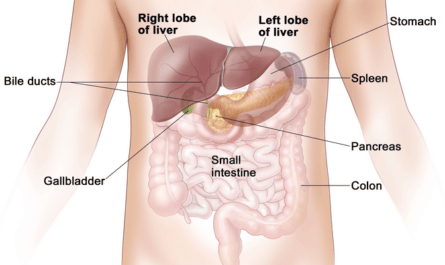
The abdomen is the part of your body running from below the breastbone down to the upper area of the pelvis. When the pain is localized to the lower right abdomen, it often signals a problem with one of the organs located in that area, such as the appendix, intestines, or reproductive organs. While some causes may resolve on their own, others require prompt medical attention. This article will discuss 15 common causes of pain in the lower right abdomen.

15 Common Causes of Pain in the Lower Right Abdomen
1. Appendicitis
One of the most well-known and potentially serious causes of lower right abdominal pain is appendicitis – inflammation of the appendix. The appendix is a small, pouch-like structure located where the small and large intestines meet. It sits on the lower right side of the abdomen.
Appendicitis often begins with a dull ache around the navel that gradually shifts to the lower right abdomen, becoming sharper and more severe. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fever, and abdominal swelling or rigidity.
Appendicitis is considered a medical emergency. If left untreated, the inflamed appendix can rupture, leading to a life-threatening infection called peritonitis.
If you experience severe, persistent, along with fever, vomiting, or other concerning symptoms, seek immediate medical attention. Appendicitis requires surgical removal of the appendix, typically through an appendectomy.
2. Constipation
While not typically a serious condition, constipation can cause significant discomfort, including pain in the lower right abdomen. Constipation occurs when bowel movements become difficult or infrequent. This is often due to a lack of fiber or fluids in the diet.
As stool accumulates in the colon, it can lead to bloating, cramping, and abdominal pain that may be more pronounced on the lower right side.
In addition to increasing fiber intake and staying hydrated, regular physical activity can help relieve constipation and the associated abdominal discomfort.
Over-the-counter laxatives or stool softeners may also provide relief, but it’s important to follow dosage instructions carefully and consult a healthcare provider if constipation persists for more than a few days.
3. Intestinal Gas
Excessive gas buildup in the intestines can also cause pain in the lower right abdomen. This gas can result from swallowing too much air, eating gas-producing foods, or digestive issues.
While generally harmless, trapped gas can lead to bloating, cramping, and discomfort that may be more noticeable on the lower right side of the abdomen.
To alleviate gas pain, try over-the-counter remedies like simethicone or activated charcoal, which can help expel excess gas. Avoiding gas-producing foods, chewing slowly, and staying hydrated can also help prevent gas buildup.
However, if gas pain is severe or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it’s best to consult a healthcare provider.

4. Gastroenteritis
Commonly known as the “stomach flu,” gastroenteritis is an inflammation of the stomach and intestines, often caused by a viral or bacterial infection.
In addition to nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, gastroenteritis can cause abdominal cramps and pain, which may be more pronounced in the lower right abdomen. While usually self-limiting, severe cases can lead to dehydration and may require medical attention.
To manage gastroenteritis symptoms, it’s important to stay hydrated by sipping small amounts of clear fluids like water, broth, or electrolyte drinks.
Avoid solid foods until the vomiting and diarrhea have subsided, and gradually reintroduce bland, easy-to-digest foods like bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast.
If symptoms persist for more than a few days or you notice signs of dehydration such as dizziness, seek medical care.
5. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
IBS is a chronic disorder that affects the large intestine, causing abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation.
The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but it’s thought to be related to a combination of factors, including gut motility issues, food sensitivities, and stress.
While IBS can cause generalized abdominal discomfort, some individuals may experience more localized pain in the lower right abdomen.
Managing IBS often involves a combination of dietary changes, stress management techniques, and medications to alleviate specific symptoms.
Working closely with a gastroenterologist or dietitian can help identify the best treatment approach for your case.
6. Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that can affect any part of the digestive tract, including the small and large intestines.
When the inflammation occurs in the lower right portion of the colon or the terminal ileum, it can cause pain and tenderness in the lower right abdomen. Other symptoms may include diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, fever, and rectal bleeding.
Crohn’s disease is a chronic condition that requires long-term management, often involving a combination of medication, dietary changes, and, in some cases, surgery.
If you experience persistent abdominal pain, bloody stools, or other concerning symptoms, it’s important to seek medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause.
7. Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is a condition that occurs when small pouches (diverticula) in the colon become inflamed or infected. While diverticula can develop anywhere in the colon, they are most common in the lower left side.
However, if diverticula form on the lower right side of the colon, they can cause pain and tenderness in that area, along with fever, nausea, and changes in bowel habits.
Mild cases of diverticulitis may be treated with antibiotics, a liquid diet, and rest. More severe cases may require hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics and, in some instances, surgery to remove the affected portion of the colon.
If you experience severe abdominal pain, fever, or rectal bleeding, seek prompt medical attention. These can be signs of a more serious complication, such as an abscess or perforation.
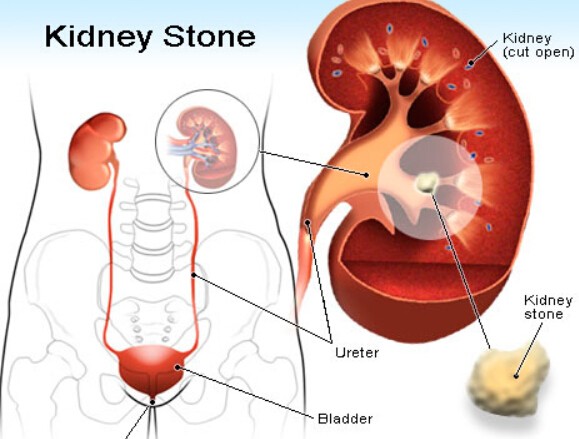
8. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys and can cause severe pain as they try to pass through the urinary tract.
While kidney stone pain often starts in the back or side, it can radiate to the lower abdomen, including the lower right side, as the stone moves closer to the bladder.
In addition to severe, cramping pain, kidney stones can cause nausea, vomiting, and blood in the urine. If you suspect you have a kidney stone, it’s important to seek medical attention. Some stones may require surgical removal or other interventions to prevent complications like urinary tract infections or kidney damage.
9. Ovarian Cysts
In women, ovarian cysts – fluid-filled sacs that develop on the ovaries – can cause lower right abdominal pain if the cyst is located on the right ovary.
Other symptoms may include pelvic pain, irregular menstrual cycles, pain during intercourse, and bloating or fullness in the abdomen.
While most ovarian cysts are benign and resolve on their own, some may require medical treatment or surgical removal. This is important especially if they grow large, cause persistent pain, or show signs of rupturing or twisting.
If you experience severe or persistent pelvic or abdominal pain, it’s important to seek medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
10. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus.
When endometrial tissue implants on the right side of the pelvic region, it can cause pain and discomfort in the lower right abdomen, particularly during menstrual periods.
In addition to pelvic and abdominal pain, endometriosis can cause heavy or irregular periods, painful intercourse, and infertility. While there is no cure for endometriosis, treatment options include pain medication and hormonal therapy.
In some cases, surgery to remove endometrial growths. If you experience severe or persistent pelvic or abdominal pain, especially around your menstrual cycle, it’s important to discuss your symptoms with a healthcare provider.
11. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs, including the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. It’s often caused by sexually transmitted infections, but it can also occur after childbirth or gynecological procedures.
In addition to pelvic pain, PID can cause lower abdominal pain, fever, abnormal vaginal discharge, and irregular menstrual bleeding.
PID is a serious condition that requires prompt treatment with antibiotics to prevent long-term complications, such as infertility, ectopic pregnancy, or chronic pelvic pain.
If you experience pelvic or lower abdominal pain accompanied by fever, abnormal vaginal discharge, or other concerning symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
12. Inguinal Hernia
An inguinal hernia occurs when part of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall, often in the groin area.
While inguinal hernias are more common on the right side in men, they can occur on either side in both sexes. In addition to a bulge in the groin or lower abdomen, inguinal hernias can cause pain or discomfort in the lower right abdomen. This is important especially when coughing, bending, or lifting heavy objects.
While not necessarily a medical emergency, inguinal hernias should be evaluated and treated by a healthcare provider, as they can become incarcerated (trapped) or strangulated.
Treatment typically involves surgical repair to push the protruding tissue back into the abdomen and reinforce the weakened area of the abdominal wall.
13. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
While UTIs are more commonly associated with pain or burning during urination, they can also cause lower abdominal discomfort, including in the lower right abdomen.
This is especially true if the infection has spread to the kidneys (pyelonephritis). This can cause pain in the lower back or abdomen, along with fever, nausea, and vomiting.
UTIs are typically treated with antibiotics, but it’s important to seek medical attention promptly. Untreated infections can lead to more serious complications, such as kidney damage or sepsis.
Drinking plenty of fluids and practicing good hygiene can help prevent UTIs. However, some individuals may be more prone to recurrent infections due to underlying medical conditions or anatomical factors.
14. Abdominal Muscle Strain
Strenuous physical activity or sudden movements can sometimes lead to a strain or tear in the abdominal muscles. This can cause localized pain and tenderness.
While abdominal muscle strains are generally not serious, they can be quite painful and may require rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain medication for relief.
If the pain is severe or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as fever or vomiting, it’s important to seek medical evaluation.
15. Abdominal Adhesions
Abdominal adhesions are bands of scar tissue that can form after abdominal surgery or infection. These adhesions can cause partial bowel obstructions or bind organs together. This can lead to abdominal pain, bloating, and digestive issues. Depending on the location of the adhesions, the pain may be more pronounced in the lower right abdomen.
In some cases, abdominal adhesions may require surgical intervention to remove or separate the scar tissue and alleviate symptoms. However, many cases can be managed conservatively with pain medication, dietary changes, and other supportive measures.
If you experience persistent or severe abdominal pain, especially after abdominal surgery or infection, it’s important to discuss your symptoms with a healthcare provider.
How to Prevent Lower Right Abdominal Pain?
While not all causes of lower right abdominal pain can be prevented, there are several lifestyle measures that can help reduce your risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eating a diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation, which can contribute to abdominal discomfort.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, can help soften stools and prevent constipation, as well as support overall digestive health.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can help stimulate bowel movements and improve overall digestive function, reducing the risk of abdominal pain and discomfort.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can exacerbate conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and contribute to abdominal pain. Incorporate stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises into your routine.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Proper hygiene, particularly in the genital and anal areas, can help prevent infections that may lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or other conditions that can cause lower abdominal pain.
- Seek Prompt Medical Care: If you experience persistent or severe abdominal pain, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can often prevent more serious complications and improve outcomes.
Remember, while abdominal pain can be concerning, many causes are treatable, and early intervention can often prevent more serious complications. By being aware of the potential causes and seeking medical attention when necessary, you can take proactive steps toward resolving your lower right abdominal pain and restoring your overall health and well-being.
When to Seek Emergency Care?
While many causes of lower right abdominal pain can be managed on an outpatient basis, there are certain situations where immediate medical attention is necessary. Seek emergency care if you experience any of the following:
- Severe, sudden, or worsening abdominal pain
- Pain accompanied by fever, vomiting, or inability to pass gas or stool
- Abdominal tenderness or rigidity
- Bloody stools or vomit
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, or signs of shock (rapid heart rate, cold clammy skin)
These symptoms could indicate a potentially life-threatening condition. This includes a ruptured appendix, bowel obstruction, or internal bleeding.