Lower back pain, also known as lumbago, usually occurs suddenly and can range from mild to severe. Experiencing lower right back pain can be frustrating and terrifying. This pain may be mild and dull or sharp, stabbing and severe. This kind of back pain often affects only one side of the body, and the symptoms can be reduced by rest.
Most of us are affected by this pain at some point. However, women are more likely to suffer from lower back pain than men because of women’s menstrual cycles. There are many possible causes of this common condition. For example, kidney problems, muscle trauma, fractures, inflammation of organs, and digestive problems can cause lower back pain.
The best way to treat the problem is by understanding what causes it. In this article, you will learn 14 common causes of lower right back pain with treatments. This information will help you relieve back pain effectively.
14 Common Causes of Lower Right Back Pain
1. Muscle Strain
A muscle strain, also known as a pulled muscle, refers to damage to your muscle or attaching tendons. The strain can damage muscle fibers and small blood vessels, causing local bleeding or bruising. This will stimulate the nerve endings in the area and cause pain. You may feel pain in your lower right back when the specific muscle is used. Strain not only appears on the lower back but can also occur in your neck, shoulder, or thigh.
A muscle strain usually occurs due to fatigue, overstretched, or improper use of the muscle. This may be because you suddenly lift a heavy object, put excessive pressure on your muscles, or do not correct while you are doing lifts.
How to relieve your muscle strain at home? First, you should remove the tight clothing to relax the muscles. Then, you can use ice to reduce inflammation and pain. Wrap a small ice pack or frozen vegetables with a towel and apply it to the painful area for 20-30 minutes every time.
Remember not to apply the ice packs on bare skin. You’d better avoid using heat in the early stages, as this can increase swelling and pain. Finally, you can take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as naproxen or ibuprofen to reduce pain. However, it is best to consult your doctor before taking the medication.
2. Sciatica
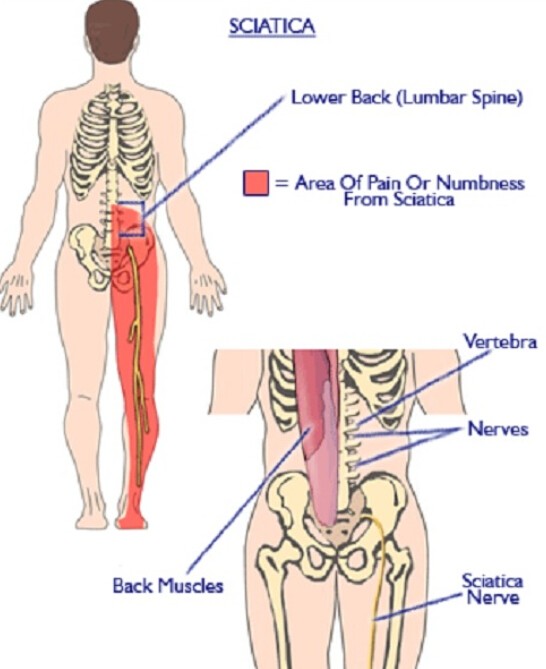
Sciatica refers to pain caused by the stimulation of the sciatic nerve. This is usually caused by a bone spur or a herniated disk in the spine.
Sciatica can cause shooting pain in your lower right back. Depending on where the sciatic nerve is affected, the pain may spread to your hips, legs, feet, or even toes. You may also feel burning or tingling in the leg or difficulty moving the leg. Typically, sciatica only affects only one side of the body, and the pain will worsen when sitting.
Although sciatica can be severe, in most cases, minor pain usually disappears or is relieved by non-surgical treatment within a few weeks. Common treatments include self-care, muscle relaxants, or anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID). But if the pain persists for more than a week and gradually gets worse, you’d better seek your doctor.
If you experience numbness in your calves, sudden severe pain, or inability to control your bowel or bladder, you need to get immediate medical care immediately.
3. Degenerative Disc Disease
There are instances when the lumbar discs become problematic and start to break down. This condition actually affects people who are 20 and above. Usually, as the condition worsens, people who have this condition find it harder to walk around since they find it harder to stabilize themselves.
At the same time, the pain because of the inflammation may become unbearable. The only fortunate thing about this condition is that there are several treatments for this to be prevented as soon as the condition has been checked.
4. Isthmic Spondylolisthesis
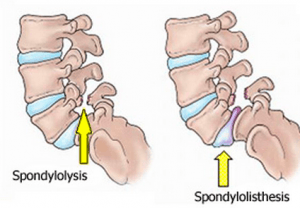
Isthmic Spondylolisthesis occurs when the vertebra slips forward and falls on the disc below it. This spinal condition can be caused by a fracture or a defect of the pars interarticularis. This is a common condition that causes right lower back pain. It can also cause some pressure on nerves which can worsen the pain.
Isthmic Spondylolisthesis usually occurs in children but only begins to manifest itself when a person reaches 20 and above. In most cases, isthmic spondylolisthesis can be treated without surgery. You can relieve the symptoms with bed rest, over-the-counter medication, steroid injections, or physical therapy. However, if some neurologic problems such as incontinence occur, you should see your doctor immediately.
5. Spinal Compression Fracture
A compression fracture refers to the fracture of a bone in the spine. This is typically caused by osteoporosis, a loss of bone mass, or other diseases that weaken the bone, such as cancer.
When this fracture occurs, you may feel pain in your lower back. This pain is not just a dull type of ache, and sometimes it can be severe. The fracture can be caused by the simplest things: a fall, a sneeze, a cough, or the lifting of a heavy object. Mainly, this occurs because the bones have already degenerated, and the pressure causes the fracture.
Common treatments include bed rest, physical therapy, or over-the-counter medication to relieve pain. In rare cases, surgery may be needed when symptoms worsen.
6. Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is a rare but serious condition of bone infection. This is usually caused by a bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus. Older or people who have problematic immune systems are more prone to this type of condition. Some chronic conditions such as diabetes can also increase the risk of osteomyelitis.
Osteomyelitis can cause lower right back pain and swelling around the affected bone. Other symptoms include fever, irritability, fatigue, nausea, and warmth in the area of the infection.
Common treatment includes antibiotics, surgery, or both. Antibiotics can help control the infection effectively. But more serious osteomyelitis may require surgery to remove the infected tissue.
7. Herniated Disk
Herniated Disk is probably one of the most common causes of lower back pain. A herniated disk occurs when the cushion that sits between the spinal vertebra pushes through a crack in the annulus. Patients may suffer from numbness, weakness, and shooting pain in the buttocks, arms, or legs.
An injury or a sudden movement may cause this. Sometimes, people who have this do not even realize that they already have this condition. Heat and cold treatments can help relieve the initial pain. You should try to avoid any activity that aggravates the lower back pain.
There are times when a herniated disk can be serious. You should go to the hospital immediately if you have lost control of your bowels or cannot move.
8. Fractured Spine
Other parts of the body can be fractured, but this can be a severe condition if you fracture your spine. This can occur when people have just gone through an accident or sudden movement.
People who are over 60 years of age may be more prone to this type of condition. You can tell that you have a fractured spine if every movement that you make is just painful. This is an emergency and if you believe that you have a fractured spine, make sure that you will try your best not to move because you have to be brought to the hospital.
9. Kidney Pain
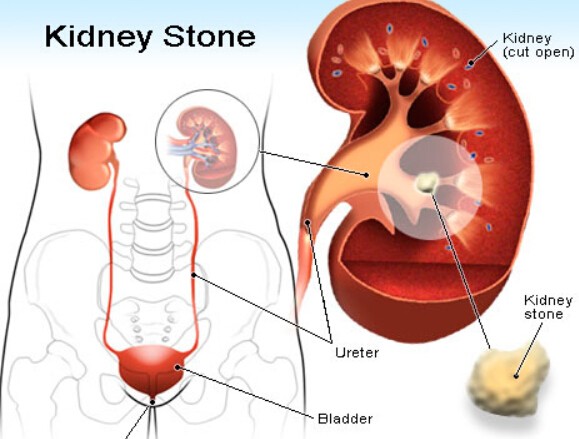
This is one of the common causes of lower right back pain. Kidney stones are small “pebbles” made of salts and minerals that form inside your kidneys. When the stones move from your kidneys through the urinary tract, you will feel severe pain.
Since the kidneys are located near the back, the back becomes affected if something is wrong with your kidneys. The type of pain in the lower back may be on the left side or the right side, depending on the affected kidney. You may feel pain that ranges from a dull ache to sudden sharpness in your groin or back.
According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders, the pain from kidney stones usually comes and goes or is constant for a long time. The pain usually occurs on just one side of your back. Other common symptoms include restlessness, hematuria, vomiting, sweating, nausea, and urinary urgency.
Small kidney stones usually do not require treatment as the stones can spontaneously through urination. You need to drink a lot of water. You can also try apple cider vinegar which can help dissolve mineral buildup in your kidneys.
10. Kidney Problems
In addition to kidney stones, kidney infections can also cause pain in your lower back or groin. A kidney infection is an inflammation caused by bacteria. You may also have other symptoms, including weakness, fever, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. In addition, you may feel a burning sensation when urinating, and your urine has a strange smell and is cloudy.
To keep your kidneys healthy, you need to drink a lot of water. Water can help kidneys detoxify and remove waste. At the same time, you need to avoid excessive caffeine, alcohol, salt, and sugar. If the fever persists, you need to seek medical help immediately.
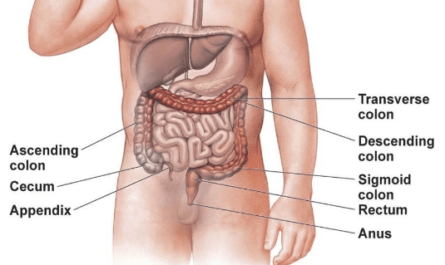
11. Gastrointestinal Problems
Some gastrointestinal problems such as ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), diverticulitis, etc., can cause right or left back pain. These gastrointestinal problems are often accompanied by abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea, especially after eating. You can improve your digestive system health by changing your diet, drinking warm water, or taking probiotic supplements.
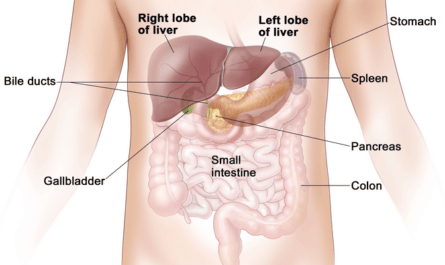
12. Gallbladder or Liver Problems
These problems are less common causes of lower right back pain. However, in some cases, they can also cause back pain. Gallbladder inflammation usually causes right upper quadrant or back pain, especially after your meals. Liver problems can cause abdominal or back pain accompanied by jaundice, nausea, fatigue, or loss of appetite.
13. Appendicitis
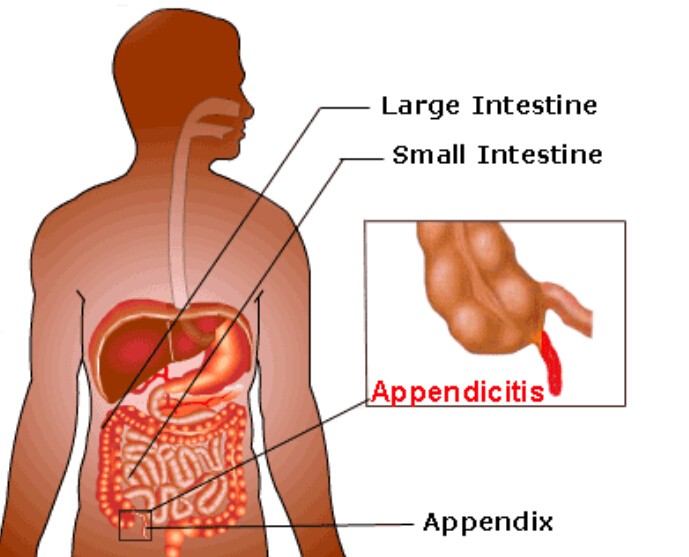
The appendix is a small pouch-like tissue sac located on the right side of the abdomen. Appendicitis can cause severe pain on the right side of the lower back. In addition, appendicitis can also cause a dullness in your upper back or rectum.
This pain often comes suddenly from behind your belly button, with a focal point in the lower right abdomen. Other symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and fever. Appendicitis is a serious illness, so if you have any signs of appendicitis, you should see your doctor immediately.
14. Pregnancy
Women in pregnancy often suffer from lower back pain due to the changes in the pelvic area and weight gain. This is especially common in the second and third trimesters. The abdominal pain and cramps may persist during your pregnancy. You can try using a heat bag on your back above your hips to ease the pain. If the pain persists, you should see a doctor immediately.
When to See a Doctor for Low Right Back Pain
Seek medical attention immediately if you also experience any of the following:
- Pain is accompanied by fever or chills
- Severe trauma or injury to your spine
- Numbness and tingling in the leg or foot
- Night sweats or weight loss rapidly
- Difficulty controlling bladder or bowel function
- Sudden abdominal or back pain that affects your daily activities
- Some parts of the back can be painful to touch
- Difficulty in moving around even with simple activities such as sitting and walking
- Muscle spasms or lower back pain lasts for a long time
Even if you do not experience the symptoms mentioned above, but you are suffering from lower back pain, get to know the actual cause of the pain. You may be surprised by the conditions that are causing your discomfort.
Final Words
Lower right back pain can be mild to extremely severe. It is best to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis as the pain could sign a severe medical condition. Some natural treatments for back pain include chiropractic adjustments, regular full-body exercise, essential oils, OTC medications, Epsom salt baths, and improving posture in mild cases. In severe cases, you need to seek medical help immediately.