Pain in the heel of the foot is a common condition that can affect people of all ages. The pain can be felt at the bottom or back of the heel and can range from mild discomfort to severe pain. This will make it difficult to walk or stand. This condition can be caused by various factors such as plantar fasciitis, heel spurs, Achilles tendonitis, or simply wearing the wrong shoes.
If left untreated, the pain can worsen and lead to long-term damage, making it crucial to seek timely medical attention. Fortunately, many effective treatments are available, from simple lifestyle changes to more invasive procedures. In this article, we will explore the common causes of heel pain and the best ways to manage it.
Symptoms of Pain in Heel of Foot
The symptoms of pain in the heel of the foot can vary depending on the underlying cause, but some common symptoms include:
- Sharp or stabbing pain in the heel(Resource)
- Pain that is worse in the morning or after periods of rest
- Pain that improves with activity but worsens after prolonged activity
- Tenderness or swelling in the heel
- Difficulty walking or standing for long periods
- Pain that worsens when standing on hard surfaces
- Numbness or tingling in the heel or foot.
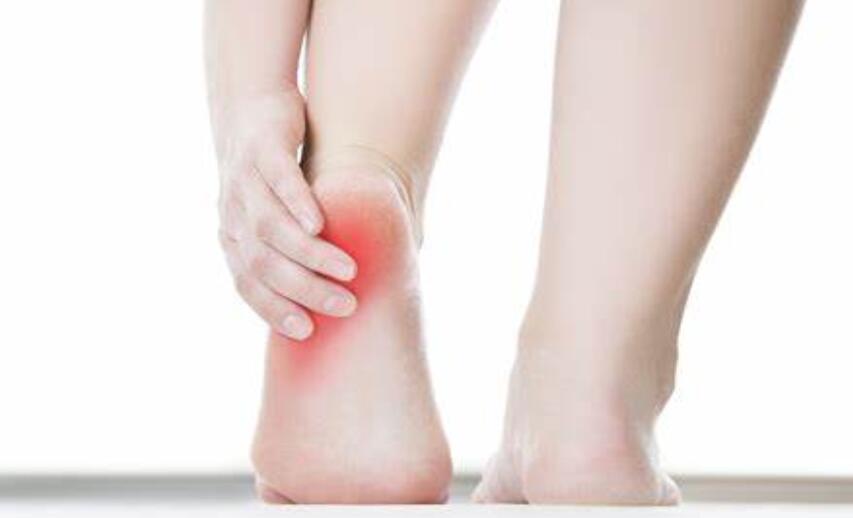
14 Causes of Pain in Heel of Foot
There are several causes of heel pain, including:
1. Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is caused by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes. The inflammation can result from overuse, repetitive strain, or injury to the fascia.
The most common symptom of plantar fasciitis is pain in the foot heel. The pain is usually worse in the morning or after prolonged periods of sitting or standing. It may also be accompanied by stiffness, swelling, or a burning sensation in the heel.
Treatment for plantar fasciitis typically involves a combination of rest, stretching, and strengthening exercises. Over-the-counter pain medication, such as ibuprofen, can help to reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy and orthotics, such as shoe inserts or custom-fitted shoes, may also be recommended.
2. Heel Spurs
Heel spurs are bony growths that develop on the underside of the heel bone, often caused by strain and stretching of the plantar fascia. They can cause severe pain and discomfort in the heel of the foot, especially when standing or walking.
Treatment for heel spurs typically includes rest, stretching exercises, and physical therapy to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Over-the-counter pain medications and corticosteroid injections may also be recommended.
Custom orthotics and supportive footwear may also help reduce pressure on the heel. In rare cases where conservative treatments do not relieve symptoms, surgical intervention may be required to remove the heel spur.
3. Metatarsalgia
Metatarsalgia is characterized by pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot near the base of the toes. This pain can also extend to the heel of the foot, causing discomfort and difficulty with walking or standing.
There are several potential causes of metatarsalgia, including high-impact activities such as running or jumping, ill-fitting shoes that do not provide proper support, and foot deformities such as bunions or hammertoes.
Treatment for metatarsalgia may involve rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain medications to manage symptoms. Additionally, wearing shoes and undergoing physical therapy exercises can help alleviate pain and prevent further damage.
4. Achilles Tendinitis
Achilles tendonitis is a condition that causes pain and inflammation in the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. It is often caused by overuse, repetitive strain, or a sudden increase in physical activity.
Symptoms of Achilles tendinitis include pain, stiffness, and swelling in the heel and lower leg. Treatment options include rest, ice, compression, elevation, and physical therapy to improve strength and flexibility in the affected area.
Pain and anti-inflammatory drugs may also be prescribed to help alleviate pain and swelling. In severe cases, a walking boot or cast may be required to immobilize the affected area and promote healing.
5. Bursitis
Bursitis is a painful condition that can affect any joint in the body, including the heel of the foot. It is caused by inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles. Bursitis symptoms in the heel may include pain, swelling, redness, and stiffness.
Treatment for bursitis typically involves rest, ice, compression, elevation, pain medications, and anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and swelling. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to provide additional relief.
6. Sever’s Disease
Sever’s disease, also known as calcaneal apophysitis, is a common cause of heel pain in growing children and adolescents. It occurs when the growth plate at the back of the heel becomes inflamed due to repetitive stress or strain. Symptoms of Sever’s disease may include pain, swelling, and tenderness in the heel, particularly during physical activity or exercise.
Treatment for Sever’s disease typically involves rest, ice, compression, elevation, and physical therapy to improve strength and flexibility in the affected area. Pain and anti-inflammatory drugs may also be recommended to reduce pain and swelling.
7. Stress Fracture
A stress fracture is a small crack in a bone that occurs due to repetitive stress or overuse. It can cause pain and discomfort in the heel of the foot, especially during physical activity. Symptoms of a stress fracture may include pain, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area.
Treatment for a stress fracture typically involves rest, immobilization, and protection of the affected area. Sometimes, a cast or walking boot may be required to immobilize the foot and promote healing. Pain and anti-inflammatory drugs may also be prescribed to reduce pain and swelling.
8. Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Tarsal tunnel syndrome is a condition that occurs when the tibial nerve, which runs down the back of the leg and into the foot, is compressed or squeezed as it passes through a narrow tunnel in the ankle. This can cause pain, numbness, and tingling in the heel of the foot, as well as weakness or a burning sensation.
Treatment for tarsal tunnel syndrome typically involves rest, ice, compression, elevation, and physical therapy to improve strength and flexibility in the affected area. Pain and anti-inflammatory drugs may also be prescribed to reduce pain and swelling.
9. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a common condition that occurs when the cartilage in the joints of the body breaks down, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. It can affect any joint in the body, including the heel of the foot, and is often caused by repetitive stress or injury.
Treatment for osteoarthritis in the heel typically involves a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Pain medications and anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to reduce pain and swelling.
10. Corns and calluses
Corns are small, round areas of thickened skin that typically form on the tops and sides of the toes, while calluses are larger and form on the soles of the feet. Both conditions can cause burning or aching pain in the affected area.
Common causes of corns and calluses include wearing shoes that are too tight or loose or do not provide adequate support or cushioning.
Treatment for corns and calluses may involve soaking the feet in warm water, using a pumice stone or file to gently remove thickened skin, and applying moisturizing creams or lotions. In more severe cases, a doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections or surgery to remove the corn or callus.
11. Foot Tendonitis
Foot tendonitis is a condition in which the tendons that connect the foot bones to the calf muscles become inflamed or irritated. This can cause pain and discomfort in the heel of the foot, as well as swelling and stiffness.
There are several potential causes of foot tendonitis, including overuse of the foot muscles and tendons, particularly in activities that involve repetitive movements such as running or jumping.
Treatment for foot tendonitis may involve rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain medications to manage symptoms.
12. Foot arch pain
Foot arch pain is a condition that can cause pain in the heel of the foot. The arch of the foot comprises a complex system of bones, muscles, and ligaments that support the foot and absorb shock during movement. When the arch is strained or injured, it can cause pain that radiates to the heel.
Common causes of foot arch pain include overuse, flat feet or high arches, wearing poorly fitting shoes, or sudden changes in activity level. Symptoms may include pain in the heel or arch of the foot, swelling, and difficulty walking or standing for long periods of time.
Treatment for foot arch pain typically involves rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain medication. Wearing supportive shoes or inserts can help to relieve pressure on the arch and promote healing. Physical therapy may also be recommended to strengthen the foot muscles and improve flexibility.
13. Flat feet
Flat feet, also known as fallen arches, can cause pain in the heel of the foot. It occur when the arch of the foot collapses, causing the entire foot to flatten and putting extra pressure on the heel.
Common symptoms of flat feet include pain and tenderness in the heel of the foot, as well as in the arch and the ball of the foot. The pain may be worse after prolonged periods of standing or walking and may be accompanied by swelling or a feeling of stiffness in the foot.
Treatment for flat feet typically involves wearing supportive shoes or inserts that provide extra cushioning and arch support. Physical therapy may also be recommended to stretch and strengthen the foot muscles and improve overall foot function.
14. Running injuries
Running injuries can cause pain in the heel of the foot. Common running injuries that can cause heel pain include plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendonitis, and stress fractures. Symptoms may include pain in the heel that worsens during or after running, swelling, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected foot.
Treatment for running injuries typically involves rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain medication to reduce inflammation and promote healing. Physical therapy may also be recommended to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the foot and lower leg.
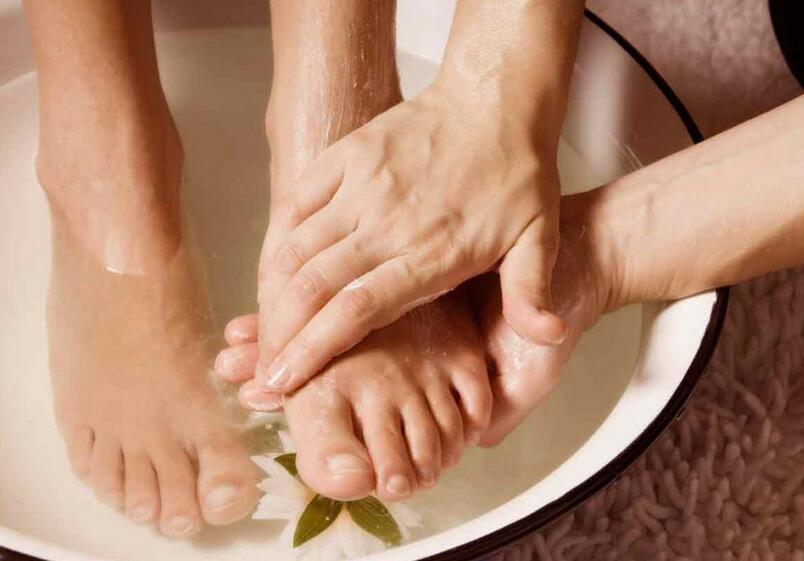

Home Remedies for Heel Pain of the Foot
Here are some more detailed step-by-step instructions for some common home remedies for heel pain:
1. Rest and Ice
Resting the affected foot is crucial for allowing the area to heal. Additionally, applying ice to the painful area can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
To use ice therapy, fill a plastic bag with ice or a frozen gel pack, wrap it in a towel, and apply it to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
2. Stretching exercises
Stretching is one of the most effective home remedies for heel pain. Calf stretches, and plantar fascia stretches can help to relieve pain and improve flexibility.
To stretch the calf muscles, stand facing a wall and place your hands on the wall. Step back with one foot, keeping it flat on the ground, and bend the opposite knee while keeping the back leg straight.
Hold the stretch for 30 seconds and repeat on the other side. To stretch the plantar fascia, sit on the floor and loop a towel around the ball of your foot.
Gently pull the towel toward you, keeping your knee straight until you feel a stretch in the arch of your foot. Hold the stretch for 30 seconds and repeat several times.
3. Massage
Massage is a popular alternative therapy that can help alleviate heel pain in the foot. It involves the manipulation of the soft tissues and muscles in the affected area to increase blood flow, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. A professional therapist can massage the heel at home using a foam roller or tennis ball.
To perform self-massage, place a foam roller or tennis ball under the heel and apply gentle pressure as you roll it back and forth.
You can also use your fingers to apply pressure to the affected area in a circular motion. Be sure to start with gentle pressure and gradually increase as tolerated.
4. Proper Footwear
Choosing proper footwear is an essential part of managing heel pain in the foot. Here are some tips for selecting the right shoes:
- Supportive and Cushioned Soles: Shoes with cushioned and supportive soles can help absorb shock and reduce pressure on the heel. Look for shoes with a thick, shock-absorbing sole.
- Arch Support: Shoes with good arch support can help distribute weight evenly and reduce pressure on the heel. Consider adding an arch support insert if your shoes don’t have enough support.
- Proper Fit: Make sure your shoes fit properly, with enough room for your toes to wiggle and a snug hold around the heel. Avoid shoes that are too tight or too loose.
- Low Heels: High heels can put a lot of pressure on the heel, so choosing shoes with a low heel or no heel is best.
- Avoid Flip-Flops and Thin-Soled Shoes: Shoes with thin, unsupportive soles or flip-flops can exacerbate heel pain by providing little to no support for the foot.
Following these tips and choosing proper footwear can help alleviate heel pain and reduce the risk of future injuries.
5. Epsom Salt Soak
Epsom salt, also known as magnesium sulfate, is a popular home remedy for many ailments, including heel pain in the foot. It has been found to have anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties, making it a great addition to a foot soak.
To use Epsom salt to relieve heel pain, fill a basin with warm water and add one cup of Epsom salt. Soak your foot for 15-20 minutes. The warm water will help increase blood flow to the area, while the Epsom salt will help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
For best results, you can repeat this soak once or twice a week. You can also try adding essential oils, such as lavender or peppermint, to enhance the relaxing and healing benefits of the foot soak.
When to see a doctor?
Heel pain can be a common and usually minor issue, but in some cases, it may indicate a more severe condition that requires medical attention.
- The pain is severe and persistent even after home remedies and rest.
- There is a visible deformity or swelling in the foot.
- There is a sudden onset of pain after an injury.
- The pain is accompanied by fever, redness, or warmth in the affected area.
- There is difficulty in walking or putting weight on the affected foot.
- The pain is recurring or chronic.
- There is a history of diabetes or peripheral arterial disease.
- There is a history of cancer or prolonged use of corticosteroids.
It is always best to consult a doctor if there is any concern or uncertainty about the cause of heel pain or if the pain persists despite home remedies and rest.