How to identify different types of skin rashes? Skin rashes can be a common occurrence, but accurately identifying them is crucial for proper treatment. With numerous causes and varying symptoms, it can be challenging to pinpoint the exact rash. This article will explore the different types of skin rashes, symptoms, and tips on how to identify them effectively.
What Are Skin Rashes?
Skin rashes are abnormal changes in the skin’s appearance, texture, or color. They can manifest as redness, bumps, blisters, or dry patches. Skin rashes can be a symptom of various underlying conditions, including infections, allergic reactions, environmental factors, and chronic skin conditions. Identifying the root cause of a rash is essential for appropriate treatment.
Symptoms Accompanying Skin Rashes
Skin rashes can be accompanied by various symptoms, depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Itching: Itching, also known as pruritus, is a common symptom associated with many skin rashes. It can range from mild to severe and may worsen with scratching. Persistent scratching can lead to skin damage, increased inflammation, and secondary infections.
- Swelling: Rashes caused by allergic reactions or infections can lead to localized swelling or edema. Swelling can be mild or pronounced, depending on the severity of the reaction or infection.
- Redness: Skin rashes often cause redness or erythema in the affected areas due to inflammation. The intensity of redness can vary, ranging from mild pinkness to deep red.
- Pain: Some rashes, particularly those associated with infections or underlying conditions, can be painful or tender to touch. Pain can range from mild discomfort to severe, depending on the severity of the rash and its underlying cause.
- Dryness: Dryness and flakiness of the skin are common in rashes like eczema or psoriasis. The affected skin may feel rough, scaly, or have areas of peeling.
- Blisters or Pimples: Certain rashes may present with blisters or pustules, which can contain fluid or pus. These can be a sign of an underlying infection or inflammatory process.
Identifying the specific symptoms accompanying a skin rash can provide valuable clues in determining the cause and appropriate management.
How to Identify Different Skin Rashes?
Identifying different skin rashes can be challenging, but several key factors can help in the process:
- Appearance: Carefully observe the color, texture, and pattern of the rash. Note any unique characteristics that may aid in identification. For example, the raised, circular border with a clear center is seen in ringworm rashes.
- Location: Determine the specific areas of the body where the rash is present. Some rashes have predilection sites or tend to occur in specific regions. For instance, the facial redness and flushing associated with rosacea.
- Duration: Consider how long the rash has been present. Some rashes may come and go quickly, while others persist for longer durations. This information can help differentiate between acute and chronic conditions.
- Accompanying Symptoms: Take note of any accompanying symptoms like itching, pain, or fever, as they can provide important diagnostic information. For example, the presence of a fever with a rapidly spreading rash may indicate a bacterial infection.
- Medical History: Consider the individual’s medical history, including any known allergies, chronic conditions, or recent exposures. This information can help identify potential triggers or predisposing factors.
It is important to remember that accurately identifying a skin rash may require the expertise of a healthcare professional. If you are unsure about the cause or appropriate treatment, it is advisable to seek medical advice.
Common Types of Skin Rashes
Skin rashes can present in various forms, each with its own unique characteristics. Understanding different types of skin rashes can help in their identification and differentiation. Let’s explore some common types:
1. Contact Dermatitis
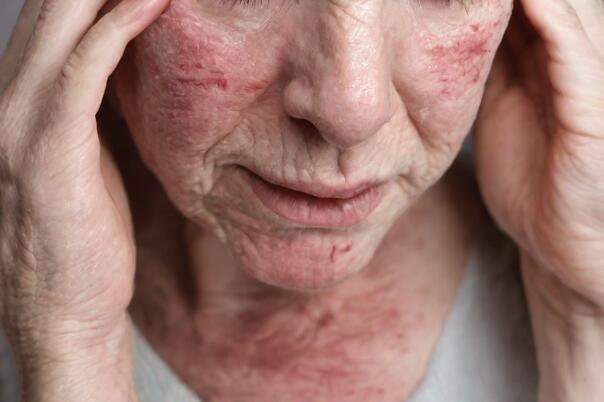
Contact dermatitis is a common rash caused by direct contact with irritants or allergens. It typically appears as red, itchy, and inflamed skin. Common triggers include chemicals, certain plants, cosmetics, and metals. Avoiding the trigger and using soothing topical treatments like corticosteroid creams can help alleviate symptoms.
Contact dermatitis can be categorized into two types: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. Irritant contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with a substance that damages the skin’s protective barrier. Allergic contact dermatitis, on the other hand, is an immune-mediated reaction that occurs when the skin is exposed to a specific allergen.
2. Eczema
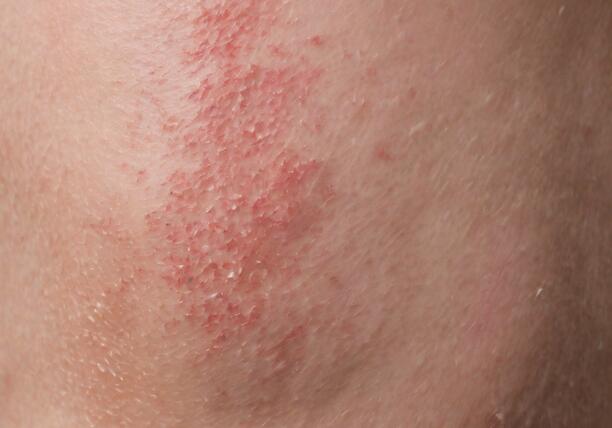
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition. It presents as dry, itchy, and scaly patches of skin. Eczema can be triggered by environmental factors, allergens, stress, or genetics. The exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
There are different types of eczema, including atopic dermatitis (the most common form), contact dermatitis, nummular eczema (coin-shaped patches), and seborrheic dermatitis (which affects the scalp and face). Treatment may involve moisturizers, topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, and avoiding known triggers.
3. Psoriasis
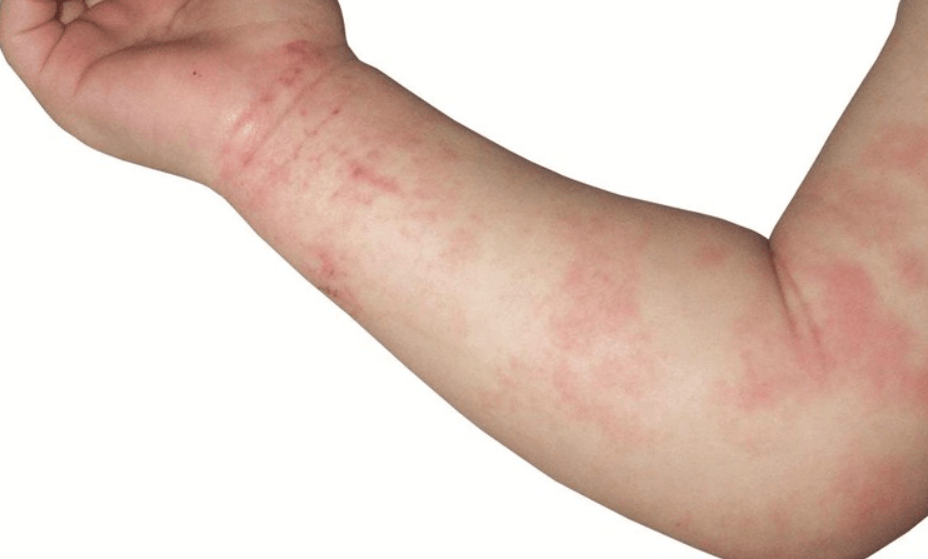
Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin condition characterized by thick, red, and scaly patches of skin. It may cause itching, pain, and discomfort.
The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is thought to involve genetic and environmental factors. Psoriasis can manifest in different forms, such as plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, and pustular psoriasis.
Treatments for psoriasis include topical creams, phototherapy (light therapy), oral medications, and biologic agents. It is important to work with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan.
4. Hives (Urticaria)
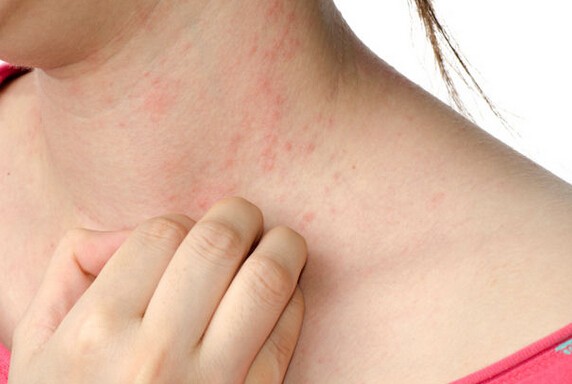
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts that appear suddenly and can vary in size and shape. They are often caused by allergic reactions to foods, medications, insect bites, or infections. Hives usually resolve on their own within a few hours or days, but antihistamines can help relieve symptoms. Chronic hives, which last for more than six weeks, may require further evaluation and treatment.
Hives can be categorized into acute urticaria (short-term) and chronic urticaria (long-term). Identifying and avoiding the trigger is essential in managing hives.
5. Rosacea
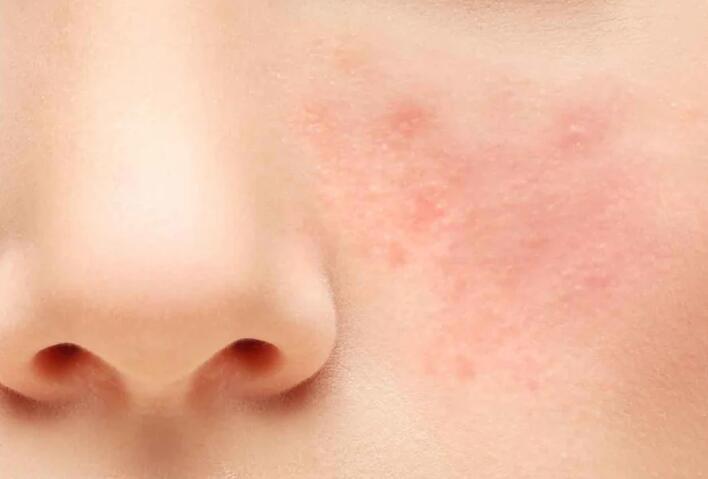

Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, flushing, and small visible blood vessels. It may also lead to bumps, swelling, and eye irritation. The exact cause of rosacea is unknown, but factors such as genetics, abnormal blood vessels, and an overactive immune system may contribute to its development.
Rosacea can be classified into four subtypes: erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (redness and visible blood vessels), papulopustular rosacea (redness with bumps and pimples), phymatous rosacea (thickening of the skin), and ocular rosacea (affects the eyes). Treatment options include topical medications, oral antibiotics, laser therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
6. Ringworm (Tinea)
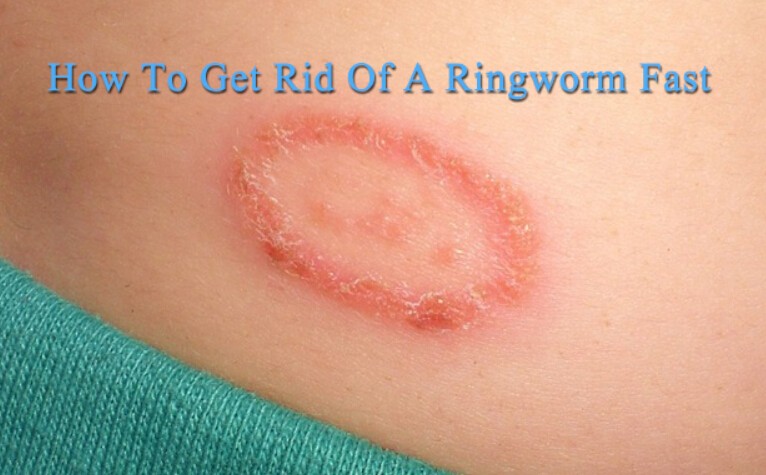
Ringworm, despite its name, is not caused by worms but rather by a fungal infection. It can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, scalp, and nails. Ringworms appear as circular, red, scaly patches with a raised border. It is highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct contact or from contaminated surfaces.
Ringworm can be classified based on the affected area, such as tinea corporis (body), tinea capitis (scalp), tinea pedis (feet, commonly known as athlete’s foot), and tinea cruris (groin, commonly known as jock itch). Antifungal creams, powders, or oral medications are used for treatment, and maintaining good hygiene is essential to prevent its spread.
7. Shingles (Herpes Zoster)
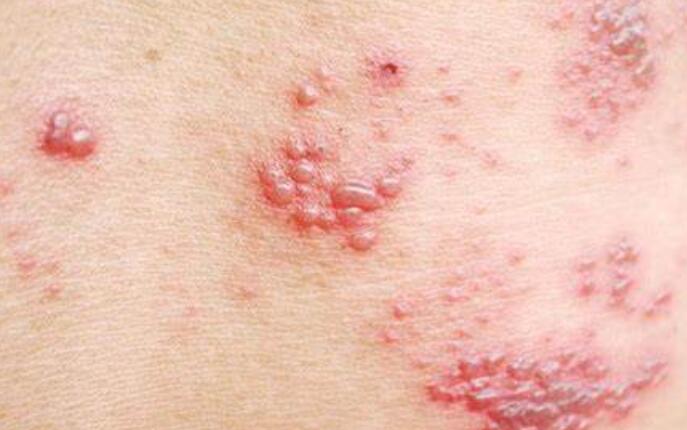
This condition is a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox. After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus can remain dormant in the body and reactivate later in life, causing shingles. It presents as a painful, blistering rash that typically occurs on one side of the body, following the path of a nerve.
Shingles can cause nerve pain, and early treatment with antiviral medications can help reduce the severity and duration of the rash. Pain management strategies, such as over-the-counter pain relievers and prescription medications, may also be recommended.
6 Best Home Remedies for Mild Skin Rashes
1. Cold Compress
Cold compresses provide immediate relief by numbing the affected area and constricting blood vessels, which helps reduce inflammation. The cold temperature also helps soothe itching and provides a calming effect on the skin.
- Step 1: Fill a bowl with cold water or wrap a few ice cubes in a clean cloth.
- Step 2: Gently apply the cold compress to the affected area for about 10-15 minutes.
- Step 3: Repeat this process several times a day to reduce itching, inflammation, and swelling.
2. Oatmeal Bath
Oatmeal contains anti-inflammatory and soothing properties that can help alleviate itching and irritation associated with skin rashes. It forms a protective barrier on the skin, reducing moisture loss and promoting hydration.
- Step 1: Fill a bathtub with lukewarm water.
- Step 2: Add one cup of colloidal oatmeal to the bathwater.
- Step 3: Soak in the oatmeal bath for 15-20 minutes.
- Step 4: Pat your skin dry gently and moisturize afterward to lock in moisture.
- Step 5: Repeat the oatmeal bath once daily until the rash improves.

3. Aloe Vera Gel
Aloe vera has long been used for its soothing and healing properties. It contains compounds that help reduce inflammation and promote skin regeneration. Aloe vera also provides a cooling sensation, which can help alleviate itching and discomfort.
- Step 1: Extract fresh gel from an aloe vera leaf or use store-bought aloe vera gel.
- Step 2: Apply a thin layer of the gel directly to the affected area.
- Step 3: Leave it on for 20-30 minutes, then rinse with cool water.
- Step 4: Repeat this process 2-3 times a day to reduce inflammation, and itching, and promote healing.
4. Coconut Oil
Coconut oil is rich in fatty acids that help moisturize and nourish the skin. It has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe and protect the skin. Coconut oil forms a protective barrier on the skin, preventing further irritation and promoting healing.
- Step 1: Take a small amount of virgin coconut oil in your palm.
- Step 2: Gently massage the oil onto the rash-affected area.
- Step 3: Leave it on without rinsing.
- Step 4: Repeat this process 2-3 times a day to moisturize the skin and reduce itching.
5. Calamine Lotion
Calamine lotion contains a combination of ingredients, including zinc oxide and ferric oxide, that help soothe and protect the skin. It forms a protective barrier, providing relief from itching and inflammation. Calamine lotion also has a cooling effect, which can help alleviate discomfort.
- Step 1: Shake the bottle of calamine lotion well.
- Step 2: Apply a thin layer of calamine lotion to the affected area.
- Step 3: Let it dry completely before covering the area with clothing.
- Step 4: Repeat this process 2-3 times a day to soothe the skin, reduce itching, and promote healing.
6. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce itching and inflammation associated with skin rashes. It also helps balance the pH level of the skin, promoting healing. However, it is important to dilute apple cider vinegar before applying it to the skin to avoid any potential irritation.
- Step 1: Dilute raw, unfiltered apple cider vinegar with equal parts of water.
- Step 2: Soak a cotton ball in the diluted vinegar solution.
- Step 3: Gently dab the cotton ball onto the affected area.
- Step 4: Leave it on for 10-15 minutes, then rinse with cool water.
- Step 5: Repeat this process 2-3 times a day to relieve itching and inflammation.
How to Prevent Skin Rashes?
Prevention plays a crucial role in managing and minimizing the occurrence of skin rashes. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
- Identify and avoid triggers: Pay attention to substances, chemicals, or allergens that may cause irritation or allergic reactions and minimize contact with them.
- Practice good hygiene: Take regular showers using mild, fragrance-free soaps, and avoid scrubbing your skin vigorously. Pat your skin dry gently and moisturize afterward.
- Choose skin-friendly products: Opt for hypoallergenic, fragrance-free products suitable for sensitive skin and avoid harsh chemicals, fragrances, and dyes.
- Protect your skin from the sun: Wear sunscreen with a high SPF, seek shade, and wear protective clothing to minimize sun exposure and potential skin irritation.
- Moisturize regularly: Keep your skin hydrated by applying a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer after bathing to prevent dryness and itching.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, stay hydrated, exercise regularly, and manage stress levels to promote overall skin health and reduce the risk of rashes.
- Avoid overheating: Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing, especially in warm environments, to prevent excessive sweating and minimize the risk of skin rashes.
- Keep your environment clean: Regularly clean and dust your living space, wash bedding and towels regularly, and avoid exposure to potential irritants or allergens.
- Stay hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water daily to keep your skin hydrated and maintain its natural moisture balance.
When to See a Doctor?
While many skin rashes can be managed with self-care measures, there are instances when medical attention is necessary. It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional under the following circumstances:
- The rash is severe, painful, or rapidly spreading.
- The rash is accompanied by fever, chills, or other systemic symptoms.
- The rash persists or worsens despite self-care measures.
- The rash is interfering with daily activities or affecting the quality of life.
- There is a history of known allergies or underlying medical conditions.
A healthcare professional can accurately diagnose the underlying cause of the rash and recommend appropriate treatment options based on the individual’s specific needs.