Tinea unguium, also known as skin fungus infection of the nail(onychomycosis), is characterized by yellowish or white patches on the nails. Tinea unguium usually occurs on the toenails, also known as tinea pedis. It can cause thick and unsightly nails and is uncomfortable but not painful. This condition usually occurs in puberty, and the frequency will increase with age. (Resource)
Tinea unguium can be caused by many reasons, such as touching damp surfaces, infected people, or pets. Fungal nail infections are often difficult to treat but are easily treatable if caught early. This article will discuss tinea unguium symptoms, causes, and treatment.
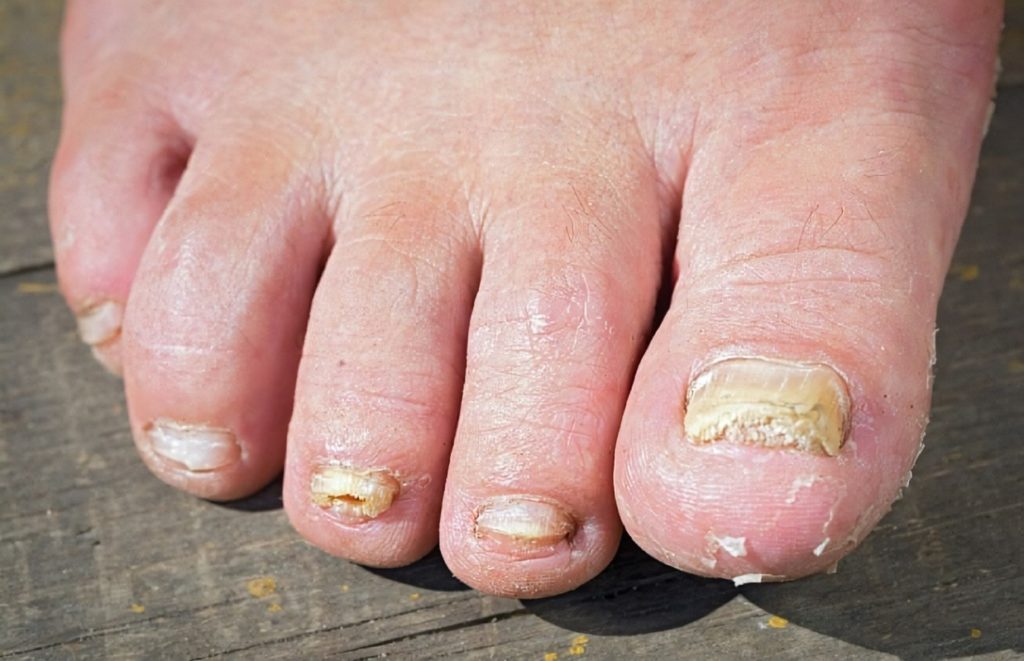
Symptoms of Tinea Unguium
1. Thickened
Nail fungus can cause your nails to thicken because of the build-up of dead skin cells, debris, and fungus beneath them. Your nails will appear thickened and yellow or white. There may also be some black discoloration of the nail if it has been infected for a while.
2. Itching
It’s normal for your nails to itch. If you have tinea unguium, you may experience an intense itching sensation on your toe or fingernails. The itch is often worse at night when you’re lying in bed, listing to figure out where the itching is coming from. The itching, though annoying, is not necessarily a sign that you have nail fungus.
3. Nail discoloration
If the infection is severe, it can be challenging to treat because of the discoloration of the nails. These greasy patches can be yellow or brownish and extend from the cuticle toward the nail root. (Resource)
4. Nail separation
Nail fungus often causes nail separation. This results from the thickening and hardening of the nail, making it more challenging to cut through it. When this happens, the nail can split due to a lack of blood supply or trauma to the nail itself when you scratch an itch.
5. Hanging nails
One common symptom is that your nails will hang down instead of flat against your finger as they usually should be. This is more prevalent in toenails than fingernails.
6. Nail deformities
One of the most common nail fungus symptoms is nail deformity. This can include brown spots, ridges, bumps, flaky, rough, and brittle nails that break easily.
7. Ingrown nails
When your nail becomes infected, it can cause the nail to become ingrown and appear shorter than usual.
8. Crumbling nails
If you have nail fungus, you may notice that your nails are cracking and crumbling more quickly than usual. The texture of your nails can become rough, brittle, and flaky. (Resource)
Common Causes of Tinea Unguium
1. Sweaty Feet
It is essential to remember that a humid work environment is one of the leading causes of tinea unguium. If your feet are sweaty, you are more likely to risk infection in the toenails. This means you will often decrease your circulation if you wear shoes that don’t adequately ventilate the feet away from sweating.
2. Nail biting
A common cause of tinea unguium is nail-biting, which can lead to an infection of the nail bed underneath. Nail biting is often considered a bad habit but can also signify stress or boredom.
3. You Have Another Fungal Infection, Such as Athlete’s Foot
Tinea unguium can be a symptom of other fungal infections. You may have another fungal infection in your feet and nails because of sweaty feet or friction on the skin. This is why you should always thoroughly clean and dry the feet, which will help prevent the spreading of any other infections.
4. Use Communal or Shared Showers
If you are in a communal shower, such as at the gym or college dorms, you can quickly spread the infection to another person who uses that shower. This is why you should avoid sharing communal or shared showers if possible.
5. Using Poor Hygiene Products
If you have a poor hygiene routine, this can cause your toenails to become infected with fungus. This is why it’s essential to keep your feet clean and dry at all times and clean your shoes regularly.
5. Having a Genetic Predisposition to Fungal Infection
Another possible cause for tinea unguium has a genetic predisposition to fungal infections, meaning it’s harder for you to fight off an infection than others. This doesn’t mean you’re doomed to get tinea unguium, but you might have accelerated fungus growth due to a weaker immune system.
6. Wear Artificial Nails
Artificial nails can easily cause tinea unguium because they often contain wax-based products. This creates a thick and slippery surface that can promote fungus growth.
7. Not Treating Your Nails Properly
Treating your nails regularly with a protective coat, medicating and moisturizing to keep them from becoming thick and crusty. If you don’t properly take care of yourself, you will not be able to fight off infections such as tinea unguium.
Diagnosis of Tinea Unguium
To make an accurate diagnosis of tinea unguium, a medical professional will do a thorough examination. They will run your nails under the microscope, which can reveal whether or not they are infected with fungus.
They may also be able to perform a biopsy on the pin to see if an actual fungus is growing in the nail matrix so that you know what kind of infection you have. (Resource)
Treatment for Tinea Unguium
Treating Tinea Unguium can be challenging, and it often requires a combination of topical and oral antifungal medications. Here are some common treatments for Tinea Unguium:
- Topical antifungal medications: Topical medications, such as nail lacquers or creams, are often used to treat mild cases of Tinea Unguium. These medications are applied directly to the affected nail and surrounding skin and work by killing the fungus.
- Oral antifungal medications: If the infection is more severe or widespread, your doctor may prescribe oral antifungal medications, such as terbinafine or itraconazole. These medications are taken for several weeks and target the fungus throughout the body.
- Laser therapy: Laser therapy is a relatively new treatment for Tinea Unguium that uses a laser to target and destroy the fungus. This treatment can be effective, but it is often expensive and may require multiple sessions.
- Surgical removal of the nail: In severe cases, your doctor may recommend surgical removal of the infected nail. This procedure is typically done under local anesthesia and involves removing the entire nail or a portion.
- Combination therapy: Your doctor may recommend a combination of treatments, such as topical and oral antifungal medications or combining laser therapy with medication.
It’s essential to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect you have Tinea Unguium. The longer you wait to seek treatment, the more challenging it may be to treat the infection.
Home remedies for Tinea Unguium
Here are some popular home remedies for Tinea Unguium:
- Tea tree oil: Tea tree oil is a natural antifungal agent that can be applied directly to the affected nail. However, it’s important to note that tea tree oil can irritate the skin and should be diluted before use.
- Apple cider vinegar: Apple cider vinegar is another popular home remedy for Tinea Unguium. It can be applied directly to the affected nail or used as a foot soak. However, there is limited scientific evidence to support the effectiveness of apple cider vinegar in treating nail fungus.
- Garlic: Garlic is a natural antifungal agent that can be applied directly to the affected nail. Crush a few garlic cloves, apply the paste to the nail, and then cover it with a bandage.
- Baking soda: Baking soda has antifungal properties and can be used as a foot soak. Add 1/2 cup of baking soda to warm water and soak your feet for 15-20 minutes.
- Coconut oil: Coconut oil is a natural antifungal agent that can be applied directly to the affected nail. Apply a small amount of coconut oil to the nail and surrounding skin, then cover it with a bandage.
While these home remedies may provide some relief from the symptoms of Tinea Unguium, they are not a substitute for medical treatment. If you suspect you have Tinea Unguium, it’s essential to seek medical attention from a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. (Resource)
Prevention of Tinea Unguium
There are several preventative measures you can take to reduce your risk of developing this condition:
- Keep your nails clean and dry: Regularly wash and dry your hands and feet, paying particular attention to your nails. Fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, so keeping your nails dry and clean can help prevent fungus growth.
- Wear breathable shoes and socks: Choose shoes and socks made of breathable materials like cotton or leather to help reduce moisture and promote air circulation around your feet.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Do not share towels, nail clippers, shoes, or socks with others, as this can increase your risk of contracting the infection.
- Protect your nails in public places: Wear shower shoes or flip-flops when using public showers, pools, or locker rooms to avoid coming into contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Trim your nails properly: Trim your nails straight across and keep them short to reduce the risk of injury or trauma, making your nails more susceptible to fungal infections.
- Be cautious with artificial nails: Avoid using artificial nails or nail polish, as they can trap moisture and create an environment for fungi to grow.
Following these preventative measures can reduce your risk of developing Tinea Unguium and other fungal infections.
Complications of Tinea Unguium
Tinea Unguium can cause several complications if left untreated, including:
- Nail deformity: Tinea Unguium can cause the nails to become thickened, discolored, and distorted, leading to an unpleasant appearance and potential pain and discomfort.
- Pain and discomfort: The infected nail may become painful, tender, and sensitive to pressure or touch, making it difficult to walk, wear shoes, or use your hands for certain tasks.
- Secondary bacterial infections: The affected nail may become prone to bacterial infections, exacerbating the symptoms and making the condition more challenging to treat.
- Spread to other nails: If left untreated, Tinea Unguium can spread to other nails, leading to a more extensive and challenging infection.
- Skin infections: In severe cases, the fungus can spread from the nails to the surrounding skin, causing a fungal skin infection known as tinea pedis or athlete’s foot.
When to See a Doctor
Most people can treat tinea unguium with over-the-counter medications. This is why it’s essential to see a doctor if you’re trying to figure out what you have or if your symptoms worsen.
Doctors can also provide a diagnosis and see whether or not your toenails are infected with fungus, which helps to determine what kind of treatment you’ll need.
Conclusion
Toenail fungus is more common than many people realize and can be challenging to get rid of without the help of a doctor. This is why it’s essential to be proactive about your health and appearance.
By taking care of your feet and nails regularly with the proper hygiene products, you can prevent yourself from getting infected in the first place.
If you do find yourself with an infection, you must visit a doctor as soon as possible so that you can get the treatment needed to reverse your symptoms.