Pain in the right lower pelvic groin region can be a concerning symptom that may indicate various underlying conditions. Understanding the anatomy and potential causes of this pain is crucial for prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. This article will explore the 16 possible causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Right Lower Pelvic Groin Region
The right lower pelvic groin region is a complex area involving several structures, including muscles, tendons, ligaments, and organs. It encompasses the lower abdomen, the right side of the pelvis, and the groin area. Key structures in this region include:
- Hip Joint: The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint that connects the thigh bone (femur) to the pelvis. It allows for a wide range of motion and provides stability during activities such as walking, running, and jumping.
- Iliopsoas Muscle: This muscle group consists of the iliac and psoas major muscles, which play a crucial role in hip flexion and rotation. The iliopsoas muscles help stabilize the pelvis and are involved in movements such as lifting the leg and bending at the waist.
- Appendix: The appendix is a small tube-like structure located in the lower right abdomen. Although its exact function is still unclear, it is believed to play a role in the immune system. Inflammation of the appendix can cause a condition known as appendicitis, which can result in severe pain in the right lower pelvic groin region.
- Inguinal Canal: This canal is located in the groin region and allows structures, such as blood vessels and nerves, to pass through. It is a common area for the development of hernias, which can also cause pain in the right lower pelvic groin region.

Symptoms Associated with Pain in the Right Lower Pelvic Groin Region
The specific symptoms experienced with pain in the right lower pelvic groin region may vary depending on the underlying cause. However, common symptoms include:
- Dull or Sharp Pain: Pain in the right lower pelvic groin region can range from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation. The intensity and nature of the pain may vary depending on the cause.
- Difficulty Walking or Moving: Pain in this area can make it challenging to walk, move the right leg, or engage in activities that involve the lower body.
- Swelling or Tenderness: Inflammation or injury in the right lower pelvic groin region may lead to swelling or tenderness upon touch.
- Changes in Bowel or Urinary Habits: Some conditions causing pain in this region, such as appendicitis or urinary tract infections, can lead to changes in bowel or urinary habits. These changes may include increased frequency, urgency, or discomfort during urination or bowel movements.
16 Causes of Pain in the Right Lower Pelvic Groin Region
Pain in the right lower pelvic groin region can arise from various conditions, including:
1. Muscle Strain or Injury
Overexertion, sudden movements, or improper lifting techniques can lead to muscle strains or tears in the pelvic and groin area. Activities such as sports, exercise, or lifting heavy objects without proper form can contribute to muscle strain. The resulting pain is often localized and can be aggravated by movement or pressure.
2. Appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix is a common cause of pain in the right lower pelvic groin region. The pain typically starts around the belly button and gradually moves to the lower right abdomen.
As the inflammation progresses, the pain may radiate to the right lower pelvic groin region. Other symptoms of appendicitis include fever, loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting. Appendicitis requires immediate medical attention and surgical removal of the appendix.
3. Hernia
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. Inguinal hernias, specifically, can cause pain in the groin area, including the right lower pelvic region.
These hernias often develop in the area where the abdominal muscles meet the thigh. Common symptoms of a hernia include a visible bulge, pain during physical activity or lifting, and a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the groin.
4. Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on the ovaries. While they can occur on either side, the presence of ovarian cysts on the right ovary can cause pain in the right lower pelvic groin region.
The pain may be sharp or dull and can vary in intensity. Additional symptoms may include bloating, changes in menstrual patterns, and discomfort during sexual intercourse.
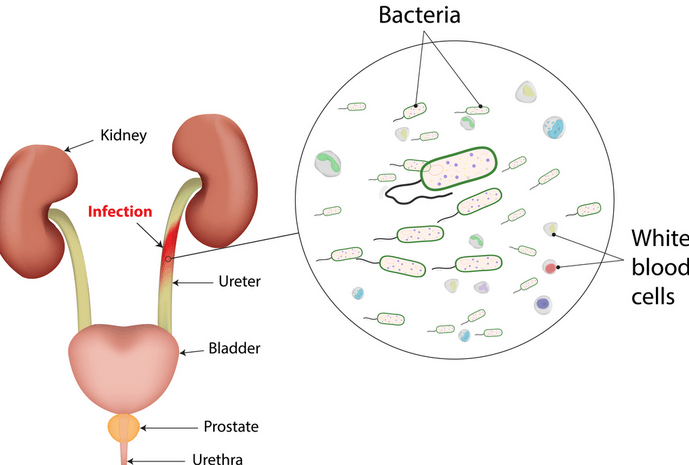
5. Urinary Tract Infections
Infections in the urinary tract, such as a bladder or kidney infection, can cause pain in the lower abdomen and pelvic region. These infections often result from bacteria entering the urinary tract through the urethra. In addition to pelvic pain, symptoms of a urinary tract infection may include a frequent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, cloudy or bloody urine, and fever.
7. Gynecological Conditions
Various gynecological conditions can cause pain in the right lower pelvic groin region. Conditions such as endometriosis, ovarian torsion, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and ectopic pregnancy can all result in localized or radiating pain in the pelvic area. These conditions require medical evaluation and appropriate treatment.
8. Gastrointestinal Issues
Certain gastrointestinal issues, such as constipation, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), can cause referred pain in the right lower pelvic groin region. The pain may be associated with bloating, changes in bowel habits, and discomfort during bowel movements.
9. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits that form in the kidneys and can cause severe pain as they pass through the urinary tract. If a stone lodges in the right ureter, it can lead to pain in the right lower pelvic groin region. Other symptoms of kidney stones may include blood in the urine, frequent urination, and a persistent urge to urinate.
10. Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
Dysfunction of the pelvic floor muscles, which support the pelvic organs, can result in pain in the right lower pelvic groin region. Conditions such as pelvic floor muscle spasms or pelvic floor dysfunction can cause chronic pelvic pain that may radiate to the groin area.
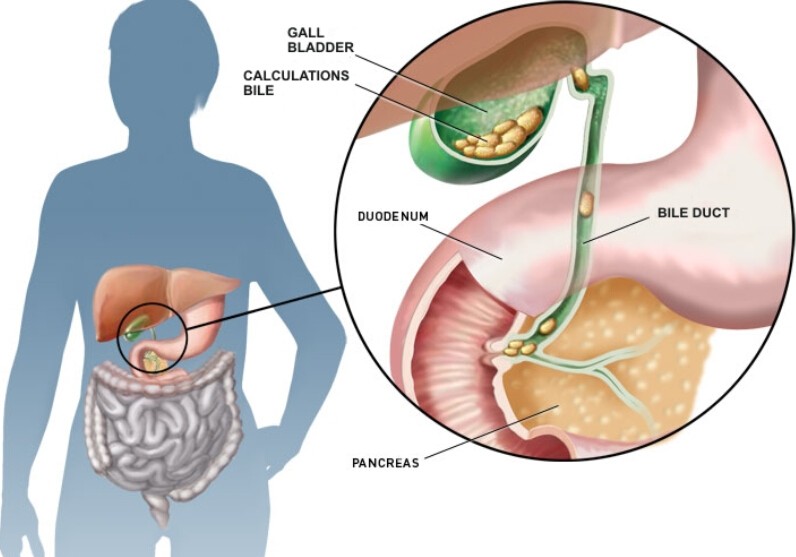
11. Gallbladder Issues
Gallbladder problems, such as gallstones or inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), can cause pain that may be felt in the right lower pelvic groin region. The pain typically presents as a sharp, cramp-like pain in the upper abdomen that may radiate to the right side or groin.
12. Prostatitis
Inflammation of the prostate gland, known as prostatitis, can cause pain in the lower pelvic region, including the right side. This condition is more common in males and can be associated with urinary symptoms such as pain or difficulty urinating.
13. Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis occurs when small pouches (diverticula) in the colon become inflamed or infected. While diverticulitis typically causes left-sided abdominal pain, in some cases, it can cause pain on the right side, including the right lower pelvic groin region. Other symptoms may include fever, changes in bowel habits, and bloating.
14. Ovarian Torsion
Ovarian torsion is a condition in which the ovary twists, cutting off its blood supply. This can cause severe pain in the lower pelvic region, including the right side. Ovarian torsion is a medical emergency and requires immediate medical attention.
15. Musculoskeletal Issues
Various musculoskeletal issues, such as pelvic joint dysfunction or sacroiliac joint dysfunction, can cause pain in the right lower pelvic groin region. These conditions may result from injury, overuse, or structural imbalances and can be associated with localized or radiating pain.
16. Nerve Entrapment
Nerve entrapment or irritation in the pelvic region, such as ilioinguinal nerve entrapment or genitofemoral nerve entrapment, can lead to pain in the right lower pelvic groin region. These conditions may occur due to compression or irritation of the nerves, resulting in chronic or intermittent pain.
Treatment Options for Pain in the Right Lower Pelvic Groin Region
The treatment approach for pain in the right lower pelvic groin region depends on the underlying cause. Common treatment options include:
- Rest and Self-Care Measures: For muscle strains or minor injuries, resting the affected area, applying ice or heat, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers may be sufficient. Proper rest allows the muscles and tissues to heal.
- Medications for Pain Relief: In cases of more severe or chronic pain, your healthcare provider may prescribe pain medications or anti-inflammatory drugs to alleviate symptoms. These medications can help manage pain, reduce inflammation, and promote healing.
- Physical Therapy or Rehabilitation Exercises: Physical therapy can play a crucial role in the treatment of pain in the right lower pelvic groin region. A physical therapist can provide targeted exercises and stretches to strengthen the affected muscles, improve flexibility, and promote proper biomechanics. Physical therapy may include modalities such as heat or cold therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to aid in pain management and tissue healing.
- Surgical Interventions: In cases of certain conditions, such as hernias, appendicitis, or ovarian cysts that do not resolve on their own or cause significant pain and complications, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery aims to repair or remove the underlying issue and alleviate the associated pain. The specific surgical procedure will depend on the diagnosed condition and the individual’s overall health.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on your specific condition, symptoms, and individual factors.

Prevention and Lifestyle Tips for Pain in the Right Lower Pelvic Groin Region
While not all causes of pain in the right lower pelvic groin region can be prevented, you can take certain measures to reduce the risk. Consider the following:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put a strain on the pelvic and groin muscles, increasing the risk of injury. Aim for a healthy body weight through proper diet and regular exercise. Consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
- Practice Proper Body Mechanics: When engaging in physical activities or lifting heavy objects, use proper body mechanics to avoid unnecessary strain on the pelvic area. This includes lifting with your legs instead of your back and avoiding sudden or jerky movements.
- Stay Hydrated and Maintain Good Urinary and Bowel Habits: Proper hydration and regular urination can help prevent urinary tract infections, which can contribute to pelvic pain. Drink an adequate amount of water daily and empty your bladder regularly. Additionally, maintaining regular bowel habits and avoiding constipation can help reduce strain on the pelvic muscles.
- Incorporate Regular Exercise and Stretching: Engage in exercises that strengthen the core and pelvic muscles. Strengthening exercises, such as pelvic floor exercises (Kegels), can help support the pelvic organs and reduce the risk of certain conditions. Additionally, stretching before physical activity can help improve flexibility and prevent muscle strains.
It’s important to note that individual factors and medical conditions may influence the appropriateness of certain exercises or lifestyle recommendations.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention?
While most cases of pain in the right lower pelvic groin region can be managed with conservative measures, certain symptoms require immediate medical attention. If you experience any of the following, seek emergency care:
- Severe or Worsening Pain: If the pain becomes severe, unbearable, or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it may indicate a medical emergency.
- High Fever, Chills, or Signs of Infection: Symptoms such as high fever, chills, or signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, or swelling in the area, may indicate a serious underlying condition.
- Vomiting or the Inability to Eat: Persistent vomiting or the inability to eat or drink may suggest a more severe condition that requires immediate medical attention.
- Sudden Changes in Bowel or Urinary Function: If you experience sudden changes in bowel or urinary habits, such as the inability to pass urine, blood in the urine, or severe constipation, seek medical attention promptly.
It’s important to trust your instincts and seek medical help if you are concerned about your symptoms. Prompt medical evaluation can help identify and address potential complications or serious conditions.
Conclusion:
Pain in the right lower pelvic groin region can be caused by various factors, including muscle strains, appendicitis, hernias, ovarian cysts, and urinary tract infections. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for managing the pain and addressing the underlying cause. If you experience persistent or severe pain in this area, consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan.