Bruises, also known as contusions, are common in our lives. They typically arise from trauma to the skin, resulting in discoloration due to blood leaking from damaged blood vessels into the surrounding tissues. While most bruises go away within about 1-2 weeks. However, there are instances it may take a little longer to heal. This article will explore the 12 possible causes of bruises that won’t go away.
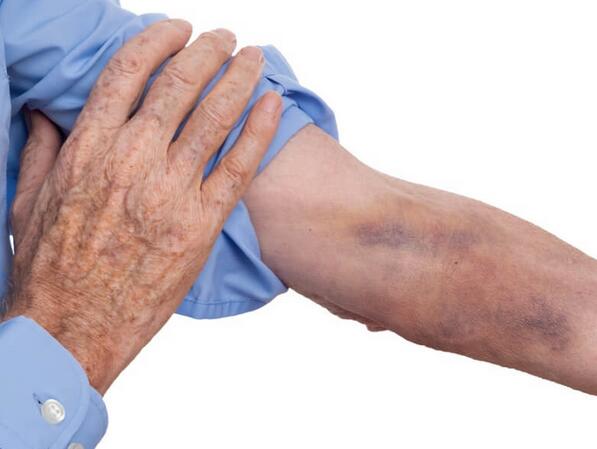
12 Common Causes of Bruise Won’t Go Away
The common causes of the bruise on the arm that won’t go away are given below.
1. Trauma to Deep Tissues
Trauma to deep tissues is a significant factor in bruises that won’t disappear. Unlike superficial bruises, these injuries can affect blood vessels and tissues beneath the skin. This will lead to more substantial and long-lasting bruising.
Falls, sports injuries, and accidents are common causes of deep tissue trauma that can result in persistent bruises.
2. Blood Disorders
Certain blood disorders can affect clotting abilities and lead to bruises that take longer to heal. Conditions such as hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, or platelet disorders can hinder the body’s natural healing process, causing bruises to persist.
3. Medications
Certain medications, particularly blood thinners like warfarin or aspirin, can increase the likelihood of developing bruises. These medications interfere with clotting, making it difficult for bruises to heal promptly.
- Omega 3 Fatty Acids: A Supplemental Risk
Omega 3 fatty acids, although beneficial in many ways, can increase the risk of bleeding and bruising when taken in high doses.
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): Medications for Depression and Anxiety
Some individuals taking SSRIs, commonly prescribed for depression and anxiety, have reported increased bruising.
- Blood Thinners: Warfarin, Heparin, and Low-Dose Aspirin
Long-term use of blood-thinning medications, such as warfarin, heparin, and low-dose baby aspirin, can contribute to bruises that do not fade quickly.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Potentially Thinning the Blood
Certain anti-inflammatory medications, known as NSAIDs, may possess blood-thinning properties, which can heighten the risk of internal bleeding and persistent bruising.
4. Aging
As we age, our skin becomes thinner and loses some of its protective fatty tissue. This natural aging process makes blood vessels more susceptible to damage.
This will result in bruises that are slower to fade. Additionally, reduced collagen production in older individuals further delays the healing of bruises.
5. Vitamin Deficiencies
A deficiency in essential vitamins, particularly vitamins C, K, and D, can impact the body’s ability to repair damaged blood vessels and tissues. Adequate levels of these vitamins are crucial for efficient clotting and healing.
Here are some specific nutrients that may play a role in the persistence of bruises:
- Vitamin C: The Wound Healer
Vitamin C is crucial for accelerating wound healing and maintaining healthy blood vessels. Inadequate levels of vitamin C can impede the healing process, leading to prolonged bruising.
- Zinc: Nourishing the Skin
Zinc is responsible for nourishing the skin and promoting wound healing. Insufficient zinc levels may result in anemia and excessive bruising.
- Vitamin K: Vital for Blood Clotting
Vitamin K is necessary for proper blood clotting. Individuals with vitamin K deficiencies may experience more bruises and slower healing times.
6. Sun Exposure

Excessive exposure to the sun’s harmful UV rays can weaken blood vessels and make the skin more prone to bruising. Prolonged sun exposure can cause damage that interferes with healing. This will result in bruises that last longer than usual.
7. Infections
Viral and bacterial infections can compromise the body’s immune system and weaken blood vessels. When the immune response is impaired, bruises may take longer to heal. Infections such as cellulitis, sepsis, or certain sexually transmitted diseases can lead to persistent bruising.
8. Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can cause recurring or chronic bruising. Conditions like leukemia, liver disease, kidney disease, or autoimmune disorders can disrupt normal blood clotting and healing mechanisms. This will lead to bruises that won’t go away.
9. Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Heavy alcohol consumption can interfere with blood clotting and lead to prolonged bruising. Alcohol dilates blood vessels and impairs platelet function, making it more difficult for bruises to heal.
10. Allergies
Allergic reactions can cause inflammation and weaken blood vessels, making them more susceptible to damage. If you suspect allergies cause your ongoing bruising, consult an allergist to identify potential triggers.
11. Cancer
Certain types of cancer, such as leukemia or lymphoma, can manifest as persistent bruising. Cancerous cells can infiltrate blood vessels, disrupting normal clotting mechanisms and leading to unexplained bruises.
If you have concerns about persistent bruising and suspect an underlying cancer condition, it’s crucial to seek medical evaluation promptly.
12. Diabetes
People with diabetes may experience slower wound healing and prolonged bruising. This is due to impaired blood circulation and compromised tissue repair processes. Proper blood sugar control is essential to minimize the risk of persistent bruising.
Home Remedies for Bruises That Won’t Go Away
1. Arnica
Arnica is a widely recognized natural remedy for bruises. It has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce swelling and promote healing.
Apply arnica gel or cream topically to the affected area several times daily. Remember to avoid using arnica on broken skin.
2. Cold Compress
Applying a cold compress to a bruise can help reduce swelling and pain. Wrap a few ice cubes in a clean cloth or use a cold pack and gently press it against the bruise for about 10 minutes. Repeat this process a few times a day for optimal results.
3. Warm Compress
After the initial 24 hours of a bruise, applying a warm compress can help increase blood circulation and promote healing.
Soak a clean cloth in warm water, wring out the excess, and gently apply it to the bruised area. Leave it on for 10-15 minutes and repeat it several times daily.
4. Pineapple

Pineapple contains bromelain, an enzyme known for its anti-inflammatory properties. Consuming pineapple or drinking fresh pineapple juice can help reduce swelling and speed up the healing process. Alternatively, you can apply fresh pineapple directly to the bruise for relief.
5. Witch Hazel
Witch hazel is a natural astringent that can help reduce inflammation and improve blood circulation. Soak a cotton ball in witch hazel and apply it to the bruise a few times a day. This remedy can also help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with bruises.
6. Comfrey
Comfrey is an herb traditionally used to heal bruises and minor wounds. Its anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce swelling and promote healing. You can make a poultice by crushing comfrey leaves and applying them directly to the bruise.
7. Essential Oils

Certain essential oils, such as lavender, chamomile, and helichrysum, possess soothing and healing properties that can aid in the recovery of bruises. Dilute a few drops of essential oil in a carrier oil, such as coconut or almond oil, and gently massage it into the bruised area.
8. Vitamin K Cream
Topical creams containing vitamin K can help speed up the healing process of bruises. Vitamin K plays a crucial role in blood clotting and can reduce the appearance of bruises when applied directly to the affected area.
9. Epsom Salt Soak
Epsom salt is known for reducing inflammation and relieving muscle soreness. Dissolve a cup of Epsom salt in warm bathwater and soak in it for 15-20 minutes. This remedy can help improve blood circulation and promote the healing of bruises.
10. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is a versatile remedy that can help fade bruises. Dilute apple cider vinegar with water and apply it to the bruised area using a clean cloth. The acidic properties of apple cider vinegar can help reduce discoloration and promote faster healing.
11. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera has soothing and healing properties that can benefit bruises. Apply fresh aloe vera gel to the bruise, or use aloe vera cream or lotion. This natural remedy can help reduce pain and inflammation and promote skin repair.
12. Rest and Elevate
Rest and elevation are among the simplest yet most effective remedies for bruises. Resting the affected area and elevating it above heart level can help reduce swelling and promote faster healing. Take breaks and avoid putting unnecessary pressure on the bruise
When to see a doctor?
A simple bruise does not need a doctor. If you have a bruise for some days and it turns to heal with the signs of lighter color and yellow, you are safe. This color formation occurs on the outer edges of the bruise if the bruise is healing. On the contrary, if a bruise appears purple or blue and spreads further, you should see a doctor immediately.
In addition, If a bruise hasn’t started healing within two to three weeks or if you notice other concerning symptoms such as pain, swelling, or unusual discoloration, it’s advisable to seek medical attention.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can massaging a bruise make it heal faster?
Gentle massage around the bruised area can stimulate blood flow and promote healing. However, it’s crucial to avoid applying excessive pressure or massaging directly on the bruise, as this can worsen the injury and delay healing. If you’re unsure about massaging a bruise, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
2. Should I avoid physical activity if I have a bruise that won’t go away?
Light physical activity is generally safe and may even promote blood circulation, which can aid in the healing process.
However, it’s important to avoid strenuous activities or activities that may further traumatize the affected area. If you have concerns, consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
3. Can natural supplements help with persistent bruising?
Some natural supplements, such as bromelain (derived from pineapple) or arnica Montana, are believed to have anti-inflammatory properties that may aid in reducing bruising and promoting healing.
However, consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements is essential to ensure their safety and efficacy.
4. Can certain foods or supplements help in bruise healing?
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is essential for overall health and can indirectly support healing. Foods rich in vitamins C, and K, and antioxidants, such as citrus fruits, leafy greens, and berries, may aid in bruise healing. However, it’s important to note that a well-rounded diet cannot replace medical treatment or address underlying causes of delayed bruise healing.
5. Is it normal for bruises to change colors as they heal?
Yes, it is normal for bruises to change colors as they heal. Initially, bruises may appear red or purple due to the broken blood vessels leaking blood beneath the skin. Over time, the bruise may turn blue, green, yellow, and eventually fade away. The changing colors indicate the body’s natural healing process.
6. When should I be concerned about a bruise that won’t go away?
Suppose a bruise persists for an unusually long time, causes severe pain, or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as fever or unexplained bleeding. In that case, it’s important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can evaluate the underlying cause of the persistent bruise and recommend appropriate treatment.