Have you ever noticed a cloudy or stringy substance in your urine? That’s likely mucus. Mucus in urine is an abnormal condition where there is an excessive amount of mucus present in the urine. Normally, urine is a clear, yellowish fluid that passes out of the body. However, when there is excess mucus in urine, it can appear cloudy and thick and sometimes have a foul odor. While a small amount of mucus in urine is normal, excessive mucus can signal an underlying health issue. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for mucus in urine.
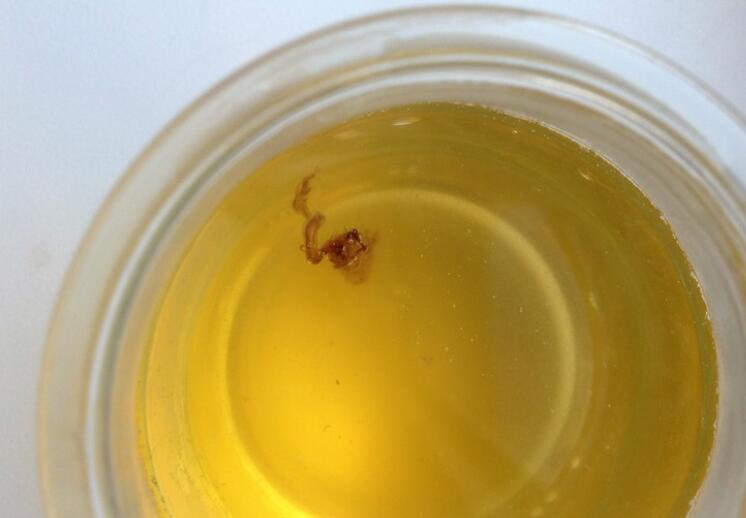

Understanding Mucus: Nature’s Protective Barrier
Before delving into the specifics of mucus in urine, it’s essential to understand the role of mucus in our bodies. Mucus is a thick, sticky substance produced by the mucous membranes lining various organs, including the respiratory, digestive, and urinary tracts.
Mucus acts as a natural barrier, protecting these delicate tissues from irritation, infection, and dehydration. It traps harmful particles, such as bacteria, viruses, and dust, preventing them from entering the body and causing harm.
In the urinary tract, a small amount of mucus is normal and helps maintain a healthy environment. However, when the body produces excessive mucus, it can be a sign of an underlying condition that requires medical attention.
Here are some types of mucus that can be present in urine:
- Clear or white mucus: This is the most common type of mucus found in urine and is usually nothing to be concerned about.
- Cloudy or milky mucus: Cloudy or milky mucus in urine may be a sign of a urinary tract infection (UTI) or a kidney infection.
- Red or pink mucus: Red or pink mucus in urine can be a sign of blood in the urine, which may be due to a urinary tract infection, kidney stones, bladder cancer, or other conditions.
- Brown or black mucus: Brown or black mucus in urine can be a sign of liver or kidney problems, or it may be due to certain medications or foods.
Symptoms of Mucus in Urine
In addition to the presence of mucus in urine, other symptoms may include:
- Cloudy or discolored urine: Mucus can make urine appear cloudy or discolored, ranging from a hazy appearance to a thick, milky consistency.
- Strong or foul odor: Infections or other underlying conditions can cause urine to have an unpleasant, pungent odor.
- Pain or burning during urination: Inflammation or irritation in the urinary tract can cause discomfort or a burning sensation when urinating.
- Frequent urination: The urge to urinate more often than usual can be a sign of a urinary tract issue, as the bladder tries to expel the irritating substance.
- Fever or chills: In some cases, mucus in urine may be accompanied by fever or chills, indicating a more serious infection or inflammatory process.
- Abdominal or back pain: Depending on the underlying cause, you may experience pain or discomfort in the abdomen or lower back region.
Here are ten common reasons for mucus in urine:
1. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
This is one of the most common causes of mucus in the urine. UTI is an infection that affects the bladder, urethra, or kidneys, which can cause inflammation in the urinary tract and lead to the release of mucus in the urine. Symptoms of UTI include a burning sensation during urination, frequent urination, and cloudy or bloody urine. (Resource)
2. Interstitial Cystitis (IC)
IC is a chronic condition that affects the bladder, causing symptoms such as urinary urgency, frequency, and pelvic pain. In some cases, IC can cause inflammation and irritation in the bladder, leading to the production of excess mucus. This can result in the presence of mucus threads in the urine.
3. Bladder infections
Bladder infections, also known as cystitis, can cause mucus in urine. Other symptoms of bladder infections include pain during urination, frequent urination, and pelvic pain.
4. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can cause irritation and inflammation in the urinary tract, leading to the release of mucus in the urine. Symptoms of kidney stones include pain in the sides or lower back, bloody or cloudy urine, and a burning sensation during urination. (Resource)
5. Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis is an infection caused by an overgrowth of bacteria in the vagina and can lead to the release of mucus in the urine. Symptoms of bacterial vaginosis include abnormal vaginal discharge, itching, burning, and pain during urination.
6. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
STIs can cause inflammation and irritation in the urinary tract and lead to the release of mucus in the urine. Symptoms of STIs include pain during urination, abnormal discharge, and pain in the lower abdomen.
7. Enlarged Prostate
An enlarged prostate can cause inflammation in the bladder and urethra, releasing mucus in the urine. Symptoms of an enlarged prostate include difficulty urinating, frequent urination, and a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. (Resource)
8. Food Allergies
Food allergies can cause inflammation in the digestive tract, leading to the release of mucus in the urine. Symptoms of food allergies include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
9. Pregnancy
Pregnancy can cause inflammation in the urinary tract, leading to the release of mucus in the urine. Symptoms of pregnancy include nausea, vomiting, and fatigue.
10. Cancer
In rare cases, mucus in urine can be a sign of bladder or kidney cancer. Cancerous growths can cause irritation and inflammation of the urinary tract, producing excess mucus.
In some cases, mucus in urine can be a symptom of bladder cancer. This type of cancer is more common in older adults, and other symptoms may include blood in the urine and frequent urination.
11. Prostatitis
Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland, which can cause mucus in urine as well as other symptoms such as pain in the groin or pelvic area, difficulty urinating, and fever.
12. Diabetes
People with uncontrolled diabetes may experience mucus in their urine. This is because high blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to abnormal urine production.
13. Medications
Certain medications can cause mucus threads in urine as a side effect. Some of these medications include:
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics can disrupt the balance of bacteria in the body, including the urinary tract, leading to the production of excess mucus.
- Diuretics: Diuretics are medications that increase urine output. They can also increase the concentration of certain substances in the urine, leading to the production of excess mucus.
- Laxatives: Some laxatives can irritate the intestinal lining, leading to the production of excess mucus.
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can irritate the bladder and urinary tract, leading to the production of excess mucus.
- Steroids: Steroids can suppress the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections that can cause mucus threads in urine.
14. Normal discharge
The body produces a small amount of mucus to lubricate the urinary tract, and this can sometimes be present in the urine.This is typically not a cause for concern unless there are other symptoms present. However, if there is a significant amount of mucus threads in the urine, it may indicate an underlying medical condition or infection.
15. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
IBS is a chronic condition that affects the digestive system. It can cause inflammation and irritation in the intestines, which can lead to the production of excess mucus. Some people with IBS may also experience urinary symptoms, including mucus threads in urine.
16. Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that affects the colon and rectum. It can cause inflammation and irritation in the intestinal lining, which can lead to the production of excess mucus. People with ulcerative colitis may also experience urinary symptoms, including mucus threads in urine.
17. Dehydration
When the body is dehydrated, the urine can become concentrated and appear cloudy, which may be mistaken for mucus in urine. Drinking more water can help alleviate this symptom.
It is essential to consult a healthcare provider if you experience mucus in urine, as it can be a sign of an underlying medical condition that requires prompt treatment. (Resource)
Diagnosis and Treatment for Mucus in Urine
If you notice mucus in your urine, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Your doctor may recommend the following:
Urine Analysis: A simple urine test can detect the presence of mucus, bacteria, or other abnormalities that may indicate an underlying condition. This test can also help identify the specific type of bacteria causing an infection, if present.
Imaging Tests: In some cases, your doctor may order imaging tests, such as an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, to examine the urinary tract and identify any structural abnormalities, blockages, or kidney stones.
Antibiotics: If a urinary tract infection is the cause of mucus in urine, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to clear the infection. It’s essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed to prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Pain Medication: Over-the-counter or prescription pain medication may be recommended to alleviate discomfort or pain associated with mucus in urine, especially in cases of kidney stones or severe inflammation.
Lifestyle Changes: Depending on the underlying cause, your doctor may suggest lifestyle changes, such as increasing fluid intake, practicing good hygiene, or modifying your diet to include more fiber and probiotics.
Surgery: In severe cases, such as kidney stones or structural abnormalities, surgical intervention may be necessary to address the root cause of mucus in urine. This may involve procedures like lithotripsy (breaking up kidney stones) or correcting anatomical defects.
Bladder Instillations: For conditions like interstitial cystitis, your doctor may recommend bladder instillations, which involve introducing medication directly into the bladder through a catheter. This can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Pelvic Floor Therapy: In some cases, pelvic floor muscle dysfunction can contribute to urinary tract issues and mucus production. Pelvic floor therapy, which involves exercises and techniques to strengthen and relax these muscles, may be recommended.
Prevention and Self-Care for Mucus in Urine
While some causes of mucus in urine may be unavoidable, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk and promote overall urinary tract health:
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out bacteria and dilute urine, reducing the risk of infections and irritation. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water per day, and more if you’re physically active or live in a hot climate.
- Practice good hygiene: Maintaining proper hygiene, especially after using the restroom, can help prevent the spread of bacteria and reduce the risk of urinary tract infections. Always wipe from front to back, and avoid using harsh soaps or douches that can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the urinary tract.
- Avoid holding urine: Holding urine for extended periods can increase the risk of infections and irritation. Try to urinate every 3-4 hours to keep the bladder from becoming overly full.
- Wear breathable underwear: Tight-fitting or non-breathable underwear can trap moisture and promote bacterial growth, increasing the risk of infections. Choose cotton underwear and avoid synthetic materials that don’t allow proper air circulation.
- Maintain a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and probiotics can support a healthy urinary tract and immune system. Cranberry juice, in particular, has been shown to help prevent urinary tract infections by preventing bacteria from adhering to the bladder wall.
- Manage chronic conditions: If you have a chronic condition like diabetes or kidney disease, it’s essential to follow your doctor’s recommendations for managing these conditions. Keeping them under control can help reduce the risk of complications, including mucus in urine.
- Avoid irritants: Certain foods, beverages, and medications can irritate the bladder and urinary tract, potentially leading to increased mucus production. Common irritants include caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, and certain medications like blood pressure drugs or muscle relaxants.
When to Seek Medical Attention?
While a small amount of mucus in urine may not be cause for immediate concern, it’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent or worsening symptoms: If mucus in urine persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as fever, chills, or severe pain, seek medical attention promptly. Ignoring these signs can lead to more serious complications.
- Blood in urine: The presence of blood in urine can be a sign of a more serious condition, such as kidney stones, bladder cancer, or a urinary tract infection, and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional immediately.
- Difficulty urinating: If you experience difficulty starting or stopping the flow of urine, or if you have a complete inability to urinate, seek medical attention immediately. This could be a sign of a blockage or other serious issue.
- Severe pain: If you experience severe, persistent pain in the abdomen, lower back, or groin area, it’s important to seek medical attention right away, as this could indicate a serious underlying condition.
- Pregnancy: If you’re pregnant and notice mucus in your urine, it’s essential to inform your obstetrician or healthcare provider, as this could be a sign of a urinary tract infection or other pregnancy-related complication.