The pain behind the ears or in the ears can be very uncomfortable and irritating. It can range from mild and dull to sharp and severe. Numerous conditions can lead to pain behind the ears.
Most people experiencing this pain usually take medication to alleviate the pain. However, pain in the ears should be checked by an expert before taking any medication. Without proper diagnosis and treatment, the pain can get worse and lead to severe complications.
A person may have a fever if an ear infection causes pain, and this condition requires medical treatment right away. Without the correct medication, the infection can spread to other body areas. With the infection close to the brain, this infection can be difficult. In addition to fever, pain behind the ears can be accompanied by swelling of the lymphatic glands, headaches, etc.
Causes of Pain Behind the Ears
If you are experiencing pain behind the ears, you must seek medical attention immediately to get proper treatment. The following are the most common causes.
1. Otitis Media
Otitis media or an ear infection is the most common cause of ear pain or behind the ears. Children and adults usually experience this ear condition, which affects the middle ear (the air-filled space behind the eardrum that contains the ear’s vibrating bones). Ear infections usually clear up on their own. Treatments may start with monitoring the cause and controlling the pain.
Signs and symptoms of otitis media may also include:
- Pulling at an ear
- Crying more than usual (children)
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Difficulty sleeping
- Difficulty hearing
- Fluid discharge from the ears
In infants and severe conditions, otitis media commonly need antibiotics to remove the infection. However, intense and persistent infection and fluids may lead to impaired hearing, the spread of disease, speech delays, and the tearing of the eardrum. If you have an ear infection, visit your doctor immediately.
2. Mastoiditis
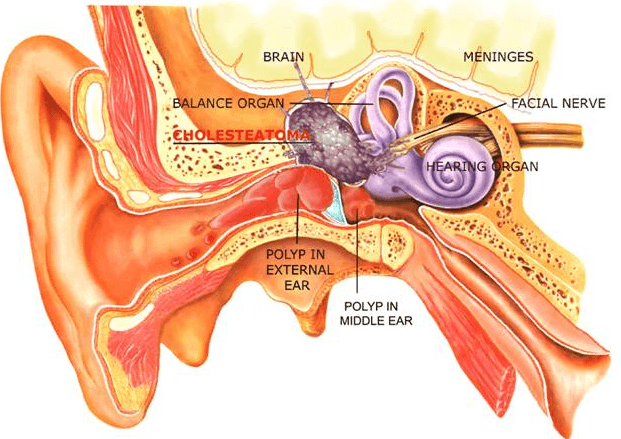
The mastoid bone, located behind the ear, consists of air spaces that assist in draining the middle ear. Bacterial infection and inflammation of the mastoid cells lead to mastoiditis. This may result from an untreated ear infection or otitis media. Due to ear infections, the bacteria from the middle ear can spread to the mastoid bone. This condition may affect children and adults.
Mastoiditis can also result from the blockage of drainage due to cholesteatoma, a type of cyst in the middle ear. Signs and symptoms of mastoiditis may include:
- Drainage from the ears
- Irritability and lethargy
- Fever
- Swelling of the earlobe, redness behind the ear
- Drooping or bulging of the ear
Your doctor will check the ear to see the presence of an infection. Other tests may also be required to confirm the diagnosis, such as Ear culture (removal of the fluid and substances), blood tests, X-ray, MRI, and CT scan. Chronic mastoiditis is treated with regular ear cleanings by a doctor, eardrops, and oral antibiotics. Surgery may be required if the treatments are not effective.
3. Temporomandibular Joint Disorders
Another cause of pain behind the ears is a temporomandibular joint disorder. The Temporomandibular joint connects the jaw to the temporal bones of the skull. This allows you to move your jaw correctly to chew, yawn and talk. Problems with the jaw and its muscles caused by an injury can result in TMD or TMJ. Other causes include arthritis, clenching or grinding the teeth, stress, and movement of the disc between the ball and socket of the joint.
The signs and symptoms of TMD or TMJ include:
- Pain in the face, jaw, and around the ear when chewing, speaking or opening the mouth.
- Pain or tenderness in the shoulders and neck
- Locked Jaw
- Clicking or grating sounds when opening the mouth or chewing
- Uncomfortable chewing
- Tired feeling or swelling of the face
If you develop one or more of these symptoms, visit your doctor immediately. You may also have other conditions, such as gum disease, sinus problems, arthritis, or tooth decay. A proper diagnosis of the problem is needed for you to have appropriate treatment.
4. Swimmer’s Ear
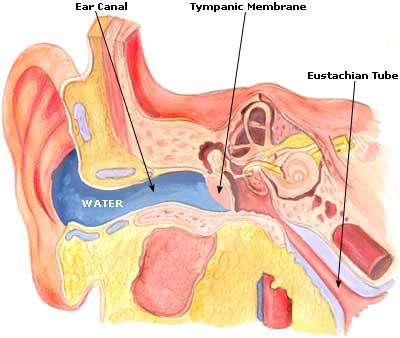
The swimmer’s ear, also known as otitis externa, is an outer ear canal infection. This is brought on by water stuck in the ear after swimming. It creates a damp environment that leads to the growth of bacteria. Other factors that lead to a swimmer’s ear include cotton swabs, putting fingers inside the ear, or other objects. Damaging the thin skin lining the ear canal allows bacteria to enter.
Signs and symptoms of mild swimmer’s ear include itchiness in the ear canal, mild redness inside the ear, mild discomfort, and drainage of odorless fluid. For moderate and advanced progression, you may experience the following:
- Intense itching
- Excessive discharge of fluid or pus
- Decreased hearing
- Fever
- Swelling in the lymph nodes
- Swelling of the outer ear and severe pain
If you are experiencing any symptoms of a swimmer’s ear, go to your doctor immediately. The common treatment for a swimmer’s ear is eardrops. The advanced stage of infection will require further testing and more medications.
5. Blocked Eustachian Tube
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the throat. This tube helps drain fluid from the ears and keeps the air pressure at an accurate level. The tubes open momentarily when you yawn or swallow to allow the air in to ensure that the pressure outside the ears is the same as the pressure in the middle ears. If the external force is too high, it results in ear pain or hearing problems.
Sinus infections, allergies, and colds can block the Eustachian tubes, which leads to changes in the level of pressure. Fluid may also gather in your middle ear and result in pain. The ear pain can be experienced as the pressure changes, such as driving up the mountains, flying in an airplane, or diving.
Blocked Eustachian tubes can be treated with simple exercises. You can also close your mouth, hold your nose, and blow gently like you are blowing your nose. You may also chew a pack of gum to correct the pressure. If these do not help, your doctor may suggest over-the-counter medicines, decongestants, or antibiotics.
6. Ceruminosis
Earwax is essential in our body, as it is a natural part of our defenses. It cleans and protects the ear canal by trapping dirt. It also slows down the growth of bacteria. Ceruminous or earwax blockage occurs when earwax builds up in the ear or becomes too solid to drain naturally. Signs and symptoms of ceruminous or earwax blockage may include:
- Ear pain
- A feeling of fullness in the ear
- Noises in the ear
- Dizziness and cough
- Hearing problem
Go to your doctor if you are experiencing any signs or symptoms. It may indicate another health condition. Do not remove the earwax yourself. A doctor should also remove Wax as your ear canal and eardrum are delicate and damaged.
7. Tooth Abscess
A tooth abscess is an infection at the root or between a tooth and the gum. This is usually caused by tooth decay. Other causes are gum disease, gingivitis, and chipped or broken tooth. These problems open the tooth enamel, letting bacteria enter and infect the tooth’s pulp. If not treated immediately, the infection could spread to the bones that support the tooth.
The symptoms of an abscessed tooth include:
- A toothache
- Fever
- Sensitivity to cold or hot
- Pain when chewing
- Bitter taste and foul smell of breath
- Swelling or redness of gums
- Swollen neck glands
- Open, draining sore on the gum
If you are experiencing any signs or symptoms, visit your dentist immediately. The abscess should be trained to remove the infection. Root surgery may also be recommended to eliminate the diseased root tissue. Another way to treat pimples is by incision.
8. A headache
The ear is close to the brain, and the pain from a headache can seep down to the ears. But that is not always the case.
- Hemicrania Continua – This is a one-sided headache that also affects the ears. The common treatment to alleviate the pain is anti-inflammatory drugs such as Indomethacin.
- An ice-pick Headache – This headache usually affects the eyes, occurs behind the ear, and lasts for only a few seconds.
Other headaches that can cause pain behind the ears are:
- A cervicogenic headache
- A cold stimulus or an ice cream headache
- Primary Yawning a headache
- Sudden Unilateral Neuralgiform headache with Conjunctival Infection and Tears
- A nummular Headache
Read: How to Get Rid of Headaches at the Base of the Skull
9. Swollen Lymph Nodes
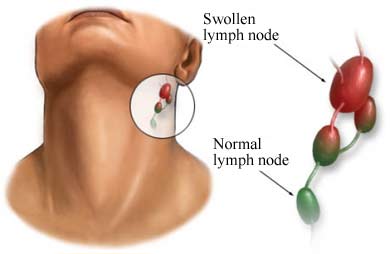
A part of the body’s immune system, lymph nodes are located in many body areas. Lymph nodes are usually swollen in the groin, armpit, and neck. Enlarged or swollen lymph nodes can result in pain behind the ears or back of the head.
Many reasons can lead to swelling, such as cold, infection, inflammation, or cancer. It is best to visit your doctor for a proper diagnosis and the right treatment. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics if the cause is due to infection.
When to see a doctor?
Pain behind the ears can be a symptom of various underlying conditions, ranging from minor issues to more serious medical conditions. While some causes of pain behind the ears may not require immediate medical attention, there are instances when it is important to see a doctor. Here are some situations when you should consider seeking medical advice for pain behind the ears:
1. Severe or worsening pain: If the pain behind your ears is severe or getting worse over time, it is recommended to see a doctor. This could be a sign of a more serious condition that requires medical intervention.
2. Head injury: If you have experienced a recent head injury and are experiencing pain behind the ears, it is important to seek medical attention. Head injuries can cause various complications, and a doctor can evaluate the severity and provide appropriate treatment.
3. Fever or infection: If you have pain behind the ears accompanied by fever, redness, swelling, or discharge, it could be a sign of an infection. Infections such as otitis media (middle ear infection) or mastoiditis (infection of the mastoid bone) may require medical treatment with antibiotics.
4. Neck stiffness or headache: If the pain behind your ears is associated with neck stiffness, headache, or other neurological symptoms, it could be a sign of meningitis. Meningitis is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
5. Jaw or dental issues: Problems with the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) or dental issues can sometimes cause pain that radiates to the area behind the ears. If you suspect that your ear pain is related to jaw or dental problems, it is recommended to consult with a dentist or an oral and maxillofacial specialist.
6. Persistent or recurring pain: If you have been experiencing persistent or recurring pain behind the ears, it is advisable to see a doctor for further evaluation. Chronic pain may indicate an underlying condition that needs to be addressed.