Shoulder blade pain is also known as interscapular pain. It refers to physical discomfort, aching, and soreness around the shoulder blades. The space between the shoulder blades consists of multiple formations. Pain can derive from any of these structures, and treatment must understand where it comes from.
Some pains may disappear due to mild strains or tired muscles caused by working in front of a computer for long periods, heavy lifting, exercises, or poor posture. In these cases, the pain will dissipate and should not be a cause for concern.
However, some reasons could result from an injury, disorder, or severe health condition that requires medical intervention. It is vital to understand its underlying causes to remove the shoulder blade’s pain quickly. This article will discuss 22 common causes of pain between shoulder blades with treatment.
22 Common Causes of Pain Between Shoulder Blades
Here are 22 common causes of shoulder blade pain with treatment.
1. Cervical Arthritis (Spondylosis)

Cervical Spondylosis is a common condition among people aged 60 and above. It involves changes to the bones, joints, and neck discs caused by wear and tear. This condition is a common cause of pain between the shoulder blades.
Signs of osteoarthritis develop as the disks degenerate, which worsens with age. For most people, there are no signs or symptoms. When symptoms appear, they usually include stiffness and pain in the neck.
If nerve roots or spinal cord become pinched, it may result in weakness, tingling, numbness in arms, hands, legs, or feet, loss of bowel or bladder control, difficulty walking, and lack of coordination.
2. Bad Posture
Bad posture contributes to pain between the shoulder blades. Many people suffer from the damaging effects of poor posture.
When the spine is in an unusual position, the muscles, joints, and vertebrae are also stressed and receive pressure. If wrong positioning continues, it can result in body pains, including shoulder blades, upper or lower back pain, and arm and neck pain.
Some factors contributing to postural dysfunction include a lack of awareness of proper posture, a sedentary lifestyle, job-related demands, poor core stability, lack of exercise, and joint stiffness.
3. Herniated Disk
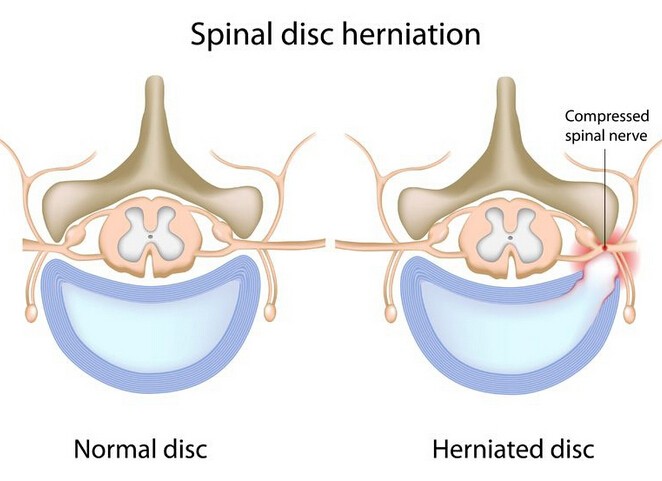
A herniated disk is a problem with one of the disks (rubbery cushions) between the vertebrae (individual bones that stack up to make the spine).
Also called a ruptured or slipped disk, it is usually caused by age-related wear and tear. It may also occur when using back muscles for lifting heavy objects. Besides, accidents and injuries can also result in this condition.
The common signs and symptoms include arm or leg pain, neck and shoulder pain, tingling sensation or numbness, and weakness of the muscles.
4. Heart Attack
One of the possible causes of pain between shoulder blades is a heart attack. This occurs when a buildup of cholesterol, fat, and other substances blocks blood flow to the heart. Heart attacks can also cause pain between the shoulder blades.
The interrupted flow of blood can damage areas of the heart muscle. A heart attack’s common signs and symptoms include tightness, pressure, pain, aching, or squeezing sensation in the chest or arms extending to the neck, back, or jaw. Other symptoms are shortness of breath, cold sweat, indigestion, abdominal pain, nausea, and heartburn.
Call your local emergency number immediately if you or someone you know is experiencing some of these symptoms.
5. Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spaces within the spine. This puts pressure on the nerves and may result in muscle weakness, numbness, and tingling sensation in arms, hands, feet, legs, and neck pain.
While some people have a naturally small spinal canal, this condition may also occur due to herniated disks, bone overgrowth, tumors, spinal injuries, and thickened ligaments. If not treated immediately, it may progress and cause balance problems, incontinence, or paralysis.
The tests to diagnose spinal stenosis include X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or CT scan. Depending on the severity, doctors may prescribe pain relievers, physical therapy, steroid injection, decompression procedure, or surgery.
6. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is also one of the possible causes of pain between shoulder blades. This condition affects millions of people around the world.
It occurs when the protective cartilage of the bones starts to wear down with age and may worsen over time. Its symptoms include joint stiffness, pain, the grating sensation when using the joint, tenderness, bone spurs, and loss of flexibility.
Although symptoms can be managed, the primary cause cannot be reversed. Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and other remedies can help enhance joint function. The pain may be alleviated with certain medications and physical therapy.
7. Trauma
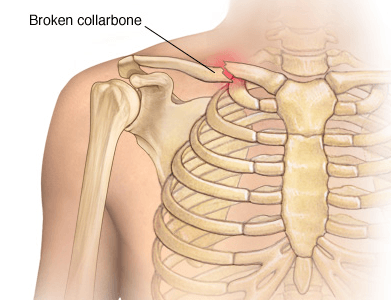
Injuries are one of the common causes of pain between shoulder blades. Shoulder issues develop from overuse, everyday wear, tear, or an injury. Specific conditions that may result in trauma include rotator cuff tears and acromioclavicular joint separation.
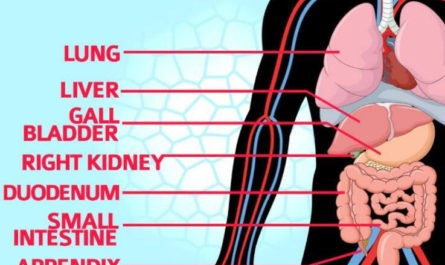
8. Cancer
Lung cancer may cause pain in the shoulder blades by putting pressure on the nerves near the upper part of the lungs. Pancoast tumors, a type of lung cancer, can affect tissues near the shoulders. It also causes shoulder pain that extends to the arms.
Other cancers that may cause acute or severe pain in this area are liver, mesothelioma, esophageal, and lymphomas. Cancers that spread to the bones in the neck region may result in pain between the shoulder blades.
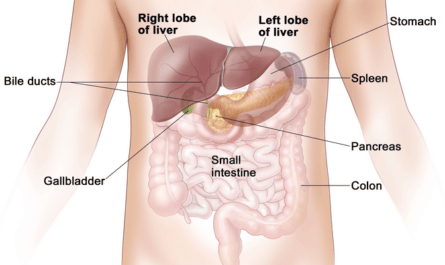
9. Gallbladder Disease
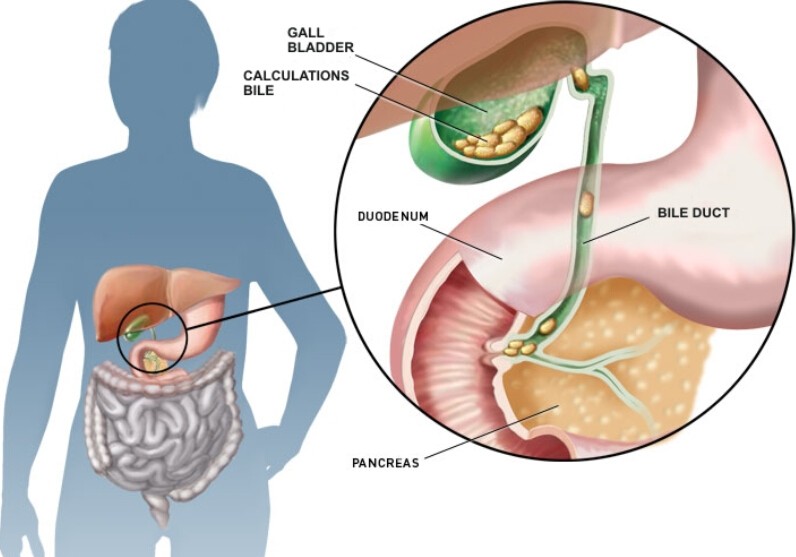
The gallbladder is a small sac located beneath the liver that stores the bile produced by the liver. The buildup of bile causes inflammation of the gallbladder or cholecystitis.
Other causes of the rash include tumors or bile duct blockage. This may lead to severe and life-threatening conditions if not treated immediately.
The signs and symptoms of gallbladder disease include severe pain in the upper right abdomen, pain radiating to the back or shoulder, nausea, vomiting, and fever. Treatments for cholecystitis may consist of fasting, pain medications, and antibiotics.
10. Nerve Entrapment
In some cases, pain between the shoulder blades can be caused by nerve entrapment, such as thoracic outlet syndrome and myofascial pain syndrome.
Thoracic outlet syndrome occurs when nerves or blood vessels in the space between the first rib and collar bone are compressed. Common causes of these conditions include physical trauma, anatomical defects, repetitive injuries, and pregnancy.
Myofascial pain syndrome involves an aching pain in a muscle that worsens or persists. Sensitive areas or trigger points of tight muscle fibers may develop in the muscles after overuse or injuries. People who always experience anxiety and stress are likelier to form trigger points.
11. Acid Reflux
Acid reflux may also cause pain between the shoulder blades. This common condition is caused by stomach acid moving into the esophagus (food pipe).
Common risk factors for this condition include lying down after a meal, eating large portions, snaking close to bedtime, and drinking alcohol, coffee, or carbonated drinks. Taking medications, being overweight, and being pregnant may also cause symptoms of acid reflux.
12. Shingles
Shingle is a viral infections that can occur in any body area. Caused by the varicella-zoster virus, shingles are not a life-threatening disease but can lead to extreme discomfort.
Other symptoms of shingles may include sensitivity to touch, red rashes, burning or tingling sensation, pain, numbness, and sensitivity to touch.
13. Pulmonary Embolism
A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a pulmonary artery in the lungs. This is commonly caused by blood clots from the legs or other body parts that travel to the respiratory system. The clot prevents blood from flowing to the lungs, making this condition life-threatening if not treated immediately.
Other signs of pulmonary embolism include difficulty breathing, chest pain like having a heart attack, and a cough that may produce blood. You may also experience leg pain, fever, dizziness, irregular heartbeat, and discolored skin.
14. Muscle Strain

Muscle strain is the most common cause of pain between shoulder blades. This can result from excess lifting, poor posture, sleeping on an old mattress, physical activities, and sports that involve twisting, such as tennis and golf.
15. Stomach Ulcers
Also known as gastric ulcers, stomach ulcers are painful sores in the stomach lining. Its common symptom is pain or burning sensation in the middle of the abdomen, between your belly button and chest.
Other signs of ulcers include nausea or vomiting, bloating, acid reflux, and heartburn. Pain may also worsen when you drink, eat, or take antacids. In some cases, shoulder pain can be the sole symptom of a benign gastric ulcer.
Stomach ulcers are commonly caused by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) and the long-term use of NSAIDs. Most can be treated with doctors’ prescriptions. In rare cases, surgery may be necessary.
16. Liver Congestion
Liver congestion occurs when the liver finds it difficult to keep in need of detoxification. One of the possible causes of pain between shoulder blades is other symptoms. Your liver may be sluggish or congested, including poor digestion, skin problems, weight gain, and fatigue.
You may also experience chemical sensitivities, sweet cravings, hormonal imbalances, white coating on your tongue or bad breath, abdominal pain, and other gall bladder problems.
A congested liver can be treated with natural remedies, nutrient support, and proper detoxification. You can also ask for advice from a professional to support your body and help you feel better.
17. Angina
Angina causes pain in the shoulder blades, neck, arms, back, or jaw, with accompanying chest pain. The discomfort or pain may be described as squeezing, pressure, pain, or fullness in the middle area of the chest.
Other symptoms include shortness of breath, dizziness, sweating, nausea, and fatigue. For others, the symptoms of angina may feel like indigestion.
This condition occurs when blood flow to the heart muscle is reduced. This prevents the heart from getting enough oxygenated blood. The common cause of angina is coronary artery disease (CAD).
18. Scoliosis
A person has scoliosis when the spine curves sideways instead of running straight down the middle. The curve’s angle may be small, medium, or large. Tips that measure more than 10 degrees are already considered scoliosis. This condition is noticeable when the person stands. The hips or shoulders do not appear to be straight or lean slightly.
If not treated properly, the spine may twist or rotate. This makes one side of the ribs curve farther. For any signs or symptoms of scoliosis, it is essential to visit a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
19. Exercise
If you just started a new exercise involving your upper body, you may experience pain between the shoulder blades for two or three days. Sore muscles after exercises are known as delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS). This occurs when you change your exercise routine, begin a new exercise problem, or increase the intensity or duration of your workouts.
20. Heavy Lifting

When you pitch every weekend or lift weights, you put pressure and wear and tear on your shoulder joints, tendons, and muscles.
The uncomfortable feeling after a challenging workout is a side effect of muscle rebuilding. This is normal when heavy lifting is done correctly. The pain should disappear after three to five days.
However, not warming up properly, carrying too much weight, and using poor lifting methods may cause overuse injuries like strains/sprains, tendonitis, and bursitis.
21. Fibromyalgia
One of the possible causes of pain between shoulder blades is fibromyalgia. It is a health condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain.
Fibromyalgia symptoms usually appear after an infection, surgery, physical trauma, or significant psychological stress.
Fibromyalgia may co-exist with other conditions, such as migraine, headaches, bladder syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, and temporomandibular joint disorders. You may suffer from mood or memory problems, difficulty sleeping, and fatigue.
22. Gallstones
Gallstones form when your bile contains high cholesterol levels, your gallbladder does not flush properly, or when your bitterness has too much bilirubin. Bilirubin is produced when the body breaks down red blood cells. This condition is a common cause of pain between the shoulder blades.
Health conditions that cause the liver to produce excessive bilirubin include specific blood disorders, biliary tract infections, and liver cirrhosis.
Gallstones may not show any signs or symptoms. When they cause a blockage, it intensifies pain in the upper right portion or center of the abdomen, back pain between shoulder blades or right shoulder, nausea, and vomiting.
Treatment for Pain Between Shoulder Blades
Treatment will depend on the underlying cause of your health condition. Here are some common treatments for shoulder blade pain.
1. Exercises and Stretches
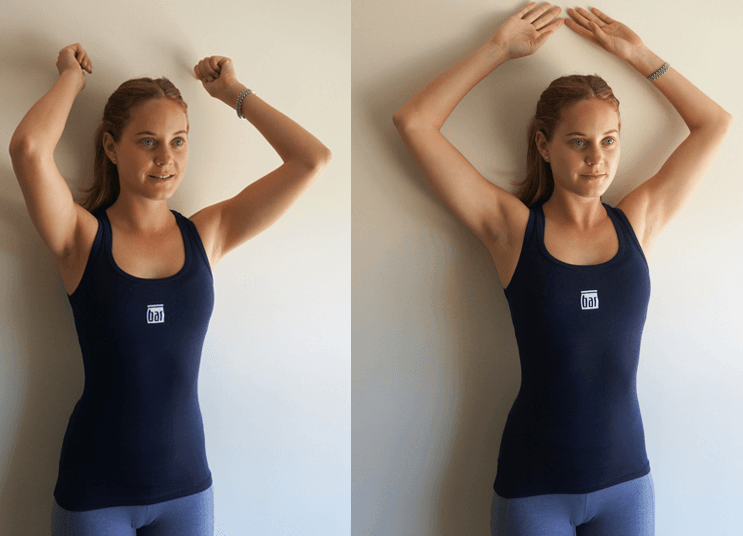

Simple stretches, exercises, and self-massages with simple tools can prevent and treat shoulder blade pain.
Method 1: Start in a seated position in a chair. Place your hands behind your head. Lean your upper back over the back of the chair to stretch your upper back as if you are hurting after waking up. Hold this position for 15 seconds and relax. Perform five repetitions.
Method 2: To stretch the pectoralis minor, get on all fours next to a knee-high object. Gently bend your arm to 90 degrees, placing it on top. Exhale and twist gently, pressing your shoulder of that arm to the other hand. Repeat this stretch with your other arm.
Method 3: You can perform the child’s pose to release tightened rhomboids. Start by kneeling on the floor. Keep your knees hip-width apart and your toes together. Sit on your heels and gently lean your upper body forward.
Your upper body should be on top of your thighs as you place your forehead on the ground. Stretch your arms over your head and rest your palms on the floor. Hold this position for 1 minute and release slowly. Perform three repetitions.
Daily exercise can help strengthen the muscles of your back. You can also ask a professional for more activities and stretches that aim between shoulder blades.
2. Proper Diet
Poor nutrition contributes to tiredness, stress, and the capacity to work. It also increases the risk of developing illnesses and other medical problems. Your diet affects your overall health. For example, eating fatty meals is one of the causes of gallbladder disease. Lack of calcium intake can speed up the process of bone degeneration.
A proper diet is not only beneficial for managing your weight, but it also influences your physical functions. Practice good eating habits to help strengthen your body and enhance your immune system. Eat plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables and choose foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Avoid processed foods and inflammatory foods.
3. Rest

For mild muscle strain caused by work, exercises, or heavy lifting, allow your body to rest to prevent further complications.
- Take short breaks at work before you start to feel overtired. Pushing yourself further will make it more difficult for your body to recover.
- Get an appropriate amount of sleep. Stay away from phones, laptops, and other electronics at night.
4. Hot or Cold Therapy
Hot compresses help treat pain between shoulder blades, swelling, and inflammation. It also relieves the pain caused by strain.
- Fill a water bag with hot water. Apply this compress to the painful areas for 10 to 15 minutes. Repeat this process a few times a day for immediate relief.
- Another option is to take a warm bath or shower. Allow your body to soak for 5 to 10 minutes. Enjoy a warm shower two times a day to alleviate the pain. If you want a warm bath, consider adding 2 cups of Epsom salt.
Cold compresses are also beneficial as the cold temperature numbs the area, alleviating pain and inflammation.
- Wrap some ice cubes in a thin towel.
- Apply it to the affected areas for ten to fifteen minutes.
- Follow this treatment a few times a day.
5. Massage
Another excellent way to alleviate shoulder blade pain is by relaxing massage. This will allow your shoulder muscles to release tension and stress.
It also helps in reducing stiffness and swelling while improving blood flow. Get the gentle massage done by your partner, friend, or anyone in your house.
- Warm-up coconut, mustard, olive, or sesame oil slightly.
- Apply the oil to the affected areas.
- Gently squeeze the muscles and apply gentle pressure to promote blood flow and alleviate pain.
- Massage for 10 minutes and place a warm towel over the shoulders.
- Perform massage therapy two to three times a day.
Do not massage the area if it is injured or very painful. It is best to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
6. Medications
In most cases, shoulder blade pain will go away with proper treatment and enough rest. Your doctor may prescribe medications to relieve discomfort and pain. These may include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Steroids
- Muscle relaxers
- Antidepressants
7. Surgery
Sometimes surgery may be required if the pain between shoulder blades is severe or caused by mendable damage.
When You Should See A Doctor
See your doctor immediately if your pain is unusual, severe, or disappears. This could be a sign of a health problem. Seek medical assistance right away if you experience the following:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Excessive sweating
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Coughing up blood
- Swelling, pain, or redness in one or both legs.
- Fever
- Paralysis on one side of the body
- Blurry vision
- Irregular or rapid heartbeat
- Difficulty speaking
- Loss of consciousness