Everyone has experienced tightness in the chest at some point in their life. Whether after a hard workout, a stressful situation, or even a period of intense emotion, tightness in the chest can signify many different things.
Tightness in the chest can be caused by physical or mental stress or an underlying medical condition. It can also be a sign of something more serious, such as a heart attack, so it is essential to be aware of the chest’s signs and symptoms of tightness.
In this article, we will explore the many causes of tightness in the chest, how to recognize it, and how to treat it. We will also discuss the importance of seeking medical attention if the condition persists or worsens.

Symptoms of Tightness in Chest
1. Chest Pain: Pain in the chest that can range from mild to severe and can be sharp, dull, or burning. It may occur in isolated areas of the chest or radiate to other body parts, such as the arms, back, or jaw.
2. Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, often accompanied by a feeling of tightness in the chest. It can be a sign of a serious medical condition, so medical attention should be sought immediately if shortness of breath is experienced.
3. Wheezing: A whistling or squeaky sound that is heard when breathing, often due to an obstruction or narrowing in the lungs or airways. It can be a sign of asthma or other respiratory disorders.
4. Palpitations: An irregular heartbeat or fluttering sensation in the chest caused by increased heart rate. It can be a sign of an underlying medical condition and should be evaluated by a doctor.
5. Anxiety: Feelings of fear, nervousness, or apprehension that can manifest as a tightness in the chest. It can be a sign of an anxiety disorder and should be addressed with a mental health professional.
6. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): A condition caused by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus. Common symptoms include chest pain, burning sensations, difficulty swallowing, and a feeling of tightness in the chest.
7. Panic Attack: An episode of intense fear or anxiety that can cause tightness in the chest. Symptoms may include rapid heart rate, sweating, trembling, and shortness of breath.
8. Costochondritis: Inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone. It is usually caused by a viral infection or overuse and can cause chest pain and a feeling of tightness in the chest.
16 Common Causes of Tightness in Chest with Treatment
1. Angina
Angina happens when there isn’t enough oxygen-rich blood going to part of your heart. It can cause pain, pressure, heaviness, squeezing, and tightness in your chest.
Sometimes, It can feel like a heart attack or indigestion. But angina symptoms are more like feeling like a heavyweight has been placed on your chest. The discomfort can also occur in your neck, jaw, back, shoulders, or arms.
You will usually know if you are suffering from Angina if you would feel pain when you are doing tasks more stressful than usual. You may also handle all sorts of pain through the different parts of your body. When you rest, the pain will go away. Some lifestyle changes, participation in sports, and a healthy diet can effectively relieve the symptoms of Angina.
2. Myocardial Infarction
Myocardial Infarction, also known as a heart attack, happens when one of the arteries that supply blood and oxygen becomes blocked. This will cause tightness and crushing in the chest. Other symptoms include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
This is a severe condition because it can have deadly outcomes when the blocked part of the heart muscle is not restored. The longer the heart attack is untreated, the greater the damage to the heart muscle.
Therefore, you must seek medical attention immediately if you suspect a heart attack. Doctors will use drugs or surgical treatments to help restore blood flow.
Read: Where is Your Heart Located? Chest Pains Related to Your Heart
3. Indigestion

Indigestion causes chest tightness, as when your digestive organs cannot digest the food well, the acid will travel upward into the esophagus. You may feel something stuck in your throat. If the condition is severe, you may expel bile and feel stomach pain that radiates to the upper back or down the arms.
There are different reasons why people suffer from indigestion. A lot of people suffer from the condition because of their poor diet. Some people eat fast food daily, so they do not get enough nutrients. At the same time, some develop indigestion because of stress, smoking, or drinking. Sometimes, a complete lifestyle change can lessen situations of indigestion and reduce the tightness in the chest.
If you experience indigestion or heartburn frequently, you should see your doctor as soon as possible. They may prescribe some antacid or heartburn medicine to relieve these conditions.
4. Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is also known as GERD. It usually occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, connecting your stomach and mouth.
GERD is a common digestive disorder, especially for pregnant women. It can cause pain, tightness, and a burning sensation in the chest when acid reflux irritates the lining of your esophagus.
In most cases, GERD can be treated with diet, lifestyle changes, and over-the-counter medications. However, some people may require stronger drugs or even surgery.
5. Ulcers
Stomach ulcers are also known as gastric ulcers. They are painful open sores on the inside lining of your stomach and small intestine.
Typically, stomach ulcers occur when acid in the digestive attacks the surface of the stomach. Helicobacter pylori bacteria usually cause this. You may feel stomach pain that lasts several days or weeks. Other symptoms include heartburn, nausea, burning, bloating, and chest tightness.
The symptoms usually appear between meals or during the night. Eating foods that can buffer stomach acids or antacid medications can help relieve painful symptoms.
6. Infection of the Gallbladder
The gallbladder is an essential organ of the digestive system, located below the liver on the right side of the abdomen. It can secrete bile, which can help the body digest food.
When your gallbladder becomes infected for various reasons, you may feel pain and tightness in your chest area. Luckily, this Infection can be easily treated. However, many people have delayed diagnosis and treatment because of this reason.
If you can get treatment as soon as possible, you may need some medicine, but surgery may be the best option if it is already severe.
7. Pleurisy
Pleurisy, also called pleuritis, occurs when the pleura becomes inflamed. This type of lung infection can cause tightness in the chest and sharp chest pain that worsens during breathing or coughing. The pain can also radiate to your shoulder blade.
Pleurisy usually is caused by injury, pneumonia, or rheumatoid arthritis. Treatments for pleurisy depend on the underlying cause.
The condition will resolve on its own when the cause is viral. If it is bacterial pneumonia, an antibiotic will help. If the condition is treated early, you can expect a full recovery.
8. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a severe condition caused by a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection of the lungs. This condition can cause stabbing chest pain and tightness in the chest area when you breathe deeply. In addition, you may suffer from gastrointestinal upset, Fever, Chills, Nausea, vomiting, and green or yellow phlegm.
Pneumonia is usually a complication of an upper respiratory tract infection. You must understand that pneumonia is a severe condition because it can let the lungs fill up with fluid, so a person cannot breathe. If left treated, it would cause danger to life, especially for the elderly and children.
There are many types of pneumonia, but you can avoid the most common ones by having a vaccine.
9. Costochondritis
Costochondritis is an inflammation of the cartilage between your breastbone and ribs. A bacterial, viral, or fungal infection usually causes this condition.
Costochondritis will cause tenderness, stabbing, and tightness in the middle of your chest. Sharp pain may radiate to your back or abdomen. If it is a complication of surgery, you may suffer from other symptoms such as redness, swelling, or pus.
Sometimes, pain from costochondritis is similar to a heart attack or other heart conditions. It occurs most often in women and people older than 40.
Mild costochondritis can improve on its own or through lifestyle changes or some natural remedies. In severe cases, medication is required.
10. Asthma
Asthma is characterized by airway inflammation in your lungs and producing extra mucus. This can lead to chest tightness, breathlessness, wheezing, morning coughing, and trouble sleeping.
Usually, the severity of Asthma can vary from mild to severe and varies from person to person. It can interfere with your daily activities and threatens life in extreme cases.
Unfortunately, Asthma cannot be treated so far, but the symptoms can be controlled with prescription medications.
11. Muscle strain
A muscle strain, or pulled muscle, is an injury to a muscle or a tendon. This condition usually occurs when your power is overstretched or torn. Some intense activities like reaching, lifting when twisting, or improper muscle use can also lead to pulled muscles.
Although muscle strain often occurs in the muscles at the back of the thigh or lower back, it can also occur in the chest. You may experience chest tightness, pain, tenderness, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
Muscle strain typically needs a while to heal, but some physical therapy can also help accelerate the healing process.
12. Shingles
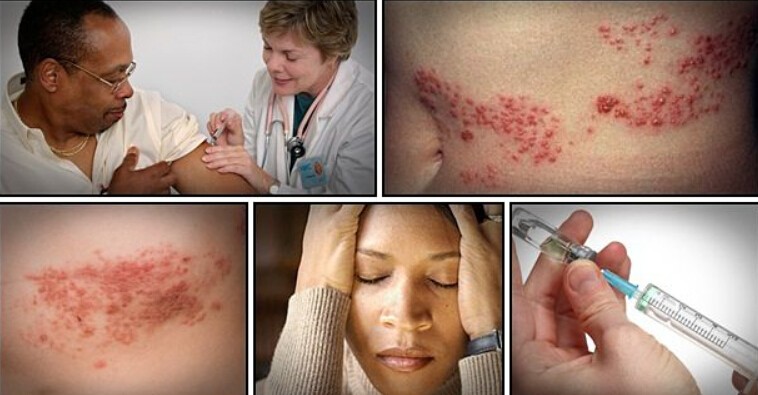
Shingle is a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) that can also cause chickenpox. Shingles can cause a painful rash, sharp pain, and tightness in the chest. This condition usually lasts between 2 to 6 weeks.
Although shingles can appear anywhere, they are often concentrated on one side of the body and wrapped around your chest. Other symptoms include fever, fatigue, itching, pain, headache, blisters, burning, numbness, tingling, and sensitivity to touch.
Shingles can be excruciating, although it is not life-threatening. If not treated, it can cause scarring and even blindness. If you suspect you have shingles, get medical attention immediately. The doctor may prescribe some antiviral drugs to help reduce the pain and risk of complications.
13. Hepatitis
When a person has hepatitis, this means that the liver is inflamed. People who have hepatitis usually report that they also experience pain and tightness in their chest area, probably because the body’s different organs are connected.
Aside from hepatitis, other types of liver inflammation can also cause tightness in the chest area. If you suspect that your liver is the reason you feel pain, have yourself checked by the doctor immediately.
14. Anxiety

According to research, about 40 million people in the United States suffer from anxiety. Chest tightness is a typical symptom of anxiety. Other symptoms include dizziness, nervousness, and breathing difficulty. In addition, anxiety can also increase your heart rate and impede your breathing.
If you feel a tightness in your chest area because of anxiety, the most effective solution is to relax. Exercise or yoga can also help you relieve anxiety.
15. Stress
Do you know that stress can cause tightness in your chest area? This is because stress can affect your thoughts, feelings, and organs in the body. Chest pains and tightness usually occur during highly stressful times. In addition, stress can increase the risk of many health problems, such as obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure.
The pain or tightness may worsen the more stressed you become. You can relieve stress with these methods, including listening to music, lifestyle changes, and counseling.
16. COVID-19 (the new coronavirus)
Do you know that COVID-19 can also cause tightness in the chest? According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), this viral disease can cause a dry cough, fever, and shortness of breath. These symptoms typically appear between 2 and 14 days after contact with the virus.
If you suffer from emergency symptoms such as bluish lips, trouble breathing, or persistent drowsiness, contact your doctor or medical services as soon as possible.
Home Remedies for Tightness in the Chest
1. Ginger Tea
Ginger tea is an effective remedy for tightness in the chest. It helps to relax the muscles and reduce inflammation. To make ginger tea, add one teaspoon of freshly grated ginger to one cup of hot water and steep for 10 minutes. Drink this tea several times a day to relieve chest tightness.
2. Herbal Tea
Herbal teas such as chamomile, peppermint, and green tea can help reduce chest tightness. To prepare, steep one or two teaspoons of your chosen herbal tea in one cup of hot water for 10 minutes. Drink several cups of this tea throughout the day to reduce tightness in the chest.
3. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is a natural remedy for chest tightness. It helps to reduce inflammation and helps to relax the muscles. To use, add one tablespoon of apple cider vinegar to one cup of warm water and drink several times a day.
4. Steam Inhalation
Steam inhalation is an effective remedy for chest tightness. It helps to reduce inflammation and helps to relax the muscles.
To use, fill a bowl with hot water, add a few drops of eucalyptus oil, and place your face over the bowl. Cover your head with a towel and inhale the steam for 5–10 minutes.
5. Turmeric
Turmeric is a natural remedy for chest tightness. It helps to reduce inflammation and helps to relax the muscles.
To use, mix one teaspoon of turmeric powder in one cup of warm milk and drink it several times a day. You can also mix one teaspoon of turmeric powder with a glass of warm water and drink it twice daily.
When to See a Doctor?
Here are some symptoms that can be a sign of a serious condition:
- A sudden feeling of a rapid heartbeat, fever, cold sweat.
- Tightness, squeezing, and pressure in the center of the chest feel like a huge pressure will constrict your chest.
- Severe chest pain spreads to your jaw, chin, neck, left arm, or back.
- Sudden diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting.
- Coughing up yellow or green mucus with difficulty breathing.
- Constant chest pain with extreme fatigue and tiredness.
- There is a severe burning sensation in the chest and abdominal pain.