Have you suffered from shoulder pain on the left or right side? The shoulder joint is one of the human body’s largest, most complex, and most mobile joints. Its complex structure comprises several tendons, muscles, bones, and ligaments that allow your shoulder to move up, down, and from side to side. It also enables your arm to move in different directions.
Your shoulder allows you to throw a baseball, swing your arms, and raise your arm over your head to touch your ear. Unfortunately, your shoulder is also vulnerable to injury due to its impressive mobility.
Shoulder pain is one of the most common complaints in the United States. The pain in your right shoulder may result from a muscle tear, nerve damage, overuse, or an accident.
The good news is – shoulder pain is usually not severe. Most of the time, the pain in your right shoulder will reduce with proper rest. However, in some cases, unexplained pain in your right shoulder may signal something more serious, like a heart attack.
Unfortunately, shoulder pain can be excruciating. If you constantly feel pain in your right shoulder, this guide is for you. In this article, we’d take you through what could be causing the pain in your right shoulder, how to ease the pain, and when to see a doctor.
12 Common Causes of Shoulder Pain on the Left or Right Side
1. Rotator cuff tendinitis
Rotator cuff tendinitis is a condition that affects the tendons and causes them to become inflamed and irritated. Moving your left or right shoulder can be extremely painful when your tendons become inflamed.
You can get rotator cuff tendinitis from sleeping on your shoulder, playing extreme sports that stress your shoulder, or keeping your shoulder in one position for too long.
Rotator cuff tendinitis is also known as:
- Impingement syndrome
- Tendonitis
- Swimmer’s shoulder
- Tennis shoulder
- Pitcher’s shoulder
The condition is prevalent in athletes who participate in sports requiring lifting their arms over their heads, like swimming, tennis, and basketball.
The pain associated with rotator cuff tendinitis may worsen over time. If the pain in your right becomes persistent and doesn’t fade with rest, it could indicate another problem.
Other symptoms associated with rotator cuff tendinitis include:
- Pain and swelling in your shoulder and side of your arm.
- Pain in your right shoulder when you raise or lower your arm
- A popping sound when raising your arm
- Stiffness in your right shoulder
- Pain that jerks you up from sleep
Sometimes, your rotator cuff tendinitis may come and go without any pain.
Treatment for rotator cuff tendinitis
To treat your rotator cuff tendinitis, your doctor advises avoiding the activities causing the pain. Your doctor will also administer OTC (over-the-counter) pain relief drugs like ibuprofen to reduce the pain in your right shoulder.
To reduce the inflammation in your shoulder, take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like naproxen (Aleve). You can also apply cold packs to your shoulder 3 – 4 times daily. If these treatments don’t work, your doctor may recommend surgery.
2. Bursitis shoulder pain
The bursas in your shoulder are tiny, fluid-filled sacs that help to reduce friction between bones in your shoulder joints. When this bursa becomes inflamed, it could lead to extreme pain in your left or right shoulder.
Your shoulder bursitis may arise from an injury, an infection, or an underlying condition. The pain accompanying your inflamed bursa may be manageable and usually affects the shoulders. However, the pain worsens when you lift objects overhead.
Other symptoms of shoulder bursitis include:
- Pain when lying down on your shoulder
- Shoulder pain occurs when you lift your arm to either side
- Pain on the outside or top of your shoulder
- Should pain occur when you circle your arm
- Pain when pushing on or opening a door
People that use their shoulders frequently are more vulnerable to getting shoulder bursitis. Other people with a higher risk of bursitis include:
- carpenters
- athletes
- musicians
- gardeners
Treating shoulder bursitis
To treat your shoulder bursitis, your doctor will recommend a lot of rest and other physical therapy, including applying ice compression to the inflamed shoulder.
Your doctor will administer pain relief and anti-inflammation medications to ease the pain. Your doctor may also extract the bursa fluid with a sterile syringe. In extreme cases, surgery to remove infected bursa fluid may be required.
3. Labral Tear of the Shoulder
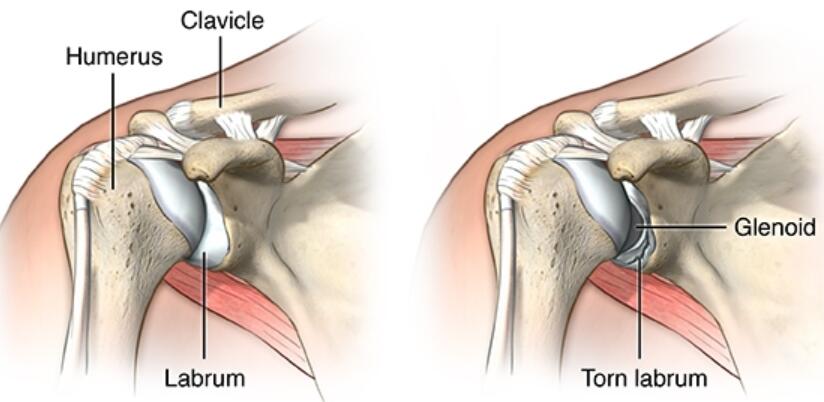
Your labrum is small fibrocartilage (rubbery tissue) that connects to the shoulder socket’s rim and keeps the joint’s ball in position. It helps your shoulder move without problems or pain.
When this cartilage tears, it could cause pain in the left or right shoulder. You could experience a labral tear from injury or old age. For example, if you repeat an overhead motion, your labrum may tear from overuse.
Labral tears of the right shoulder usually accompany intense pain and difficulty moving your shoulder.
Treatment of labral tears of the shoulder
Your doctor will prescribe pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs to treat the pain and swelling caused by a labral tear.
Once the pain subsides, your doctor will advise you to work with a physical therapist to try exercises that gradually strengthen your shoulder muscles. In some rare cases, you may require surgery to fix the labral tear in your shoulder.
4. Shoulder impingement
Shoulder impingement can cause left or right shoulder pain. Impingement syndrome of the shoulder is an injury to the muscles between bones in the shoulder area. Shoulder impingement occurs when your rotator cuff collides with your acromion (the top of your shoulder).
The condition is more common in athletes that use their shoulders frequently. For example, a baseball pitcher must repeatedly swing his arms over his head. The impact between your rotator cuff and your acromion could cause intense pain in your right shoulder.
Other symptoms of shoulder impingement in your right shoulder include:
- Minor but persistent pain in your arm
- Pain that worsens at night
- Pain that goes from the front of your shoulder to the side of your arm
- Weak arm and shoulder
Treatment for shoulder impingement
Home care is one of the simplest ways to treat your shoulder impingement. Make sure you take time off to rest; avoid strenuous activities or movements that could worsen the pain, especially if you’re an athlete.
Your doctor may also ask you to place ice compresses on your shoulder for 10 to 15 minutes 3-4 times daily. The ice packs will help reduce pain and any inflammation in your shoulder.
You can also take pain reliefs and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) to relieve pain and reduce swelling.
If these medications don’t work, your doctor might recommend surgery to repair rotator cuff tears and steroid injections to reduce swelling and pain.
5. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease that breaks down cartilage and other tissues around your joints. Although osteoarthritis can affect any joint in the body, it is very common in the knees, hips, and shoulders.
As the tissues around your shoulder joint weaken, the friction in the joint increases and cause pain in your right shoulder. Although osteoarthritis is prevalent in older people above 50, shoulder injuries can cause osteoarthritis in younger people.
Other conditions that could cause osteoarthritis in your shoulder include:
- Old Age
- A previous injury like shoulder dislocations
- Heredity
- Infection of the shoulder
- Rotator cuff tears
Top tip: Athletes participating in extreme sports are more vulnerable to developing osteoarthritis.
Treating osteoarthritis
Unfortunately, osteoarthritis cannot be reversed. However, there are different therapy methods to relieve the pain from osteoarthritis.
The key to treating shoulder osteoarthritis is getting plenty of rest and avoiding activities that strain the shoulder. For example, instead of holding up your hairdresser to blow dry your hair, you could prop it up to avoid wasting your shoulder.
Your doctor may also prescribe over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen or aspirin – these medications help soothe the pain and reduce inflammation.
Your doctor may also refer you to a physical therapist to give you exercises to improve your shoulder muscles’ function and flexibility.
You can apply moist heat or place ice packs on the shoulder for 20 minutes 3-4 times a day to relieve the pain and reduce the swelling in your right shoulder.
6. Frozen Shoulder
Frozen shoulder is a common condition that causes intense pain and stiffness in your left or right shoulder.
The condition is also known as adhesive capsulitis. The pain is caused by stiffening muscles around your shoulder joint. Although the condition can affect anybody, it is more common in women and people with health complications such as;
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular disease
- Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism)
- An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
- Tuberculosis
- Parkinson’s disease
The pain from a frozen shoulder usually starts mild and worsens over time.
Treatment for Frozen shoulder
Although your frozen shoulder can resolve on its own, it may take 12-18 months for your shoulder to heal fully. Make sure you avoid activities that may strain your shoulder.
Your doctor may recommend over-the-counter medications like Ibuprofen and Advil to soothe the pain and reduce inflammation in your right shoulder. In some cases, your doctor may administer steroid injections or recommend surgery.
7. Dislocated shoulder

A dislocated shoulder is an injury that causes your upper arm bone to pop out of your shoulder socket forcefully. The forceful removal of the arm bone from the shoulder joint may tear shoulder muscles and increase the pain’s intensity.
Symptoms of a dislocated shoulder include:
- A visibly deformed shoulder
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Intense pain
- Inability to move the joint
You may feel numb, weak, or tingling around your dislocated shoulder.
Treating a dislocated shoulder
Your doctor will fix your arm bone back in place, then administer pain reliefs and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce the pain and swelling.
You may also have to use an arm sling to hold your shoulder in its normal position. Your doctor may also refer you to a physical therapist who will recommend exercises to improve healing. In some rare cases, you may require surgery in your right shoulder to tighten loose ligaments.
8. Calcific tendinitis
Calcific tendinitis is a condition that can cause shoulder pain on the left or right side. This condition arises when calcium deposits form and lodge within the tendons of your shoulder’s rotator cuffs. The condition causes intense pain that makes moving the shoulder and arms difficult. The calcium deposits build up and cause pain in your shoulder.
Treatment for Calcific tendinitis
Your doctor will prescribe pain relief to ease the pain. If the pain in your shoulder persists, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the calcium deposits in your shoulder.
9. Heart diseases
Some heart conditions can trigger pain in your left or right shoulder. You should check for other heart attack symptoms if you have unexplained shoulder pain.
Other symptoms that may accompany the pain in your shoulder include:
- Chest pain
- Nausea or vomiting
- Sweating
- Dizziness
- Difficulty breathing
Treatment for heart diseases
To treat shoulder pain, you must address the underlying condition. The earlier you treat heart conditions, the better your chances of a full recovery.
10. Pinched nerve in the neck or shoulder
The nerve is compressed when too much pressure is applied to the nerve. This is usually caused by keeping the body in the same position for a long time. Poor sleeping posture, sitting at a desk for a few hours, and long air travel cause a Pinched nerve in the shoulder. Both medication and physical therapy can help get rid of this problem.
11. Sprains and strains
Sprains and strains are also leading causes of left or right shoulder pain. This injury is generally caused by overwork and is often common among manual workers and athletes. It would help if you judged whether to seek medical help based on the severity.
12. Arthritis
There are many symptoms of arthritis, including shoulder pain. This condition is often very common in the elderly. You can choose medication, surgery, or physical therapy to help relieve shoulder pain.
Treatment For Shoulder Pain on the Left or Right Side
The treatment of shoulder pain often depends on the cause and severity. If your pain is mild, you can treat it at home. Wrap the ice cube in a towel and place it on the painful area of your shoulder for 15 to 20 minutes each time. This can effectively help relieve pain in your shoulder. Be careful not to put ice directly on the skin; it will cause frostbite and burn it.
In addition, you can use over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids to help reduce pain and inflammation. Then compress the area with an elastic bandage or shoulder anchor to reduce swelling. Always consult your health doctor before taking medication.
Exercises for Shoulder Pain on the Left or Right Side
Shoulder Stretch: Perform this exercise a total of 10 times. Squeeze your shoulder blades together and hold for five seconds, then pull your shoulder blades forward and hold for five seconds.
Door Presses: Standing in a doorway, put your arm out directly in front of you, and place the back of your wrist against the door frame. Push your arm against the door frame holding for five seconds. Repeat this action ten times before moving onto your other arm.
Door Rest: Once again, standing in a doorway, lift both hands above your head on either side of the door entrance. Slowly lean forward, using your arms to support you until you feel some tension in your shoulders. Hold for a maximum of 30 seconds before repeating four more times.
When Should You See Your Doctor For Shoulder Pain?
Usually, the pain in your right shoulder is rarely life-threatening. In most cases, the pain in your shoulder should heal within a few weeks of home treatment.
However, the pain in your right shoulder can also cause concern, especially if the pain is not a result of an injury. You should visit your doctor if you’re experiencing symptoms such as:
- Inability to move your shoulder
- Pain that persists over for a long time
- Trouble breathing
- Dizziness
- Pain in your neck or jaw
- Chest tightness
Conclusion
If you are experiencing any form of pain in the shoulder, there could be various underlying causes. Thankfully most shoulder issues last for a short period and usually can be healed without any medical intervention.
Sometimes, if the problem is persistent and lasts long, it may indicate conditions such as osteoarthritis or other muscular issues. If the disease is severe, you’d better seek medical help as soon as possible. In extreme cases, surgery may be required.