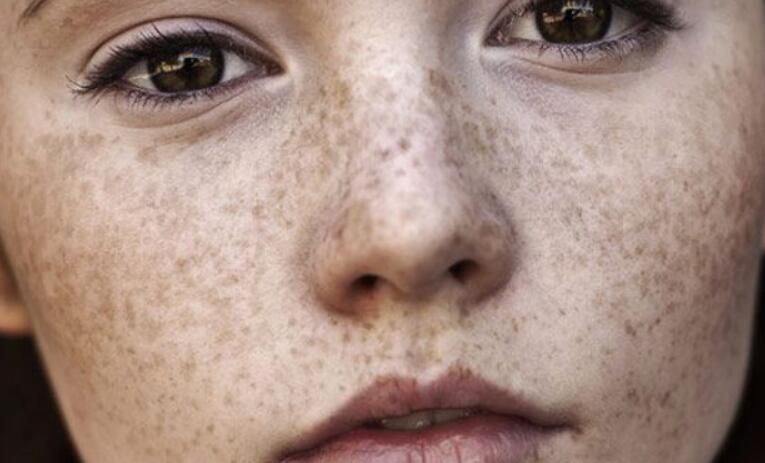
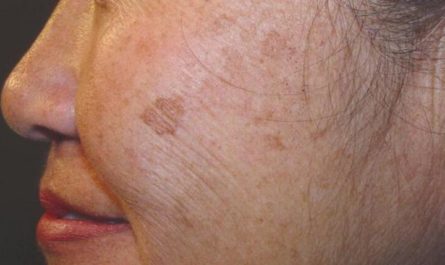
Common Causes Dark Spots on the Face
1. Sun Exposure
Excessive exposure to the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays can trigger the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Over time, this can lead to dark spots on the face.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during pregnancy or menopause, can contribute to the appearance of dark spots. This condition, known as melasma or the “mask of pregnancy,” typically affects women and is triggered by increased estrogen levels.
3. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
After experiencing inflammation or injury to the skin, such as acne, cuts, or burns, dark spots may develop as a result of increased melanin production during the healing process.
4. Aging
As we age, our skin undergoes natural changes, including a decrease in collagen production and an increase in melanin production. This can lead to the formation of age spots or liver spots, commonly seen on the face, hands, and other sun-exposed areas.
5. Skin Disorders
Certain skin conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, and lichen planus, can cause inflammation and trigger the development of dark spots on the face.
6. Medications
Some medications, including certain antibiotics, hormone therapies, and anti-seizure drugs, can increase the skin’s sensitivity to the sun and form dark spots.
7. Genetic Predisposition
Genetics can play a role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to developing dark spots on the face. Certain ethnicities, such as those with darker skin tones, may be more prone to hyperpigmentation.
8. Acne Scarring
Acne breakouts can leave behind marks and scars, including dark spots, due to the skin’s healing process. These spots can persist even after the acne has cleared.
9. Allergic Reactions
Some individuals may experience dark spots as a result of an allergic reaction to certain skincare products or cosmetics. This condition, known as allergic contact dermatitis, can cause skin discoloration and inflammation.
10. Hormonal Birth Control
The use of hormonal birth control methods, such as oral contraceptives or hormone-containing intrauterine devices (IUDs), can lead to hormonal imbalances that contribute to the development of dark spots on the face.
11. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS, a hormonal disorder that affects women, can lead to an overproduction of androgens (male hormones). This hormonal imbalance can trigger the appearance of dark spots on the face.
12. Excessive Friction
Repeated friction or rubbing of the skin, often caused by shaving or wearing tight-fitting clothing or accessories, can cause post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and the formation of dark spots.
13. Environmental Factors
Exposure to environmental pollutants, such as air pollution and toxins, can contribute to developing dark spots on the face. These pollutants can trigger inflammation and disrupt the skin’s natural balance.
14. Nutritional Deficiencies
Certain nutritional deficiencies, particularly deficiencies in vitamins C and E, can affect the skin’s health and contribute to the appearance of dark spots.
15. Smoking
Smoking tobacco products can accelerate the aging process and increase the risk of developing dark spots on the face. The chemicals present in cigarettes can damage the skin and impair its natural ability to repair and regenerate.
16. Stress
Chronic stress can disrupt the body’s hormonal balance, leading to an overproduction of melanin and the formation of dark spots on the face.
Health Conditions Causes of Dark Spots on the Face
1. Addison’s disease
Addison’s disease is a hormonal disorder that occurs when the adrenal glands don’t produce enough cortisol and aldosterone. It can cause various symptoms, including fatigue, weight loss, and skin darkening.
The dark spots on the face that can occur with Addison’s disease are known as hyperpigmentation. They are caused by increased melanin production, which can be triggered by the low cortisol levels associated with the condition. The most common medication used to treat Addison’s disease is a synthetic form of cortisol called hydrocortisone.
2. Cushing’s syndrome
Cushing’s syndrome is a hormonal disorder that occurs when the body is exposed to high levels of cortisol for an extended period of time. It can cause various symptoms, including weight gain, muscle weakness, and skin changes.
Hyperpigmentation in Cushing’s syndrome is caused by an excess of cortisol, which can stimulate melanin production in the skin. Other factors that can contribute to hyperpigmentation include sun exposure and certain medications.
3. Melasma
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes dark, discolored patches on the face, particularly in areas exposed to the sun, such as the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip. It is more common in women than men and often occurs during pregnancy or while taking birth control pills.
The exact cause of melasma is unknown, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes, sun exposure, and genetics. Pregnant women or taking birth control pills may experience an increase in estrogen, which can trigger melanin production in the skin.
Topical medications for Melasma may include hydroquinone, a skin-lightening agent that can reduce the appearance of dark patches on the skin. Other topical medications, such as tretinoin and azelaic acid, may also treat melasma.
4. Acanthosis nigricans
Acanthosis nigricans is a skin condition that causes dark, thickened patches of skin, typically on the neck, armpits, and groin. In some cases, it can also affect the face.
The condition is caused by increased insulin levels, which can be triggered by obesity, insulin resistance, or type 2 diabetes. Acanthosis nigricans can also be associated with certain medications, hormonal disorders, and genetic factors.
5. Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis is a genetic disorder that causes the body to absorb too much iron from the diet, leading to iron buildup in the organs and tissues. Over time, this can cause damage to the liver, heart, and other organs.
Hyperpigmentation in hemochromatosis is caused by the buildup of iron in the skin cells, which can stimulate melanin production. Other factors contributing to hyperpigmentation include sun exposure, hormonal changes, and certain medications.
Treatment for hemochromatosis involves reducing the amount of iron in the body to normal levels. This may involve a combination of therapeutic phlebotomy (removal of blood), iron chelation therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
6. Porphyria
Porphyria is a group of genetic disorders that affect the production of heme, a component of hemoglobin that carries oxygen in the blood. It can cause blistering, itching, and hyperpigmentation on the face, hands, and other areas exposed to the sun.
Porphyria is caused by a buildup of porphyrins in the skin cells, which sun exposure, certain medications, and hormonal changes can trigger.
Treatment for porphyria depends on the type of porphyria and the severity of the symptoms. In cases of acute porphyria, treatment may involve intravenous administration of heme, a substance that can help reduce the production of porphyrins in the body.
7. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is a skin condition that can occur after an injury or inflammation of the skin, such as acne, eczema, or psoriasis. It is characterized by dark spots or patches on the skin that develop in areas where the skin has been affected by injury or inflammation.
PIH occurs when there is an overproduction of melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color, in response to injury or inflammation. This excess melanin can cause the affected area to become darker than the surrounding skin.
Topical treatments such as hydroquinone, retinoids, and azelaic acid may be used to reduce the appearance of dark spots. These treatments work by inhibiting melanin production, the pigment that gives skin its color.
8. Seborrheic keratosis
Seborrheic keratosis is a common skin condition that can cause dark, wart-like growths to form on the face, neck, chest, or back. These growths are typically brown, black, or tan and can have a rough or waxy texture.
Seborrheic keratosis is usually harmless, but it can be unsightly and may be mistaken for skin cancer. The exact cause of this condition is unknown, but it is thought to be related to aging and sun exposure. It is more common in people over 50 and tends to run in families.
The most common method of removing seborrheic keratosis is a simple surgical procedure called curettage and desiccation. Cryosurgery, which involves freezing the growth with liquid nitrogen, may also be used to remove seborrheic keratosis.

6 Best Home Remedies for Dark Spots on Face
Here are some effective home remedies to remove dark spots on the face:
1. Lemon Juice
Lemon juice is a natural bleaching agent that can help lighten dark spots on the face. It contains citric acid, which exfoliates the skin and promotes cell turnover.
- Wash your face with warm water and an exfoliating scrub to help remove dead skin cells.
- Cut a lemon in half and squeeze the juice into a small bowl.
- Dip a cotton swab into the juice and gently apply it to the dark spots on your face.
- Leave the lemon juice on your face for 10-15 minutes.
- Rinse your face with cool water and pat it dry with a soft towel.
- Use a moisturizer after applying the lemon juice to help keep the skin hydrated.
Repeat this process twice a day for best results. Lemon juice is a natural remedy for lightening dark spots, but it can irritate sensitive skin, so be sure to conduct a patch test before applying it to your face.
2. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the appearance of dark spots on the face. It also contains vitamins and minerals that promote skin health.
- Clean your face with a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, makeup, and oil.
- Extract some fresh aloe vera gel from the plant.
- Apply the gel directly to the dark spots on your face and massage it gently.
- Leave the gel on your face for 15 minutes and rinse with lukewarm water.
- Repeat this process twice a day until the dark spots start to fade.
- Use a moisturizer after each application to keep your skin hydrated.
3. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar contains acetic acid, which can help lighten dark spots on the face. It also has antibacterial properties that can help prevent acne and other skin infections.
- Mix 1 part apple cider vinegar with 2 parts water.
- Using a cotton ball, apply the mixture to the dark spots.
- Let the mixture sit on your skin for 15 to 20 minutes.
- Rinse the area with lukewarm water.
- Repeat this process twice a day until the dark spots fade away.
- Moisturize your skin afterward to help prevent dryness.
Be sure to use a mild concentration and moisturize afterward to help prevent any dryness or irritation. With regular use, you should see a noticeable difference in the dark spots on your face.
4. Green Tea

Using green tea for dark spots on your face is a natural way to lighten and reduce the appearance of discoloration. Green tea contains antioxidants that can help reduce the appearance of dark spots on the face.
- Start by purchasing green tea leaves. You can find these at most health food stores or online.
- Place the green tea leaves in a small bowl and pour boiling water over them. Let the tea steep for about five minutes.
- Remove the green tea leaves from the bowl and strain the tea.
- Dip a cotton ball into the tea and apply it directly to the dark spots on your face.
- Let the tea sit on your skin for 10-15 minutes before rinsing it with warm water.
- Repeat this process twice a week for best results.
You can also make a face mask with green tea by mixing 2 teaspoons of green tea leaves with 1 teaspoon of honey and 2 tablespoons of yogurt. Apply the mask to your face and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing it.
5. Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce the appearance of dark spots on the face.
- Mix one teaspoon of turmeric powder with enough almond or coconut oil to form a paste.
- Gently massage the paste all over your face, avoiding the eye area.
- Leave the turmeric paste on your face for 15-20 minutes.
- Rinse the paste off your face with lukewarm water and pat dry with a clean towel.
- Apply a moisturizer to your face to keep your skin hydrated.
- Repeat this process twice a week for best results.
You can also add a few drops of lemon juice to the paste for extra brightening benefits. Be sure to do a patch test first to ensure the lemon juice does not irritate your skin.
6. Healthy Diet for Dark Spots on Face
While home remedies and medical treatments can help reduce the appearance of dark spots on the face, it’s also important to consider the role of nutrition in skin health. (Resource)Here are some dietary recommendations for preventing and treating dark spots:
- Eat a balanced diet: Eating a healthy diet rich in fresh fruits and vegetables and low in processed foods can help reduce the appearance of dark spots on the face.
- Consume foods rich in antioxidants: Certain foods, such as blueberries, spinach, and tomatoes, contain antioxidants that can help to protect the skin from sun damage and reduce the appearance of dark spots.
- Drink plenty of water: Staying hydrated is essential for healthy skin, and drinking plenty of water can help to keep the skin hydrated and reduce the appearance of dark spots.
- Avoid processed and sugary foods: Eating processed and sugary foods can cause inflammation and damage to the skin, increasing dark spots.

How to Prevent Dark Spots on the Face?
Preventing dark spots on the face can be challenging, but there are several things you can do to reduce your risk of developing them:
1. Use Sunscreen: Sun damage is a major cause of dark spots on the face, so it is important to protect your skin by wearing sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every day, even on cloudy days.
2. Wear Protective Clothing: In addition to sunscreen, wearing protective clothing such as hats, long-sleeved shirts, and sunglasses can help shield your skin from the sun’s harmful rays.
3. Avoid Tanning: Tanning can increase your risk of developing dark spots, so it is best to avoid tanning beds and prolonged exposure to the sun.
4. Use Gentle Skincare Products: Harsh skincare products can irritate the skin and worsen dark spots. Use gentle cleansers, toners, and moisturizers appropriate for your skin type.
5. Don’t Pick at Your Skin: Picking at pimples and other blemishes can cause inflammation and increase the likelihood of developing dark spots.
6. Manage Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopause, can trigger the development of dark spots. Talk to your doctor about hormonal management options if you experience these changes.
7. Consider Antioxidant Supplements: Antioxidants such as vitamins C and E can help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals. Consider incorporating antioxidant-rich foods into your diet or taking supplements as directed by your healthcare provider.
Are dark spots on the face permanent?
Dark spots on the face can be permanent, depending on the cause. If the dark spots are caused by long-term sun damage or hormonal changes such as melasma, they may be more difficult to treat and require ongoing maintenance.
However, with proper treatment and prevention measures, such as using sunscreen and avoiding prolonged sun exposure, the appearance of the dark spots may fade over time.
When to see a doctor?
While most cases of dark spots on the face are harmless and can be treated with home remedies or over-the-counter products, there are some cases where it’s important to see a doctor. Here are some signs that you should seek medical attention for your dark spots:
- If your dark spots change in size, shape, or color: This could be a sign of melanoma or another type of skin cancer, which a dermatologist should evaluate.
- If you have many dark spots: This could be a sign of a more serious underlying condition, such as hormonal imbalances or liver disease, which may require medical treatment.
- If your dark spots are accompanied by other symptoms, such as itching, pain, or bleeding: This could be a sign of a more serious skin condition, such as psoriasis or eczema, which a dermatologist should evaluate.
- If your dark spots are not responding to home remedies or over-the-counter products: In some cases, prescription-strength treatments may be necessary to treat dark spots effectively.