A contusion, commonly known as a bruise, is a type of injury that occurs when the body experiences blunt force trauma. It results in damage to the underlying blood vessels, leading to bleeding and discoloration of the skin. Contusions can vary in severity, from mild cases that resolve on their own to more severe cases that require medical intervention. This article will explore the definition, types, symptoms, and treatment options for contusions.
What is a Contusion?
A contusion is a localized injury that occurs when a part of the body experiences blunt force trauma, causing damage to the blood vessels beneath the skin. Unlike other types of injuries, such as fractures or sprains, contusions primarily affect the soft tissues rather than the bones or ligaments. The force applied to the body disrupts the blood vessels, leading to bleeding, which then manifests as discoloration, pain, and swelling.
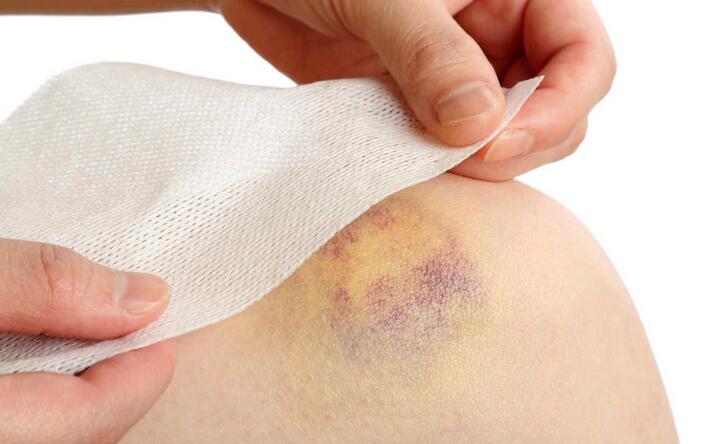
What Are The Different Types of Contusions?
Here are some common types of contusions:
- Skin Contusion: This is the most common type of contusion and affects the skin’s surface layers. It usually appears as a bruise, with discoloration ranging from red to purple or black, depending on the severity of the injury.
- Muscle Contusion: This type of contusion affects the underlying muscles. It occurs when a direct blow or trauma damages the muscle fibers, leading to bleeding and swelling. Muscle contusions can be painful and may result in limited mobility or muscle weakness.
- Bone Contusion: Bone contusions occur when there is a forceful impact on a bone, causing bleeding and injury to the underlying bone tissue. Unlike a fracture, a bone contusion does not involve a complete break or crack in the bone but can still cause significant pain and discomfort.
- Organ Contusion: Organ contusions happen when a blunt force causes injury to internal organs. For example, a direct blow to the abdomen can result in a contusion of the liver or spleen. Organ contusions can be serious and may require immediate medical attention.
- Brain Contusion: Brain contusions occur when there is a direct impact on the head, leading to bruising and injury to the brain tissue. This type of contusion can result in symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. Brain contusions are considered severe injuries and require urgent medical evaluation.
- Eye Contusion: An eye contusion is a black eye or periorbital hematoma. It occurs when there is a direct impact on the eye or the surrounding area. It causes bruising and swelling, resulting in a darkened appearance around the eye.
Common Causes of Contusions
Contusions can occur as a result of various incidents and activities. Some common causes include:
1. Accidents and Falls
Falling from heights, colliding with objects, or being involved in a motor vehicle accident can all lead to contusions. For example, slipping on a wet surface and hitting your leg on the corner of a table can result in a contusion on the shin.
2. Sports Injuries
High-impact sports or activities that involve physical contact, such as football or martial arts, can frequently result in contusions. Athletes may experience contusions from collisions with opponents, falls, or being struck by sports equipment.
3. Sudden Impact or Force
Any forceful impact on the body, such as being hit by an object or being struck by another person, can cause contusions. For instance, being hit by a baseball during a game or being involved in a physical altercation can lead to contusions.
4. Medical Procedures or Treatments
Certain medical procedures, such as injections or surgeries, can occasionally result in contusions at the injection or incision site. Medical professionals take precautions to minimize the risk of contusions during procedures, but they can still occur due to the nature of the intervention.
How to Recognize the Symptoms of Contusions
Identifying the symptoms of a contusion is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. The most common symptoms include:
- Pain: Contusions often cause localized pain, which can range from mild discomfort to severe tenderness. The intensity of the pain can depend on the severity of the contusion and the area affected.
- Swelling: The injured area may become swollen due to the accumulation of fluid caused by the body’s response to the injury. Swelling typically occurs as a natural defense mechanism to protect the injured tissue.
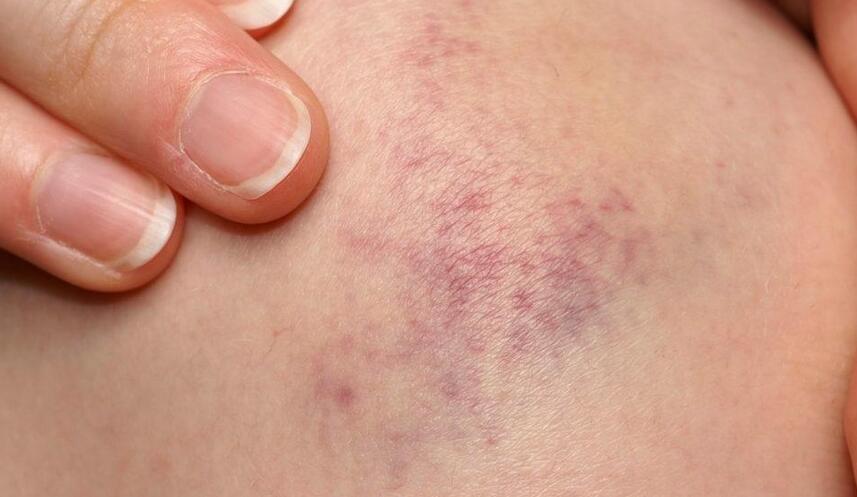
- Discoloration: Contusions typically manifest as a visible discoloration of the skin, commonly known as a bruise. Initially, bruises may appear red or purplish due to the trapped blood beneath the skin. Over time, the color changes as the body metabolizes the accumulated blood, progressing from blue or purple to green, yellow, and eventually fading away.
- Tenderness: The affected area may be tender to the touch, causing discomfort and sensitivity. The degree of tenderness can vary depending on the severity of the contusion and the individual’s pain tolerance.
The symptoms of a contusion usually develop shortly after the injury and gradually subside over time. However, in some cases, complications can arise, requiring medical attention.
Complications of Contusions
While most contusions resolve on their own without complications, there are potential risks associated with severe or improperly managed cases. The following are some possible complications:
1. Hematoma Formation
In some instances, the accumulated blood within a contusion can form a hematoma, causing increased pain and swelling. A hematoma is a localized collection of blood outside the blood vessels. Hematomas can be minor, resolving on their own, or require medical intervention such as drainage.
2. Compartment Syndrome
Severe contusions can lead to compartment syndrome, a condition characterized by increased pressure within a muscle compartment. This increased pressure can restrict blood flow and potentially damage the surrounding tissues. Compartment syndrome is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment to prevent further complications.
3. Myositis Ossificans
In rare cases, contusions can trigger the formation of bone tissue within the affected muscle, leading to limited mobility and discomfort. This condition is known as myositis ossificans.
It occurs when the body mistakenly repairs the damaged muscle tissue by converting it into bone. Myositis ossificans can be painful and may require medical intervention, such as surgery, to remove the excess bone formation.
It is important to note that complications from contusions are relatively rare, especially in mild to moderate cases. However, if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention to rule out any complications.
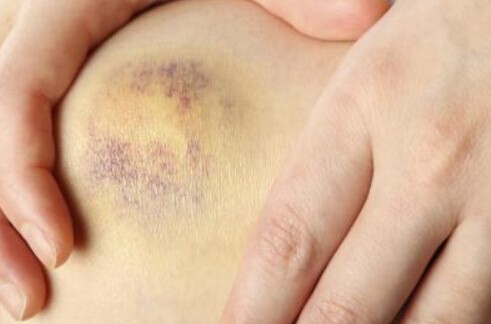
How to Diagnose Contusions
In most cases, a medical professional can diagnose a contusion through a physical examination and by reviewing the patient’s medical history. The doctor will assess the affected area for signs of bruising, tenderness, and swelling. They may also inquire about the circumstances surrounding the injury to gain a better understanding of the force and impact involved.
During the physical examination, the healthcare provider may gently press on the injured area to assess the level of tenderness, range of motion, and any associated pain. In severe cases, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans may be necessary to evaluate the extent of the injury and rule out fractures or other associated damage.
Effective Treatment Options for Contusions
Treatment for contusions primarily focuses on managing pain, reducing swelling, and promoting healing. The following treatment options are commonly recommended:
1. R.I.C.E. Method
Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (R.I.C.E.) is a standard approach for managing contusions. This method helps reduce pain, minimize swelling, and support the healing process. Here’s how to apply the R.I.C.E. method:
Rest: Resting the injured area is crucial to allow the body time to heal. Avoid activities that aggravate the contusion and allow your body to recover.
Ice: Applying ice packs or cold compresses to the contusion can help constrict blood vessels, reduce swelling, and numb the area to alleviate pain. Use an ice pack wrapped in a cloth or a bag of frozen vegetables and apply it to the injured area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day, for the first 48 to 72 hours after the injury.
Compression: Applying compression to the contusion can help reduce swelling and support the injured tissue. Use an elastic bandage or compression wrap to gently wrap the injured area. Ensure that the compression is snug but not too tight to avoid impairing blood flow.
Elevation: Elevating the injured area above the level of the heart can help minimize swelling by promoting fluid drainage. For example, if you have a contusion on your leg, prop your leg up on a pillow or cushion while sitting or lying down.
2. Medication
Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with contusions. These medications can be taken according to the recommended dosage and guidelines provided on the packaging or as advised by a healthcare professional.
3. Physical Therapy
In more severe cases, physical therapy may be recommended to restore functionality and strength to the affected area. A physical therapist can design a customized rehabilitation program to promote healing and prevent muscle stiffness or weakness. Physical therapy can also help reduce the risk of complications, such as myositis ossificans or joint contractures.
4. Home Remedies and Self-Care
Along with medical interventions, various home remedies and self-care practices can aid in the recovery process. These may include applying warm compresses to the contusion after the initial 48 to 72 hours to promote blood flow and relaxation of the injured tissues.
Gentle stretching exercises, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, can help improve flexibility and prevent muscle tightness. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, adequate hydration, and sufficient rest can support overall healing.
Immediate First Aid for Contusions
Proper first aid for contusions is important to minimize pain, swelling, and potential complications. Here are some immediate steps to take after sustaining a contusion:
1. Ice Application
Apply an ice pack or cold compress to the injured area as soon as possible, ideally within the first 24 to 48 hours. Ice helps constrict blood vessels, reduce swelling, and alleviate pain. Remember to wrap the ice pack in a cloth or use a barrier to prevent direct contact with the skin, as this can cause ice burns.
2. Rest and Immobilization
Rest the injured area and avoid putting weight or strain on it. If the contusion is on a limb, consider using a splint or brace to immobilize the area and prevent further injury. Immobilization supports the healing process and reduces the risk of exacerbating the contusion.
3. Compression
Applying compression to the contusion can help reduce swelling and provide support to the injured tissues. Use an elastic bandage or compression wrap to gently wrap the injured area. Ensure that the compression is snug but not too tight to avoid impairing blood flow.
4. Elevation
Elevating the injured area above the level of the heart can help minimize swelling by promoting fluid drainage. For example, if you have a contusion on your leg, prop your leg up on a pillow or cushion while sitting or lying down.
Remember, immediate first aid is crucial, but it should not replace proper medical evaluation and treatment. If you experience severe pain, significant swelling, or any signs of complications, seek medical attention promptly.
Advanced Treatments for Severe Contusions
In rare cases where contusions are severe or complications arise, advanced medical interventions may be necessary. These can include:
1. Surgical Interventions
Surgical drainage of large hematomas or abscesses that develop within the contusion may be required. This helps alleviate pressure, reduce the risk of infection, and promote healing. In some cases, surgical repair of damaged tissues or structures may be necessary.
2. Hospitalization
Severe contusions that lead to complications such as compartment syndrome may require hospitalization for close monitoring and specialized treatment. In a hospital setting, healthcare professionals can provide more intensive care, pain management, and surgical interventions if needed.
3. Long-Term Rehabilitation
Following severe contusions, long-term rehabilitation and physical therapy may be necessary to regain full functionality and prevent long-term complications.
Physical therapists can develop personalized rehabilitation programs tailored to the individual’s specific needs and goals. These programs may include exercises to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion, as well as techniques to improve balance and coordination.
How to Prevent Contusions?
While it is not always possible to prevent contusions entirely, certain safety measures can help reduce the risk of injury. Consider the following preventive measures:
- Safety Measures: Take precautions to minimize the risk of accidents or falls. For example, install handrails on staircases, use non-slip mats in wet areas, and keep walkways clear of obstacles or clutter.
- Protective Gear and Equipment: In sports or activities that pose a higher risk of contusions, wearing appropriate protective gear is essential. Helmets, knee pads, elbow pads, and shin guards can help mitigate the impact of potential injuries. Make sure the protective gear fits properly and is in good condition.
- Workplace Safety Protocols: Follow workplace safety guidelines and protocols to minimize the risk of contusions in occupational settings. Use personal protective equipment (PPE) as required, undergo proper training, and adhere to safe work practices.
- Environmental Awareness: Be aware of your surroundings to avoid collisions with objects or other individuals. Pay attention to potential hazards and take necessary precautions.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, stay adequately hydrated, and get sufficient rest to support overall healing. A nutritious diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and protein can promote tissue repair and strengthen the immune system. Hydration is important for maintaining optimal blood flow and aiding in the removal of waste products from the body.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of contusions and other related injuries.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between a bruise and a contusion?
A bruise and a contusion are essentially the same thing. A bruise is a visible discoloration that occurs due to a contusion, which is the underlying injury caused by blunt force trauma.
2. Are some people more prone to bruising than others?
Yes, some individuals are more prone to bruising due to various factors, such as age, medication use, and underlying medical conditions. Older individuals and those taking blood-thinning medications may bruise more easily.
3. How long does it take for a bruise to heal?
The healing time for a bruise can vary depending on its size and severity. Generally, a bruise will change color over time, starting from red or purple and gradually fading to yellow or green. Mild bruises typically heal within one to two weeks, while larger bruises may take longer.
4. Can certain foods or supplements help prevent bruising?
A diet rich in foods containing vitamin C and vitamin K can help support healthy blood vessels and clotting mechanisms. Incorporating citrus fruits, leafy greens, berries, and other nutrient-dense foods into your diet can potentially reduce the risk of bruising.
5. When should I seek medical attention for a bruise?
In most cases, bruises heal on their own without the need for medical intervention. However, you should seek medical attention if the bruise is accompanied by severe pain, swelling, or other concerning symptoms or if it does not show improvement after a reasonable amount of time.