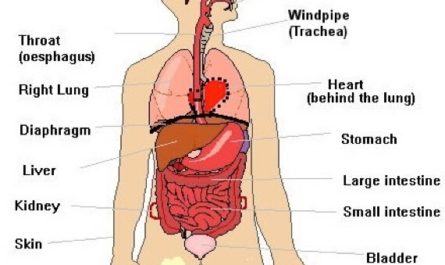
Pain under the left breast refers to discomfort or soreness experienced in the area beneath the left breast. The pain may vary in intensity and can be sharp, dull, or throbbing. It may also be accompanied by other symptoms such as tightness or pressure in the chest, difficulty breathing, nausea, and fatigue.
Pain under the left breast can be caused by various factors such as injury, inflammation, digestive problems, respiratory issues, or heart conditions. It’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe pain under the left breast. In this article, we’ll explore 14 common causes of pain under the left breast and provide tips for managing this uncomfortable symptom.

Symptoms Accompanying Left breast pain
Pain under the left breast can be accompanied by various symptoms, depending on the underlying cause. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort: This can range from a mild ache to severe pain and may be described as a burning, sharp, or stabbing sensation.
- Difficulty breathing: Some people may experience shortness of breath, wheezing, or tightness in the chest.
- Nausea or vomiting: This can occur in cases where the pain is related to digestive issues such as acid reflux or gastritis.
- Fatigue or weakness: Pain under the left breast can be exhausting and may cause feelings of weakness or fatigue.
- Swelling or tenderness: In some cases, the affected area may be swollen or tender to the touch.
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeat: This can occur when the pain is related to heart issues such as angina or heart attack.
- Anxiety or panic: Severe pain or discomfort can trigger anxiety or panic in some people.
It is essential to seek medical attention if the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms, as this could be a sign of a more severe condition.
14 Common Causes of Pain Under the Left Breast
Understanding the potential causes of this pain can help you identify the problem and get the appropriate treatment.
1. Pericarditis
Pericarditis is the inflammation of the pericardium, the thin membrane surrounding the heart. One of the common symptoms of pericarditis is left breast pain.
Acute pericarditis can cause pain to travel into the left shoulder and neck and worsen on inhalation, coughing, or lying down. In addition to chest pain, other symptoms of pericarditis can include fever, shortness of breath, cough, and fatigue.
Pericarditis can be caused by various factors, including viral infections, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications.
The following are some general steps that can be taken to manage pericarditis:
- Seek medical attention: If you suspect that you have pericarditis, it is important to seek medical attention right away. Your doctor will perform a physical exam and may order tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) or an echocardiogram to confirm the diagnosis.
- Rest: Resting and avoiding strenuous activities can help to reduce the strain on your heart and reduce inflammation.
- Pain relief: Pain relief can be achieved through nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or aspirin, or other pain relievers prescribed by your doctor.
- Treating underlying conditions: Pericarditis may be caused by an underlying condition such as a viral or bacterial infection. Treating the underlying condition may help to resolve the pericarditis.
In severe cases of pericarditis, more aggressive treatments such as corticosteroids, colchicine, or even surgery may be necessary.
2. Rib Injuries or Muscle Pains
Rib injuries or muscle pains can cause pain under the left breast. The ribs and muscles in the chest and upper abdomen can be injured or strained due to trauma, overuse, or poor posture, leading to pain in the area under the left breast.
If you are experiencing left breast pain, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause. The following are some general steps that can be taken to manage rib injuries or muscle pains:
- Rest: Resting the affected area is important to prevent further injury and allow the body time to heal. Avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain or strain the affected muscles can help to speed up the healing process.
- Ice and heat therapy: Applying ice packs or heat pads to the affected area can help to reduce pain and inflammation. Applying ice for 15-20 minutes at a time several times a day for the first 48-72 hours after injury is recommended, followed by heat therapy to promote blood flow and healing.
- Pain relief: Pain relief can be achieved through over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, or other pain relievers prescribed by your doctor.
- Physical therapy: In some cases, physical therapy may be recommended to help strengthen the affected muscles and promote healing.
3. Precordial Catch Syndrome (PCS)
Precordial Catch Syndrome (PCS) is a common condition that causes chest pain, especially in young adults. It is also known as Texidor’s twinge and is considered a benign condition, meaning that it is not a serious or life-threatening condition.
PCS typically causes sudden and sharp pain on the left side of the chest, usually near the breastbone, that lasts for a few seconds to a few minutes. The pain is often described as feeling like a “catch” or a “stab” in the chest and can be triggered by deep breathing or sudden movements.
Here are some general steps that can be taken to manage Precordial Catch Syndrome:
- Deep breathing exercises: Taking deep breaths and exhaling slowly can help to alleviate the pain associated with PCS. This can also help to prevent the recurrence of the symptoms.
- Stretching exercises: Gently stretching the chest muscles can help to alleviate pain associated with PCS. This can be done by reaching your arms up and over your head and taking deep breaths.
- Heat therapy: Applying heat to the chest area with a warm compress or heating pad can help to alleviate the pain associated with PCS.
4. Heartburn
Heartburn is a common condition that causes a burning sensation in the chest or throat. It is caused by stomach acid flowing back into the esophagus, which can cause pain under the left breast.
Several factors can contribute to heartburn, including overeating, eating spicy or fatty foods, and certain medications.
Here are some general steps that can be taken to manage heartburn:
- Lifestyle modifications: Certain lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding trigger foods, and maintaining a healthy weight, can help to alleviate heartburn symptoms.
- Over-the-counter medications: Over-the-counter antacids such as Tums, Rolaids, and Maalox can help to neutralize stomach acid and provide immediate relief from heartburn symptoms. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) such as omeprazole or lansoprazole can also be taken to reduce the production of stomach acid.
- Dietary changes: Certain dietary changes such as avoiding spicy and acidic foods, eating smaller meals more frequently, and avoiding eating before bedtime can help to alleviate heartburn symptoms.
5. Excess Digestive Gas
Gases trapped in the stomach can suddenly shoot up into the esophagus towards the chest region, resulting in sharp, shooting pain.
Surplus digestive gas due to talking while eating, fizzy drink consumption, or not chewing food properly can cause upper left abdominal pain. Air gets caught in the colon, and the resulting pain may travel to the chest.
Here are some general steps that can be taken to manage excess digestive gas:
- Dietary changes: Certain foods can cause excess gas, so it is important to identify and avoid these trigger foods. Common gas-causing foods include beans, broccoli, cabbage, onions, carbonated beverages, and high-fat or fried foods.
- Slow down when eating: Eating too quickly can cause you to swallow air, contributing to excess gas. Taking your time and chewing your food thoroughly can help to prevent excess gas.
- Probiotics: Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that live in the gut and can help to improve digestive health. Taking probiotic supplements or eating foods that are high in probiotics, such as yogurt or kefir, can help to reduce excess gas.
- Exercise: Exercise can help to promote digestion and alleviate symptoms of excess gas. Walking, running, and yoga are all good options.

6. Costochondritis
Costochondritis is an inflammatory condition that affects the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone. It can cause pain and tenderness in the affected area, which may be mistaken for pain under the left breast.
- Take pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help to reduce pain and inflammation associated with costochondritis.
- Apply heat or ice: Applying heat or ice to the affected area can help to reduce pain and swelling. Try using a heating pad or ice pack for 15-20 minutes.
- Rest: Avoid activities that worsen your pain, and take time to rest and recover. It may be helpful to avoid activities that involve repetitive or strenuous movements, as these can aggravate the condition.
- Practice good posture: Poor posture can strain the chest and exacerbate symptoms of costochondritis. Try to sit and stand with your shoulders back and your chest open.
- Physical therapy: In some cases, physical therapy may be recommended to help stretch and strengthen the chest muscles, which can reduce pain and improve the range of motion.
- Corticosteroid injections: If pain and inflammation persist despite other treatments, your healthcare provider may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
7. Cardiac Conditions
One of the most common cardiac symptoms is a tightening feeling in the chest, known as angina, which develops due to insufficient cardiac oxygen supply. Pain commonly occurs under the sternum but could radiate to the neck, shoulder, jaw, or back.
The treatment for cardiac conditions depends on the specific condition and its severity. Here are some general treatment options for common cardiac conditions:
- Coronary artery disease (CAD): Treatment for CAD may include lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise, medications such as aspirin and cholesterol-lowering drugs, and procedures such as angioplasty or bypass surgery.
- Heart failure: Treatment for heart failure may include medications such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and diuretics, as well as lifestyle modifications such as limiting salt intake and increasing physical activity.
- Arrhythmias: Treatment for arrhythmias may include medications such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or anti-arrhythmic drugs, as well as procedures such as electrical cardioversion, catheter ablation, or implantation of a pacemaker or defibrillator.
- Cardiomyopathy: Treatment for cardiomyopathy may include medications such as beta-blockers or ACE inhibitors, as well as lifestyle modifications such as limiting physical activity and avoiding alcohol.
8. Lung Issues
Lung issues such as pneumonia, bronchitis, or asthma can cause pain under the left breast. When the lungs are inflamed or infected, they may pressure nearby nerves and cause pain in the chest area. In some cases, the pain may be accompanied by coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath.
The treatment for lung issues depends on the specific condition and its severity. Here are some general treatment options for common lung issues:
- Asthma: Asthma treatment may include medications such as inhaled corticosteroids, bronchodilators, or leukotriene modifiers, as well as avoiding triggers such as allergens or irritants.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Treatment for COPD may include medications such as bronchodilators, inhaled steroids, or phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors, as well as lifestyle modifications such as quitting smoking and avoiding lung irritants.
- Pneumonia: Treatment for pneumonia may include antibiotics, cough medicine, and fever reducers, as well as rest and hydration.
- Pulmonary embolism: Treatment for a pulmonary embolism may include blood thinners, oxygen therapy, and in severe cases, surgery.
- Lung cancer: Treatment for lung cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or targeted drug therapy, depending on the type and stage of the cancer.
9. Left breast pain in women
Pain under the left breast in women can have various causes, including:
- Menstrual cramps: Many women experience menstrual cramps that can cause pain in the lower abdomen and breast area. (Resource)
- Pregnancy: As the body changes during pregnancy, women may experience discomfort and pain in the breast area.
- Breastfeeding: Women who are breastfeeding may experience pain under the left breast due to engorgement or a clogged milk duct.
- Breast cancer: Although breast cancer is more commonly associated with pain in the right breast, it can also cause pain under the left breast.
10. Acid reflux
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a condition in which stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. This can cause a burning sensation in the chest, sometimes radiating to the left side of the body, including under the left breast. Other symptoms of acid reflux may include heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing.
11. Gastritis
Gastritis is a condition where the stomach lining becomes inflamed or irritated. This inflammation can cause various symptoms, including pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen, bloating, nausea, and vomiting.
When the inflammation in the stomach is severe, it can also cause pain or discomfort in the chest, including under the left breast. This pain may be described as a burning sensation, aching, or pressure. It can sometimes be accompanied by a feeling of fullness or tightness in the chest.
12. Cysts
Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop in the breast tissue, causing pain or discomfort under the left breast. A study found that breast cysts are a common finding in women and are typically benign.
However, if the cysts are large or causing significant pain, they may need to be drained or surgically removed. Treatment for breast cysts typically involves monitoring with regular breast exams and imaging tests.
If the cysts are causing discomfort or concern, a healthcare professional may recommend aspiration or surgery. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience changes in your breast tissue or significant pain or discomfort.
13. Costochondritis
Costochondritis is a common cause of pain under the left breast. It is an inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone. Costochondritis is often misdiagnosed as a heart attack due to the similarity in symptoms. (Resource)
Treatment for costochondritis typically involves rest, pain relief medications, and physical therapy. In severe cases, steroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience chest pain, as it can be a symptom of a more serious condition such as a heart attack.
14. Hiatal Hernia
A hiatal hernia is where a portion of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. This can cause left breast pain, heartburn, difficulty swallowing, and nausea. Hiatal hernias are common and can be seen in imaging studies.
Treatment for Hiatal hernias typically involves lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and avoiding trigger foods that can exacerbate symptoms, as well as medication to reduce acid reflux. (Resource)
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the hernia. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent chest pain or difficulty swallowing.
Is pain under the left breast a sign of a heart attack?
Yes, pain under the left breast can be a sign of a heart attack, especially if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, sweating, and nausea. Pain caused by a heart attack is typically described as a pressure or tightness in the chest that can spread to other areas of the body, including the left arm, back, and jaw.
It is essential to seek immediate medical attention if you experience chest pain or discomfort, especially if it is severe or accompanied by other symptoms. Prompt treatment can help minimize the damage to the heart muscle and improve outcomes. (Resource)
How to prevent pain under the left breast?
Preventing pain under the left breast can depend on the underlying cause. Here are a few tips that may help prevent pain in the chest area:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, and reducing stress can help prevent many health issues that may lead to chest pain.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking is a major cause of heart disease, which can lead to chest pain. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of chest pain and other related health issues.
- Manage chronic conditions: If you have a chronic condition such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, work with your healthcare provider to manage it effectively. This can help reduce the risk of complications that may lead to chest pain.
- Practice good posture: Maintaining good posture can help reduce strain on the muscles and joints around the chest and back, which can help prevent pain.
- Wear comfortable clothing: Tight clothing or undergarments can pressure the chest and lead to pain. Wear loose-fitting, comfortable clothing to reduce the risk of chest pain.
- Avoid triggering foods: Certain foods may trigger heartburn or indigestion, leading to chest pain. Avoiding these foods or eating smaller, more frequent meals may help prevent chest pain.
- Practice stress-reduction techniques: Stress can contribute to chest pain. Relaxing techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help reduce stress and prevent chest pain.
When to See a Doctor?
Pain under the left breast can be caused by various reasons, ranging from minor issues to severe medical conditions. Here are some instances when you should consider seeing a doctor:
- Chest pain: If the pain is severe and accompanied by shortness of breath, dizziness, or pressure in the chest, it may be a sign of a heart attack. Seek emergency medical attention immediately.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Pain under the left breast can also be caused by gastrointestinal problems like acid reflux, gastritis, or peptic ulcers. You may want to consult a doctor if you experience symptoms like bloating, nausea, or diarrhea.
- Infections: If a fever accompanies the pain, it may be a sign of a disease. Infections like pneumonia or pleurisy can cause pain under the left breast. If you experience these symptoms, it’s essential to see a doctor.
- Muscle strain: Pain under the left breast can also be caused by a muscle strain or injury. If you’ve recently engaged in physical activity or experienced trauma to the area, you may want to consult a doctor.
- Breast issues: Pain under the left breast can also be caused by breast-related issues like mastitis, a breast abscess, or breast cancer. If you notice any unusual changes in your breast, including lumps or discharge, consult a doctor.