Low red blood cell counts, also known as anemia, can significantly impact your health and quality of life. If your red blood cell count is low, it can mean that your body is not getting enough oxygen, leading to fatigue, dizziness, and other health issues.
Additionally, anemia can make it difficult to focus and concentrate and lead to a weakened immune system. Increasing your red blood cell count is essential if it is too low.
Fortunately, there are a variety of treatments available to help with anemia, including dietary changes, supplements, and medications. By understanding the causes of low red blood cell count and how to manage it, you can lead a healthier and more fulfilling life.
What is the Low Red Blood Cell (RBC) Count?
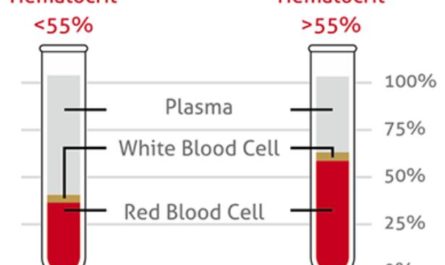
Your red blood cell count (RBC) is the number of red blood cells in your body. To measure low red blood cell count, you should know the normal RBC count.
Typically, men have an RBC of 4.7 million to 6.1 million cells per microliter (MCL). Women have a slightly lower count of 4.2 million to 5.4 million cells/mcL; the values of a pregnant woman should be slightly lower.
Children have an RBC of 4.0 million to 5.5 million cells per microliter (MCL). However, this number can vary between individuals depending on your age and the testing laboratory.
Who Can Get Anemia?
Sadly, anemia can affect anyone. However, women and people with chronic, underlying diseases are more susceptible to anemia. For example, during pregnancy, your body requires a substantial amount of red blood cells, leading to a low red blood cell count, especially since the production of red blood cells can’t match the demand.
Additionally, during menstruation, your body also loses a lot of blood, which can put you at a higher risk of iron deficiency anemia.
Common symptoms of anemia include:
- Headache
- Fatigue and Weakness
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Fast and irregular heartbeat
- Pain in joints and bones
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Pale and yellow skin
- Pale gums
What Causes Low Red Blood Count?
Several factors can Usuallyemia. The three common causes of anemia include:
1. Loss of Red Blood Cell
Bleeding is one of the most common causes of red blood cell loss. Various conditions such as an injury, surgery, or frequent blood donation can lead to red Blood Cell Loss.
In addition, heavy menstrual bleeding or a lesion in your intestinal system may also lead to chronic bleeding. These conditions are unusual Bleediare ng in your digestive tract, such as from ulcers, cancers, hemorrhoids, or urinary tract.
2. Destruction of red blood cells
Normally, the bone marrow produces new red blood cells every day. These red blood cells circulate in our body and are removed by the spleen after they become damaged or old.
However, some diseases can affect the function of the bone marrow or spleen, causing the body to destroy red blood cells faster than they can be made. These symptoms include hemolysis, Porphyria, sickle cell anemia, Vasculitis, Thalassemia, and Enlarged spleen (splenomegaly).
3. Decreased red blood cell production
Some conditions can interfere with or damage the bone marrow cells. These diseases or infections cause your body to produce fewer red blood cells than normal.
In addition, some medications, such as anti-retroviral drugs for HIV infection and chemotherapy drugs for cancer, can also lead to a low Red Blood Count. Some common diseases and conditions include:
- Cancer
- Aplastic anemia
- Chronic kidney disease
- Cirrhosis
- Hypothyroidism
- Hodgkin’s disease
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Lead poisoning
- Leukemia
- Multiple myeloma
- Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Vitamin deficiency anemia
- Myelodysplastic syndromes
4. Other Causes
Some types of anemia are hereditary in rare cases, and newborns have low red blood cell count right from birth. Other potential causes of a low red blood cell count include:
- Anemia
- Bone marrow failure
- Erythropoietin deficiency
- Leukemia
- Multiple myeloma
- Hemolysis
- Erythropoietin deficiency
- Pregnancy
- Leukemia
- Overhydration
- Bone marrow complications
- Internal and external bleeding
- Poor diet, including deficiency of vitamin B12, folate, and iron.
How to Deal With Low Red Blood Cell Count (Anemia)
1. Low RBC Count Caused by Iron Deficiency
When you don’t have enough iron in your blood, your body won’t produce enough red blood cells.
Symptoms of Anemia Caused by Iron Deficiency
- Pica (eating unusual substances like paint, dirt, or paper)
- Sore mouth
- Breaks at the corners of the mouth
- Koilonychias (A condition when the fingers curve upwards)
How to treat your iron deficiency anemia depend on its severity. Your doctor may recommend iron supplements, dietary changes, or red blood transfusions if your condition is severe.
Top tip: Taking in excess iron can also be dangerous. If you take too much iron, you may experience headaches, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue. If you start feeling these side effects, I recommend taking iron supplements between meals. Your doctor may also suggest meals rich in iron.
2. Low RBC Count Caused by Sudden Blood Loss
During pregnancy or external bleeding, you can lose a lot of blood. If your red blood cell count drops below the normal range, you must recover the lost red blood cells. Your doctor may suggest a blood transfusion or treat you with fluids.
Top tip: If the blood loss is minimal, you can also stick with the treatment for iron deficiency anemia.
3. Low RBC Count caused by the deficiency of Vitamin B12 and Folate
Unfortunately, anemia caused by Vitamin B12 and Folate deficiency can be challenging to differentiate, especially since they have similar symptoms.
If your vitamin B12 level is low, your red blood cells won’t have the same shape as a healthy red blood cell. They’ll appear bigger and irregularly shaped.
As you age, your body loses the ability to retain Vitamins B12 properly, especially if you’re a vegan.
Symptoms of Anemia Caused by Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Dementia
- Difficulty walking
- Lost sense of touch
- Stiff arms and legs
- Tingling sensation in the hands and feet
Once you detect a deficiency in vitamin B12, your doctor will put you on vitamin B12 injections. If you’re not a fan of needles and prefer taking medications orally, you can also take Vitamin B12 tablets. However, you’ll need to take them in very high dosages.
Top tip: You can take it daily as oral tablets or go for injections every three months. Once you take adequate vitamin B12, the low red blood count symptoms will improve drastically. Alternatively, you can boost the vitamin B12 level in your body by eating diets that contain fish, meat, milk, eggs, and cheese.
4. Treatment For Low RBC Count Caused by Folate Deficiency
The body needs folate to produce healthy red blood cells; when you don’t have enough folate, your red blood cells don’t live as long as they can. Once your doctor diagnoses folic acid deficiency as the cause of your anemia, he will most likely recommend folic acid supplements.
Top tip: I recommend you eat many foods rich in folate. Folate-rich sources include fresh fruits, vegetables, milk, and whole-grain cereals.
5. Treatment for Anemia Caused by Bone Marrow complications
Anemia caused by a bone marrow fault is one of the hardest types of anemia to treat. Luckily, some anemias go away without needing treatment.
Symptoms of Anemia Caused by Destruction of Red blood cells
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Death in infants
- Passing of brown or red urine
- Sores in the leg
- Symptoms of gallstones
However, the more persistent anemias will require repeated transfusions and, in extreme cases, bone marrow transplantation.
6. Treatment For Low RBC Count caused by underlying chronic disease
When red blood cells start decreasing due to an underlying condition, the best option is to treat chronic illness. Chances are, as the symptoms of the disease improve, your anemia will improve too.
To boost the number of your red blood cells, your doctor may administer Erythropoietin, a hormone that triggers the production of healthy red blood cells.
1. Add Iron-Rich Foods to your diet
Iron is crucial in the production of healthy red blood cells.
Eating iron-rich foods helps fortify the iron level in your red blood cell. Iron-rich food sources include red meat, beans, legumes, and green vegetables.
Top tip: When taking iron supplements, I recommend taking them with Vitamin C. Vitamin C helps your body absorb iron.
2. Eating food rich in folic acid
Your body needs folic acid to produce healthy red blood cells. You can boost your folic acid content by eating beans, cereals, peas, and green leafy vegetables.
3. Eat copper-rich foods
When you’re always feeling tired and weak, chances are your body doesn’t have enough copper. Additionally, copper also increases the rate of iron absorption. Eating copper-rich foods like whole grains, nuts, beans, and chocolate can improve your red blood cell count.
4. Eat more Vitamin A
Although Vitamin A deficiency can also cause anemia, there’s still little evidence on how it affects our health. Contrary to popular belief, Vitamin A also helps to reduce anemia and increase red blood cells. Excellent sources of vitamin A include sweet potatoes, carrots, watermelon, red pepper, and dark green leafy vegetables.
5. Drink Water
Anemia often comes with uncomfortable dehydration. Drinking at least 8-10 glasses of Water daily helps your body stay hydrated.
Top tip: Fortifying your drinking water with iron supplements will also help prevent and treat iron deficiency anemia.
6. Lifestyle changes
Making gradual lifestyle changes can help you manage and prevent anemia. Here are some lifestyle changes we recommend. Maintain a healthy sleep schedule; make sure you don’t stay in bed for too long.
7. Exercise
Exercise doesn’t only help you improve your health, and it can be of immense benefit if you’re dealing with anemia. When you exercise, your body tells your brain it needs more oxygen, and in turn, your body produces more red blood cells.
Top tip: Ensure you don’t overexert yourself when you exercise; when you’re feeling dizzy, lie down, and rest.