Are you experiencing the uncomfortable combination of back pain and nausea? These symptoms can be both distressing and debilitating. Back pain and nausea can be caused by a wide range of factors, from minor muscle strains to more serious health concerns. By understanding the potential causes, you can take steps to find relief and know when to seek medical attention. In this article, we’ll explore 14 common causes of back pain and nausea.
What is Back Pain?
Back pain is a common complaint that can range from mild to severe and can occur in the upper, middle, or lower back. It can be acute, lasting a few days to a few weeks, or chronic, persisting for months or even years. Common symptoms of back pain include:
- Dull, aching pain
- Sharp, shooting pain
- Stiffness or limited range of motion
- Pain that radiates to the legs or arms
What is Nausea?
Nausea is the feeling of discomfort in the stomach that often precedes vomiting. It can be caused by a wide range of factors, including digestive issues, infections, and certain medications. While nausea is not always accompanied by vomiting, it can be a distressing symptom that significantly impacts daily life.
The Connection Between Back Pain and Nausea
At first glance, back pain and nausea might seem like an odd couple. After all, your back and your stomach are two different parts of your body. However, there are several reasons why these symptoms often go hand-in-hand:
- Shared nerve pathways: Your digestive system and your back share some of the same nerve pathways. When something irritates these nerves, you may feel pain in your back and experience nausea or other digestive issues.
- Referred pain: Sometimes, pain in one area of your body can “refer” or spread to another area. For example, a problem with your gallbladder or pancreas can cause pain in your upper back and nausea.
- Underlying conditions: Certain health issues, such as endometriosis, kidney stones, or even the flu, can cause both back pain and nausea as separate symptoms.
Understanding these connections can help you and your doctor pinpoint the root cause of your symptoms and find the most effective treatment plan.

14 Causes of Back Pain and Nausea with Treatment
1. Muscle Strain or Injury
One of the most common causes of back pain is a muscle strain or injury. This can occur due to overexertion, poor posture, or sudden movements. This causes the muscles or ligaments in the back to stretch or tear. In some cases, the pain from a muscle strain can be severe enough to cause nausea or vomiting. Other symptoms may include:
- Stiffness or limited range of motion in the back
- Pain that worsens with movement
- Muscle spasms or cramping
- Tenderness or swelling in the affected area
Treatment for a muscle strain typically involves rest, ice or heat therapy, gentle stretching, and over-the-counter pain medications. In more severe cases, physical therapy may be recommended to help strengthen the muscles and prevent future injuries.
2. Spinal Disc Issues
The spine is composed of a series of bones (vertebrae) separated by soft, cushioning discs. When these discs become damaged or displaced, they can put pressure on the nerves in the spinal column, causing pain and other symptoms. Two common spinal disc issues that can cause back pain and nausea are:
- Herniated Disc: A herniated disc occurs when the soft, gel-like center of a disc pushes through a tear in the outer layer, putting pressure on nearby nerves. This can cause sharp, shooting pain in the back that may radiate to the legs, as well as numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected area. In some cases, the pain can be severe enough to cause nausea or vomiting.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Degenerative disc disease is a condition in which the spinal discs gradually deteriorate over time, losing their cushioning ability. This can lead to chronic back pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. As the condition progresses, the pain may become more severe and be accompanied by nausea or other symptoms.
Treatment for spinal disc issues depends on the severity of the condition and may include pain medications, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, or, in severe cases, surgery.
3. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that can form in the kidneys and cause severe pain as they pass through the urinary tract. The pain often starts in the lower back or side and may radiate to the lower abdomen and groin as the stone moves. Other symptoms of kidney stones may include:
- Severe, intermittent pain that comes in waves
- Pain or burning sensation when urinating
- Frequent urination
- Blood in the urine
- Nausea and vomiting
Treatment for kidney stones depends on their size and location. Small stones may pass on their own with the help of pain medication and plenty of fluids, while larger stones may require surgical intervention.
4. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
A urinary tract infection (UTI) occurs when bacteria enter the urinary system and multiply, causing inflammation and irritation. UTIs can cause back pain, particularly in the lower back, as well as nausea and other symptoms such as:
- Burning sensation when urinating
- Frequent, intense urge to urinate
- Cloudy, dark, or bloody urine
- Strong-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain (in women)
Treatment for UTIs typically involves antibiotics to eliminate the bacterial infection and pain relief medications to manage discomfort.
5. Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas, a gland located behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and hormones. Acute pancreatitis can cause sudden, severe pain in the upper abdomen that may radiate to the back, as well as nausea and vomiting. Other symptoms of pancreatitis may include:
- Fever and chills
- Rapid pulse
- Swollen, tender abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting
The most common causes of pancreatitis are gallstones and heavy alcohol use. Treatment typically involves hospitalization, pain management, and addressing the underlying cause.
6. Gallbladder Issues
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver that stores and concentrates bile, a digestive fluid. Gallbladder issues, such as gallstones or inflammation (cholecystitis), can cause sudden, severe pain in the upper right abdomen. It may radiate to the back, as well as nausea and vomiting. Other symptoms of gallbladder issues may include:
- Fever and chills
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Clay-colored stools
- Nausea and vomiting
Treatment for gallbladder issues depends on the severity of the condition and may include pain management, dietary changes, or surgical removal of the gallbladder.
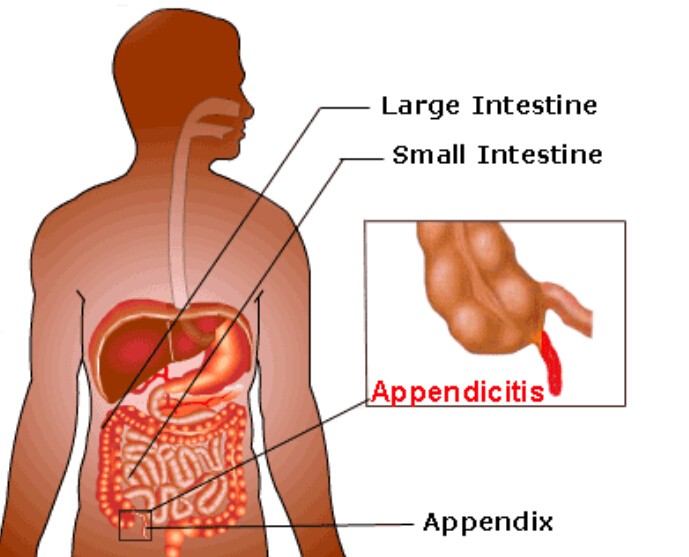
7. Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a serious condition that occurs when the appendix, a small, finger-shaped pouch attached to the colon, becomes inflamed and infected. The pain often starts as a dull ache around the belly button. It may shift to the lower right abdomen and become sharp and severe. Nausea and vomiting are common symptoms of appendicitis, along with:
- Loss of appetite
- Low-grade fever
- Abdominal swelling
- Constipation or diarrhea
Appendicitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt surgical intervention to remove the infected appendix. If left untreated, the appendix can rupture, leading to life-threatening complications.
8. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of disorders that cause chronic inflammation in the digestive tract. The two main types of IBD are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Back pain and nausea are common symptoms of IBD, along with:
- Diarrhea
- Rectal bleeding
- Abdominal cramping and pain
- Fatigue
- Unintended weight loss
Treatment for IBD typically involves a combination of medications to reduce inflammation, suppress the immune system, and manage symptoms, as well as dietary changes and stress management techniques.
9. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus, often on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or other pelvic organs. Back pain and nausea are common symptoms of endometriosis, particularly during menstrual periods. Other symptoms may include:
- Painful menstrual cramps
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Pain during or after sexual intercourse
- Infertility
- Digestive issues, such as diarrhea or constipation
Treatment for endometriosis may include pain medication, hormone therapy, or surgery to remove the endometrial tissue.
10. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive organs, usually caused by sexually transmitted bacteria. Back pain and nausea are common symptoms of PID, along with:
- Fever
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Burning sensation when urinating
- Irregular menstrual periods
PID requires prompt treatment with antibiotics to prevent long-term complications, such as infertility and chronic pelvic pain.
11. Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a condition in which the spaces within the spine narrow, putting pressure on the nerves that travel through the spine. This can cause back pain and nausea, as well as:
- Numbness or tingling in the legs or feet
- Weakness in the affected area
- Pain that worsens with standing or walking
- Difficulty with balance or coordination
Treatment for spinal stenosis may include physical therapy, pain medications, or, in severe cases, surgery to relieve the pressure on the nerves.
12. Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness in specific points on the body. Back pain and nausea are common complaints among individuals with fibromyalgia, along with:
- Fatigue and sleep disturbances
- Memory and concentration problems (“fibro fog”)
- Headaches
- Digestive issues, such as irritable bowel syndrome
Treatment for fibromyalgia typically involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and therapies such as exercise, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and stress management techniques.
13. Meningitis
Meningitis is an inflammation of the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord (meninges). This serious condition can cause back pain, nausea, and other symptoms such as:
- Severe headache
- Stiff neck
- Fever and chills
- Sensitivity to light
- Confusion or altered mental state
Meningitis can be caused by viral, bacterial, or fungal infections, as well as certain medications or medical conditions. Prompt medical attention is essential, as meningitis can be life-threatening if left untreated.
14. Pregnancy
Pregnancy can cause a variety of physical discomforts, including back pain and nausea. As the uterus grows to accommodate the developing fetus, it can put extra strain on the back muscles. This can cause hormonal changes that contribute to nausea (often referred to as “morning sickness”). Other pregnancy-related symptoms may include:
- Fatigue
- Frequent urination
- Heartburn and indigestion
- Swelling in the feet and ankles
- Mood changes
Treatment for pregnancy-related back pain and nausea may include gentle exercise, rest, and safe pain relief methods as recommended by a healthcare provider. Severe or persistent symptoms should always be evaluated to rule out potential complications.

Home Remedies for Back Pain and Nausea
1. Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold to the affected area can help reduce back pain and muscle tension. For acute pain, start with cold therapy by applying an ice pack wrapped in a towel to your back for 15-20 minutes at a time.
This can help reduce inflammation and numb the pain. For chronic back pain, switch to heat therapy using a heating pad, warm compress, or a warm bath to relax tense muscles and improve blood flow to the area.
2. Gentle Stretching and Exercise
Engaging in gentle stretching and low-impact exercises can help alleviate back pain and prevent future episodes. Try exercises like knee-to-chest stretches, pelvic tilts, bridging, and gentle yoga poses to improve flexibility and strengthen your core and back muscles. Regular aerobic exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling can also help maintain mobility and reduce pain.
3.Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter pain medications like acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), or naproxen (Aleve) can help relieve back pain and reduce inflammation. Always follow the dosage instructions on the package and consult with your healthcare provider if you have any concerns or pre-existing medical conditions.
4. Ginger
Ginger has natural anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties that can help alleviate both back pain and nausea. Try drinking ginger tea, taking ginger supplements, or incorporating fresh ginger into your meals. A 2020 review found that consuming ginger can modestly reduce muscle pain and may accelerate recovery from exercise-induced muscle pain.

5. Peppermint
Peppermint has antispasmodic properties that can help relax tense muscles in the back and alleviate pain. It also has a cooling effect that can soothe sore muscles.
You can drink peppermint tea, apply diluted peppermint essential oil to your back, or take enteric-coated peppermint oil capsules.
7. Acupressure and Massage
Applying pressure to specific points on the body, known as acupressure, can help alleviate back pain and nausea. Try pressing on the LI-4 point, located in the web between your thumb and index finger, or the PC-6 point, located three fingers below your wrist on the inner arm.
Gentle self-massage or seeking the help of a professional massage therapist can also help relax tense back muscles and promote circulation.
8. Relaxation Techniques
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate back pain and nausea. Practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, or gentle yoga can help reduce tension in your body and promote a sense of calm. These techniques can also help you cope with the emotional impact of chronic pain and improve your overall well-being.
9. Herbal Remedies
Several herbs have been traditionally used to alleviate back pain and nausea. Turmeric, known for its anti-inflammatory properties, can be consumed as a supplement or added to meals.
Boswellia, also known as Indian frankincense, has been shown to reduce inflammation and alleviate chronic back pain. For nausea, try sipping on chamomile, fennel, or lemon balm tea to soothe your stomach.
When to Seek Medical Attention?
While some causes of back pain and nausea may resolve on their own or with self-care measures, it’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe, persistent, or worsening pain
- Pain that radiates to the chest, jaw, or left arm (may indicate a heart attack)
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs
- Difficulty walking or standing
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fever or chills
- Blood in the urine or stool
- Persistent nausea or vomiting that prevents you from keeping down fluids