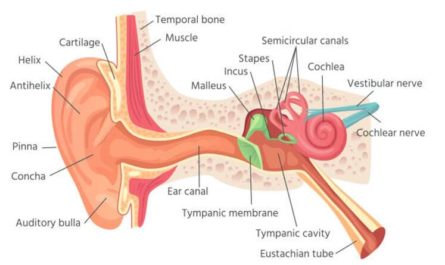
An ear lump is an abnormal growth or inflammation that can occur anywhere in or around the ear. These lumps are also called bumps, tumors, nodules, and cysts. The lumps usually appear inside the ear canal, behind the ear, and on the ear lobe. The lump behind your ear could result from an infection, inflammation, or trauma. Depending on the cause, your ear lump can vary in size, shape, and color.
Most of the time, a lump behind your ear is nothing to worry about. However, in some rare cases, ear lumps can be signs of a serious medical condition. This article discusses common causes of bumps or lumps behind the ear with treatment.
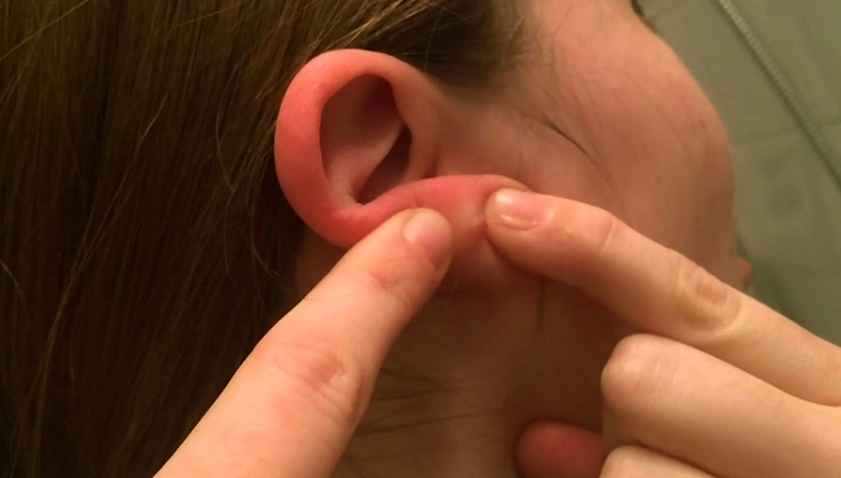
15 Causes of Bump or Lump Behind Ear
1. Lymphadenopathy
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped glands that play a crucial role in the immune system. Lymphadenopathy is the enlargement of lymph nodes, often causing a bump or lump behind the ear.
It can occur for various reasons, such as infections, inflammation, or cancer. Common infections that lead to lymphadenopathy include ear infections, sinus infections, and strep throat.
Remedy: If an infection causes lymphadenopathy, treating the underlying infection will help reduce the swelling. In most cases, it resolves on its own as the infection clears up.
However, if the lump persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional.
2. Sebaceous Cyst
A sebaceous cyst is a noncancerous growth that develops within the skin’s sebaceous glands. These cysts are often filled with a semi-fluid material and can appear as a lump behind the ear. They are typically painless but can become inflamed or infected, causing discomfort.
Remedy: Medical intervention may be required if a sebaceous cyst behind the ear becomes inflamed or infected.
A healthcare professional can drain the cyst or prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection. It’s crucial to avoid attempting to squeeze or pop the cyst yourself, as it can lead to further complications.
3. Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is an infection of the mastoid bone located behind the ear. It often develops as a complication of untreated middle ear infections.
The infection causes the mastoid bone to become inflamed, resulting in a painful lump behind the ear. Other symptoms may include fever, ear pain, and drainage from the ear.
Remedy: Mastoiditis requires prompt medical attention. Antibiotics are typically prescribed to treat the infection. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary. Timely treatment can help prevent the spread of infection and potential complications.
4. Lipoma
A lipoma is a benign tumor composed of fat cells. While they can occur anywhere on the body, they can also develop behind the ear, resulting in a noticeable lump. Lipomas are usually soft to the touch and painless.
Remedy: In most cases, lipomas do not require treatment unless they cause discomfort or cosmetic concerns. A healthcare professional can remove the lipoma through a minor surgical procedure if desired.
5. Dermoid Cyst
Dermoid cysts are congenital growths that form during embryonic development. These cysts contain tissues such as hair follicles, oil glands, and sweat glands. Although dermoid cysts behind the ear are rare, they can cause a palpable lump.
Remedy: Dermoid cysts often require surgical removal. A healthcare professional will evaluate the cyst and recommend the appropriate treatment approach.
6. Skin Infections
Skin infections, such as cellulitis or abscesses, can occur behind the ear. These infections often result from breaks in the skin, allowing bacteria to enter and cause an inflammatory response. The affected area may become red, swollen, and tender, forming a lump.
Remedy: Treatment for skin infections behind the ear typically involves antibiotics. Sometimes, a healthcare professional may need to drain an abscess to aid the healing process.
7. Abscess
When a particular area in your body becomes infected, it could cause the development of an abscess. Your body reacts to the infection by sending white blood cells to kill off the invading bacteria or virus.
When these white blood cells accumulate in the infected area, pus develops. A collection of pus in the infected area is an abscess. Abscesses could happen anywhere in the body, including the back of the ear.
Remedy: To treat an abscess, you may have to drain it to remove the pus. In some complicated cases, you may require surgery to remove the abscess. Your doctor may also recommend some antibiotics to help you combat the infection.
8. Acne
Acne is a common skin condition that affects teenagers and young adults. It occurs when your hair follicles become clogged with dead skin cells, bacteria, and oil, which in turn causes pimples and bumps.
Although acne can appear anywhere on the skin, common acne sites include the face, forehead, neck, upper, and chest. When you have acne on your neck, it could cause bumps to grow at the back of your ear.
Remedy: Some various topical creams and serums help to reduce inflammation caused by acne. Before you buy any product, I recommend you speak with a dermatologist.
9. Swimmer’s ear
Swimmer’s ear is an infection that occurs when bacteria, fungi, or virus invades the ear canal. Your ear canal runs from the eardrum to the opening of the ear.
Just like its name suggests, you can get a swimmer’s ear if the water stays inside your ear canal after swimming. The swimming water that stays back in your ear canal creates an optimum environment for bacteria and fungus to grow and cause an infection.
You can also get a swimmer’s ear from cotton swabs or any other material used for cleaning your ears. Although any individual can have a swimmer’s ear, the condition is more common in children because they have narrow ear canals that don’t drain properly.
Remedy: Swimmer’s ear usually clears up on its own within 2 days. However, if your otitis media persists, your doctor will use an ear tube to drain fluid from the middle ear.
10. Systemic diseases
Systemic diseases are illnesses that affect the whole body, including the area behind your ears. Some of these diseases can cause lumps behind the ears. Systemic diseases that cause ear lumps include:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- AIDS
- Lupus
- Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome
11. Abnormal growths
Skin growths can appear anywhere on the skin, including the back of the ear. Abnormal skin growths may be non-cancerous or cancerous. If the growth is controlled and does not spread from one spot to another, it is non-cancerous.
If the ear lump behind your ear moves from one area to another, it may be a cancerous growth.
12. Trauma or injury
If you have an injury to the head, you may notice swelling behind the ear. The ear bump caused by trauma or injury results from blood build-up under the skin. Minor and severe head injuries, such as stings and bites, can cause ear lumps.
13. Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection that affects the underlying layers of the skin. Although it can appear anywhere on the body, it is more common on the lower legs, feet, and face.
The condition can arise if Staphylococcus bacteria enter your skin through a cut or if you have a pre-existing skin infection like impetigo or eczema.
Symptoms of cellulitis include sore, pain, and reddened skin. If cellulitis is left untreated, the infection can develop into pus. In rare cases, the infection can cause blood poisoning or meningitis.
14. Lipoma
Lipomas are round, fat lumps of tissue that develop between the skin and the underlying muscle layer. A lipoma can grow anywhere on your skin, and it’s usually non-life-threatening.
Since lipomas are benign, you may not quickly notice them on the skin’s surface. However, as the lipoma increases, you may feel it with your hand. Lipomas move when touched, and in rare cases, they can be cancerous.
15. Swelling caused by cancer
In some rare cases, the lump behind your ear may result from certain types of cancer. Lumps caused by cancer are usually irregularly shaped, hard, and firmly rooted under the skin.
Potential complications of an ear lump
Typically, ear lumps aren’t life-threatening. However, if the lumps are left treated, the behind your ear could become a cause for concern. For example, ear lumps caused by cancer can spread throughout the body.
Other complications of an ear lump include:
- Hearing loss
- Ear infection
- Spread of infection
- Spread of cancer
FAQs
1. Can a bump behind the ear be a sign of cancer?
While a bump behind the ear can be related to cancer, it’s important to remember that most bumps are benign and caused by less serious conditions, such as lymphadenopathy or cysts.
However, if you have concerns or the bump persists, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
2. Are there any home remedies for a bump behind the ear?
Home remedies can relieve certain conditions causing a bump behind the ear. For example, warm compresses can help alleviate discomfort from inflamed lymph nodes or sebaceous cysts.
However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis before attempting home remedies.
3. Should I be worried if the bump is painful?
Painful bumps behind the ear may indicate an infection or an inflamed cyst. It’s advisable to seek medical attention, especially if the pain is severe, the lump is growing rapidly, or other symptoms are present.
4. When should I see a doctor about a bump behind the ear?
You should consult a healthcare professional if the bump behind your ear is causing severe pain, rapidly growing in size, accompanied by fever or other concerning symptoms, or if it persists for an extended period.
A healthcare professional can evaluate the lump, provide a proper diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment.
5. Can I prevent bumps or lumps behind the ear?
While not all causes of bumps or lumps behind the ear are preventable, maintaining good hygiene and promptly treating ear infections or other underlying conditions can help reduce the risk. It’s best to seek medical advice if you notice any concerning changes.
6. Are bumps behind the ear in children more concerning than in adults?
Bumps behind the ear in children are often related to common childhood infections and are usually less concerning than in adults. However, monitoring any lumps and consulting a pediatrician if you have concerns is essential.