular pressure with medications, eye drops, laser treatment, or surgery.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing glaucoma and preventing vision loss. Regular eye exams can help detect glaucoma in its early stages, especially if you have risk factors such as a family history of the condition or high eye pressure.
6. Cataracts
Cataracts are a common eye condition that can cause black spots or cloudy areas in your vision. A cataract is a clouding of the natural lens in your eye that occurs as you age or due to other factors such as injury or certain medications.
As the cataract grows, it can cause vision problems such as blurry or dim vision, difficulty seeing at night, and sensitivity to glare.
7. Age-related changes
Age-related changes in the eye can also cause black spots or other vision disturbances. As you age, the natural lens in your eye may become less flexible and less able to change shape to focus on close objects, a condition known as presbyopia. This can make reading or doing close work more difficult.
Additionally, age-related changes in the retina or macula can cause black spots or distortions in your vision. These changes may include the development of drusen, tiny yellow or white deposits in the retina, or the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the macula. These changes can lead to age-related macular degeneration or diabetic retinopathy.
8. Eye injuries
Eye injuries can cause black spots or other vision disturbances, depending on the location and severity of the injury. Eye injuries can result from various causes, such as accidents, sports, or exposure to hazardous substances.
Eye injuries can also cause bleeding, damage to the retina or optic nerve, or a foreign object in the eye.
Treatment for eye injuries may depend on the severity of the injury and can range from simple measures to more advanced treatments, such as surgery. If you experience an eye injury, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately to prevent further damage and preserve vision.
9. Diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that can cause black spots or other vision disturbances. Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye essential for vision. This damage can cause the blood vessels to leak or become blocked, leading to vision problems.
Early stages of diabetic retinopathy may not cause noticeable symptoms. But as the condition progresses, it can cause blurred or distorted vision, black spots or floaters, and even vision loss. People with diabetes are at higher risk of developing diabetic retinopathy, especially if their blood sugar levels are poorly controlled.
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy may include laser treatment or surgery to seal leaking blood vessels or remove abnormal blood vessels. In some cases, medication injections may also help reduce inflammation or control the growth of new blood vessels.
10. High blood pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, can cause black spots or other vision disturbances, especially if left untreated. High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels throughout the body, including those in the eye. This damage can cause the blood vessels to leak or become blocked, leading to vision problems.
Symptoms of high blood pressure in the eye may include blurred or distorted vision, double vision, or floaters. In severe cases, high blood pressure in the eye can lead to optic nerve damage or even vision loss.
Treatment for high blood pressure may include lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking, and medication to lower blood pressure. Controlling high blood pressure can help reduce the risk of eye complications and vision problems.

When to see a doctor?
Here are some signs and symptoms that may indicate the need for a visit to the eye doctor:
- New or sudden onset of black spots in vision
- Flashes of light or loss of peripheral vision
- Blurred vision or double vision
- Eye pain or discomfort
- Redness or swelling in the eye
FAQs
1. Can black spots in vision be a sign of a serious eye condition?
While most black spots in vision are harmless, they can sometimes indicate a more serious eye condition, such as retinal detachment or bleeding within the eye. It’s crucial to consult with an eye care professional if you experience sudden or significant changes in your vision.
2. Are black spots in vision treatable with medication?
In most cases, black spots in the vision do not require medication for treatment. However, if the floaters significantly affect your quality of life or are associated with an underlying eye condition, your eye care professional may recommend specific treatments or surgeries.
3. Can dietary supplements improve black spots in vision?
While certain dietary supplements claim to improve eye health, there is limited scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness in treating black spots in vision. It’s best to consult with your eye care professional before starting any dietary supplement regimen.
4. Can black spots in vision disappear on their own?
In many cases, black spots in vision gradually become less noticeable over time as the brain learns to ignore them. However, monitoring any changes in your vision is important, and seeking professional advice if needed.
5. Can black spots in the vision be prevented?
While it may not be possible to prevent black spots in vision entirely, adopting a healthy lifestyle, protecting your eyes from UV rays, and having regular eye examinations can help reduce the occurrence and severity of floaters.