The hematocrit blood test is a common diagnostic tool to measure the percentage of red blood cells (RBCs) in your blood. It provides valuable information about your overall health and helps identify potential abnormalities. This article will explore the significance of low and high hematocrit (Hct) levels, their possible causes, and what they might indicate about your health.
What is Hematocrit
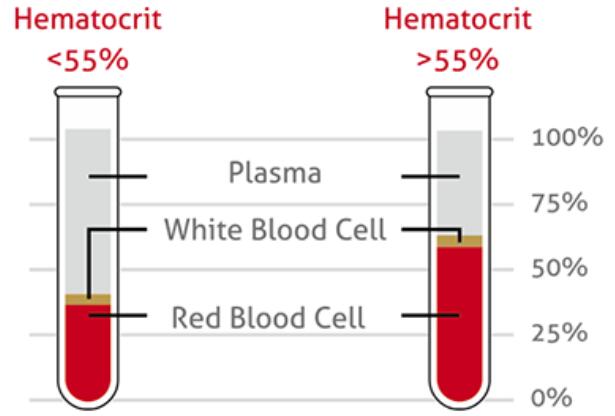
Before delving into low hematocrit levels, it is important to grasp the concept of hematocrit. Hematocrit refers to the volume of red blood cells (RBCs) in our blood. It is expressed as a percentage, representing the proportion of RBCs to the total blood volume. Hematocrit levels vary depending on age, sex, and other factors, but generally, they range from 35% to 50% in adults.
Hematocrit Blood Test: How It Works
During a hematocrit blood test, a sample of your blood is taken and processed in a laboratory. The blood sample is spun in a centrifuge, which separates the different components based on their density. This process allows the measurement of the hematocrit level.
Interpreting Hematocrit Results: What Do They Mean?
The interpretation of hematocrit results depends on various factors, including the reference range provided by the laboratory and individual patient characteristics.
Results falling outside the normal range may indicate an underlying medical condition that requires further investigation. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to understand the implications of your specific results.
Normal Hematocrit Levels: What’s Considered Normal?
The normal range for hematocrit levels varies depending on age, sex, and overall health. Generally, a hematocrit level between 38.8% and 50% for adult males is considered within the normal range. For adult females, the normal range is slightly lower, typically between 34.9% and 44.5%.
Medical Conditions Linked to Abnormal Hematocrit Levels
Abnormal hematocrit levels can be indicative of various medical conditions. Low levels are often associated with iron deficiency anemia, vitamin deficiencies, chronic diseases, or blood loss. High levels can be linked to polycythemia vera, lung, or kidney diseases. Additional tests may be required to confirm a diagnosis.
Causes of Low Hematocrit Levels
Low hematocrit levels, medically known as anemia, can be caused by various factors. Understanding the underlying causes is vital in devising an effective treatment plan. Let’s explore some of the common causes of low hematocrit levels:
1. Iron Deficiency
This is one of the leading causes of low hematocrit levels. Iron is crucial in producing hemoglobin, the protein responsible for carrying oxygen in our blood. When our body lacks iron, it hampers hemoglobin synthesis, decreasing hematocrit levels.
2. Vitamin Deficiencies
Certain vitamins, such as B12 and folate, are essential for red blood cell production. Deficiencies in these vitamins can impede the body’s ability to generate adequate healthy red blood cells, resulting in low hematocrit levels.
3. Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases, such as kidney disease and autoimmune disorders, can profoundly impact hematocrit levels. These conditions disrupt the body’s normal functioning, affecting the production and lifespan of red blood cells.
4. Bone Marrow Disorders
Bone marrow disorders, such as aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndromes, can impair the production of red blood cells, leading to low hematocrit levels. These disorders interfere with the normal development and maturation of blood cells in the bone marrow.
5. Genetic Conditions
Certain genetic conditions, including thalassemia and sickle cell disease, can contribute to low hematocrit levels. These inherited disorders affect the structure and function of hemoglobin, resulting in abnormal red blood cells and decreased hematocrit levels.
Low Hematocrit Levels: Treatment
Treating low hematocrit levels involves addressing the underlying cause of the condition. Effective management can help restore hematocrit levels to a healthy range and alleviate associated symptoms. Here are some common treatment approaches:
1. Iron Supplementation
In cases of iron deficiency anemia, iron supplementation is often recommended. Oral iron supplements or intravenous iron infusions may be prescribed to replenish iron stores in the body and stimulate the production of healthy red blood cells.
2. Vitamin Therapy
When vitamin deficiencies cause low hematocrit levels, vitamin therapy becomes essential. Vitamin B12 injections, oral supplements, and folic acid supplements can aid in restoring hematocrit levels to normal.
3. Blood Transfusion
A blood transfusion may be necessary in severe cases of anemia or when other treatment options are ineffective. This procedure involves receiving healthy red blood cells from a compatible donor to replenish the body’s blood supply and increase hematocrit levels.
4. Managing Underlying Conditions
Managing the underlying condition is crucial for individuals with chronic diseases or bone marrow disorders. This may involve medications, lifestyle modifications, or other targeted treatments to alleviate symptoms and improve hematocrit levels.
High Hematocrit Levels: Causes
1. Dehydration
Dehydration can lead to an increase in hematocrit levels. When your body lacks sufficient fluids, the red blood cell concentration in your blood increases, resulting in elevated hematocrit levels. It is essential to stay hydrated and consume adequate water throughout the day to maintain healthy hematocrit levels.
2. Smoking
Smoking tobacco products can contribute to elevated hematocrit levels. The chemicals present in cigarettes can stimulate the production of red blood cells, leading to an increase in hematocrit levels. Quitting smoking is beneficial for your overall health and can help maintain optimal hematocrit levels.
3. Chronic Lung Disease
Chronic lung diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can cause high hematocrit levels. When the lungs are compromised, the body compensates by producing more red blood cells to enhance oxygen delivery. This adaptive response can result in elevated hematocrit levels.
4. Genetic Factors
Certain genetic conditions can predispose individuals to high hematocrit levels. Polycythemia vera, a rare blood disorder, is one such condition. It causes the bone marrow to produce excessive red blood cells, leading to elevated hematocrit levels. Genetic testing and consultation with a healthcare professional are necessary to diagnose and manage such conditions.
5. Living at High Altitudes
Living at high altitudes can influence hematocrit levels. In high-altitude environments, the oxygen concentration is lower, prompting the body to produce more red blood cells to compensate for the reduced oxygen availability. This adaptation can result in higher hematocrit levels in individuals residing at high altitudes.
High Hematocrit Levels: Treatment
1. Hydration
One of the simplest ways to address high hematocrit levels is by staying adequately hydrated. Drinking plenty of water helps maintain optimal blood volume and prevents the blood from becoming too concentrated. Aim to consume at least eight glasses of water per day, and more if you engage in strenuous physical activity or live in a hot climate.
2. Phlebotomy
Phlebotomy, also known as bloodletting, is a medical procedure that involves the removal of blood from the body. It is often used to treat high hematocrit levels caused by conditions like polycythemia vera. By reducing the total blood volume, phlebotomy helps normalize hematocrit levels. A qualified healthcare professional should perform this procedure.
3. Medication
In certain cases, medication may be prescribed to manage high hematocrit levels. For instance, individuals with polycythemia vera may benefit from medications that suppress the production of red blood cells. These medications help regulate hematocrit levels and reduce the risk of complications associated with the condition.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle modifications can also contribute to maintaining healthy hematocrit levels. If you smoke, quitting is highly recommended to prevent further increases in hematocrit levels. Additionally, regular exercise and a well-balanced diet can promote overall cardiovascular health, indirectly affecting hematocrit levels.
5. Medical Monitoring
If you have high hematocrit levels, it is crucial to undergo regular medical monitoring. Your healthcare provider will conduct blood tests to assess your hematocrit levels and ensure they remain within a healthy range. Routine check-ups and close monitoring allow for early detection of any changes and timely intervention, if necessary.
FAQs
1. Can dehydration affect hematocrit levels?
Yes, dehydration can temporarily increase hematocrit levels due to a decrease in plasma volume.
2. Are hematocrit levels different for pregnant women?
Yes, hematocrit levels tend to decrease during pregnancy due to increased plasma volume.
3. Can medication influence hematocrit results?
Certain medications, such as erythropoietin or diuretics, can affect hematocrit levels. It’s important to inform your healthcare provider about your medications.
4. Are there any risks associated with the hematocrit blood test?
The hematocrit blood test is generally safe, with minimal risks. Some individuals may experience mild discomfort or bruising at the blood draw site.
5. How often should hematocrit levels be monitored?
The frequency of hematocrit level monitoring depends on individual health conditions and the recommendations of healthcare professionals. Regular monitoring is important for individuals with known hematological disorders or those undergoing treatment.
Conclusion
The hematocrit blood test provides valuable insights into your blood composition and helps detect potential health issues. Low or high hematocrit levels can indicate underlying medical conditions that require further investigation and appropriate management. Regular monitoring, proper diagnosis, and adherence to treatment plans are essential for maintaining optimal hematocrit levels and overall well-being.