Are you suffering from itchy red bumps on your skin? The skin is the largest human organ. It accounts for about 15% of all our body weight. What’s more? It’s our first line of defense against infection. Our skin also protects against microbes and harmful pathogens in the outer environment.
Unfortunately, when infections make it through the outer barrier, the skin is also one of the most affected organs. Most times, when our skin is irritated, it appears as red itchy skin bumps.
Skin rashes vary in appearance, depending on their source. While some skin bumps may be hard and firm, others may be soft and moveable. Additionally, the size of skin bumps can also vary. Some may appear small and pimple-like, while others may be as large as boils.
However, having itchy red bumps may not be a symptom of an underlying infection in some cases. Most times, your itchy red bumps may be a nasty mosquito bite. In addition, it can result from infections, allergies, or something more serious like skin cancer. This article discusses 12 common causes of Itchy Red Bumps on the skin.
12 Common Causes of Itchy Red Bumps on Your Skin
1. Hives (Urticaria)
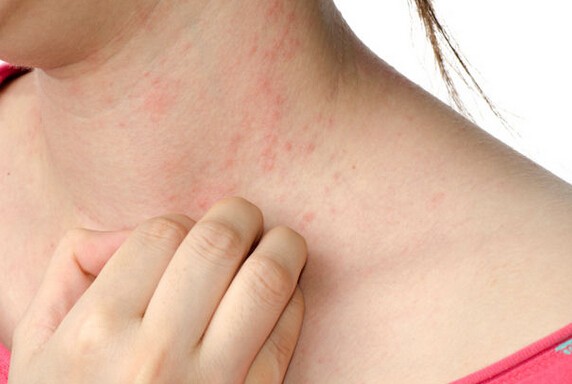
Hives are red, swollen lumps or welts that appear on your skin. Although hives are usually itchy, sometimes, they burn and sting too. Usually, hives appear when your skin is irritated.
They can appear small, like mosquito bites, or wide-ranging, spanning through several inches of your skin.
Hives can pop up on any part of your body – While they can appear on their own, in some cases, these hives may link up and span over much larger areas of your skin.
Like the itching hives aren’t bad enough, scratching your hives can cause them to spread and grow bigger.
Usually, hives can be triggered by allergic or non-allergic factors. While the non-allergic triggers may be more common, the exact cause is still a mystery.
The non-allergic factors include:
- Exposure to sunlight
- Viral infections
- Fungal infections
- Extreme temperatures
- Too much exercise
- Emotional stress
Although allergic hives don’t happen as frequently as non-allergic hives, the origins of allergic hives are well-known.
Allergic hives are usually triggered by the following:
- Foods – such as peanuts, shellfish, eggs, milk, or food additives
- Medications – antibiotics and pain reliefs like aspirin
- Latex
- Plants – grass and weeds like poison ivy, poison oak
- Cockroaches and cockroach waste
- Bites from insects
- Animal dander
- Water touching the skin
- Some chemicals in detergents, body creams, and soaps.
What if your hives are severe?
Don’t panic! Usually, hives aren’t always severe. They affect about 1 in every 5 people globally.
However, you need to see your doctor if you’re vomiting, dizzy and have difficulty breathing. When these symptoms accompany the hives on your skin, it could mean something more serious, like anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis could be life-threatening.
How to treat Hives
Luckily, you can treat most hive infections with over-the-counter antihistamines, especially if your hives are mild.
However, in extreme cases, your doctor will probably administer a combination of antihistamine and epinephrine. You can get your epinephrine in an EpiPen (epinephrine auto-injector). For more information about hives and treatment, read this article.
Top tip: If you’ve noticed symptoms of anaphylaxis with your hives, ensure you always have your EpiPen around.
Sometimes, hives can disappear after some days and re-appear after a few weeks. To prevent hives from worsening, you must avoid allergens that trigger hives.
How to prevent Hives
- Don’t scratch your skin. Itching makes hives spread faster.
- If you experience hives after using harsh soaps, avoid using them. You can use mild soaps instead.
- Wear sunscreen to protect yourself from the sunlight.
- Wash your hand immediately after you play with your pets.
- When you’re feeling itchy, apply a cold compress on the area of the hives.
- If you’re sensitive to extreme cold, ensure you wear warm clothes.
- The urge to itch can be unbearable. If your child can’t stop itching, I recommend playing a game or singing a song to distract him from scratching.
2. Allergic Reactions
Allergies are a common cause of itchy red bumps on the skin. From food to medicines to pollen, many different reasons can cause allergies. According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), about 50 million Americans experience allergic reactions yearly.
Food or medicine can cause urticaria, an itchy pink or red rash. It can appear in clusters or alone. In most cases, urticaria will disappear automatically within 1-2 days. But some chronic urticaria may last longer.
Urticaria can be treated with antihistamines or corticosteroids. However, if a severe condition, such as angioedema, or urticaria-related swelling, occurs deep in the skin, you need to consult your doctor immediately.
Sun allergy can cause an itchy red rash that some people experience after exposure to the sun. These small itchy red patches can cause skin redness, pain, and blisters. Sun allergies may be genetic or caused by drugs that make them more sensitive to the sun.
The symptoms will disappear after a few days in the sun for mild sun allergies. You may need over-the-counter, prescription corticosteroid, or phototherapy to enhance the skin’s tolerance to the sun for severe cases.
3. Eczema

You may have eczema if you notice your skin is red, dry, scaly, and itchy. Although eczema occurs very often in children, adults can have eczema too. It usually flares up on the elbows, hands, and feet. Luckily, it is not contagious.
While doctors haven’t pinpointed eczema’s exact cause, we know certain factors like allergens, stress, dry skin, excess climates, and other irritants can trigger eczema. Additionally, eczema makes you more vulnerable to other skin infections.
Naturally, eczema goes away on its own. But you may need to try several medications to eliminate the red, unpleasant itch when it emerges. You can either apply topical medications to your skin or take them orally.
Medications you can take include.
- Antibiotics
- Antihistamines to reduce the itching
- Corticosteroid cream or ointment to ease the itching
- Apply a cold compress to control the itch.
Top tip: Avoid contact with substances that trigger eczema flare-ups on your skin.
4. Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic infection that causes new skin cells to grow faster than usual. Since new skin forms more quickly than you shed off dead skin, skin tends to build up and create thick red patches covered with white or silvery scales. While the patches may be itchy and burn, in extreme cases, psoriasis lumps can bleed too. Psoriasis usually occurs on the elbows, knees, scalp, and back.
Unfortunately, there’s no specific cure for psoriasis. It can flare up on the skin and return to remission weeks after. However, many treatments can manage the symptoms. These treatments are usually administered orally, through light therapy, as ointments on your skin, or intravenously.
Medications you can take to reduce psoriasis include;
- salicylic acid
- vitamin A analogs
- corticosteroid creams
- Topical retinoids
5. Insect Bites and Stings
Aside from the pain accompanying bug bites, their bites can also leave itchy red bumps on your skin. Although they can cause discomfort, most insect bites are usually harmless. Not all bites and stings are the same. For example, mosquito bites produce a small red, round, and puffy bump.
Bites from bed bugs are quite different. Unlike mosquitoes and spider bites, bites from bed bugs produce bigger rashes.
Other insects that can produce itchy red bumps on your skin include;
- Fire Ants
- Bees
- Wasps
- Fleas
- Ticks
- Head Lice
If you enjoy spending time outdoors, you’re likely to get a bit now and then. The good news is most bites fade away in 7–14 days.
The signs of a bug bite show almost immediately. If you notice a bug bite on your skin, quickly wash the area with soap and water.
You can apply a cold compress to the bite mark if the itching is unbearable. Alternatively, you can apply calamine lotion to relieve the itching.
Top tip: Prevention is always better than cure. If you wake up from sleep with bite marks, you may have a bedbug infestation. I recommend you remove all your bedding, and clothes and treat the area with a repellent.
6. Scabies
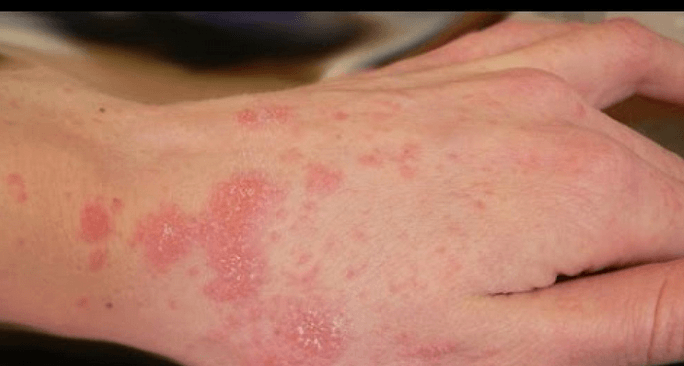
Scabies is a skin disease caused by Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis, a tiny mite. Mites are not easy to find as they can easily penetrate the skin. You may find a small scaly line with a small black spot at the end.
This is a highly contagious infection and is easily spread by sharing things such as towels, bedding, sheets, and clothing with others.
Scabies may cause small red itchy bumps similar to acne and bug bites. Your skin may also be covered with scaly in the infected area. Blisters and pustules may appear on the palms and feet, accompanied by severe itching.
Using prescription drugs is an effective way to treat scabies. If you experience the above symptoms, please see your doctor immediately. And pay attention to personal hygiene and avoid spreading it to others.
7. Dermatitis
Dermatitis is a common chronic skin disease. It can cause blistering, oozing, or flaking off the skin and multiple itchy red bumps filled with pus. Sometimes there is a feeling of swelling, tingling, or burning. Fortunately, in most cases, dermatitis is not contagious.
Usually, it will appear on the back, knees, scalp, elbows, or neck. The leading cause of dermatitis is unclear; it has many forms and may be caused by various things.
Common dermatitis includes contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, neurodermatitis, and nummular dermatitis. Contact dermatitis happens when your skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen.
Dermatitis treatment depends on the cause, type, and severity of symptoms. Mild dermatitis can be treated with home remedies.
First, clean the skin thoroughly with warm soapy water, mix one tablespoon of baking soda with two tablespoons of water to form a paste, and apply it to the skin.
Wait for 10-15 minutes and rinse with water. This method can effectively reduce itching and allergic reaction.
If the symptoms are more serious, you need to see a doctor. Doctors can use antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) to reduce allergies and itching.
How to prevent dermatitis
- Try to avoid scratching, which will aggravate the symptoms and spread the bacteria to other parts of your body.
- Use a neutral soap and bathe in warm water instead of hot water to prevent dry skin.
- Apply water-based moisturizer or oil-based moisturizer on the skin after bathing.
8. Rosacea
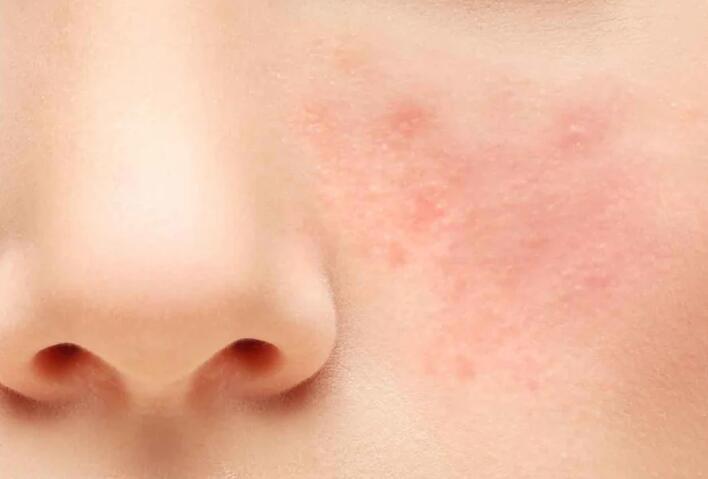

Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that affects the face. Usually, when you have rosacea, you look like you’re always blushing. Your blood vessels become visible through your skin, and it appears flushed. Rosacea also comes with a burning sensation and a swollen, bulb-shaped nose. In addition, you may feel itchy or stinging frequently, as rosacea can cause your face more sensitive.
Unfortunately, rosacea has no known cure. However, many searches found that rosacea usually is triggered by specific ingredients or lifestyle habits. These factors include drinking alcohol, heat, sweating, sun exposure, spicy foods, and contact preservatives or fragrances.
Luckily, some over-the-counter medications could help relieve the symptoms. You can use creams that mask the red patches. You’d better seek your dermatologist when you notice rosacea on your face.
Top tip: Rosacea looks a lot like acne, so they can be very difficult to differentiate. However, standard acne treatment methods don’t work for rosacea.
9. Fifth’s Disease (Slapped cheek syndrome)
Fifth’s Disease is a viral disease caused by parvovirus B19 and comes with a mild red rash. It usually affects the legs, arms, and cheeks (From its name).
Asides from the red rash, you may experience headaches, sore throat, and a runny nose.
Unfortunately, the rash may take several days before it appears. The rash emerges as blotchy red papules on the cheeks when it does. In some cases, the rashes become more pronounced when exposed to the sun.
Luckily, if you have a strong immune system, treatment isn’t necessary. You can wait for the red rash to fade away. It usually takes about 1-3 weeks. Your doctor may also prescribe over-the-counter Tylenol to ease the symptoms.
10. Hay Fever (Allergic Rhinitis)

Hay fever is prevalent in the United States. It affects about 18 million Americans per year. It usually develops when you come in direct contact with pollen from trees, weeds, grasses, and dust.
The symptoms usually include a runny nose, sneezing, coughing, watery eyes, and red, inflamed skin rash. You start noticing the signs immediately after you encounter an allergen. Unfortunately, the rash will persist as long as you remain exposed to the allergen.
Over-the-counter medications like antihistamines can work if your symptoms aren’t too severe. However, in extreme cases, you need to treat the symptoms of Hay fever with allergy shots.
Top tip: Avoid contact with pollen, especially during the pollen season.
11. Keratosis pilaris
Keratosis pilaris, also known as “chicken skin,” is a common skin condition. This is caused by a buildup of keratin(a hard protein) that helps protect the skin from harmful substances and infection.
Keratosis pilaris usually occurs when the buildup blocks the opening of a hair follicle. It can cause dry, rough patches and tiny bumps that typically appear on the cheeks, buttocks, thighs, or upper arms. The small bumps can be brown or reddish, depending on your skin tone.
Keratosis pilaris is a harmless skin condition that isn’t usually hurt or itchy. But it also can be itchy and uncomfortable when the skin gets irritated or too dry. Keratosis pilaris is considered a variant of normal skin that does not need to be treated. In addition, doctors do not know exactly why keratin builds up now. It may be associated with some genetic diseases or other skin conditions, and it usually disappears by age 30.
However, you can reduce the appearance of the bumps with moisturizers and prescription creams. In addition, some products containing exfoliating ingredients like lactic acid or urea can also help improve the appearance of the skin.
Top tip: Make sure to keep the skin moisturized, as dry skin worsens this condition.
12. Folliculitis
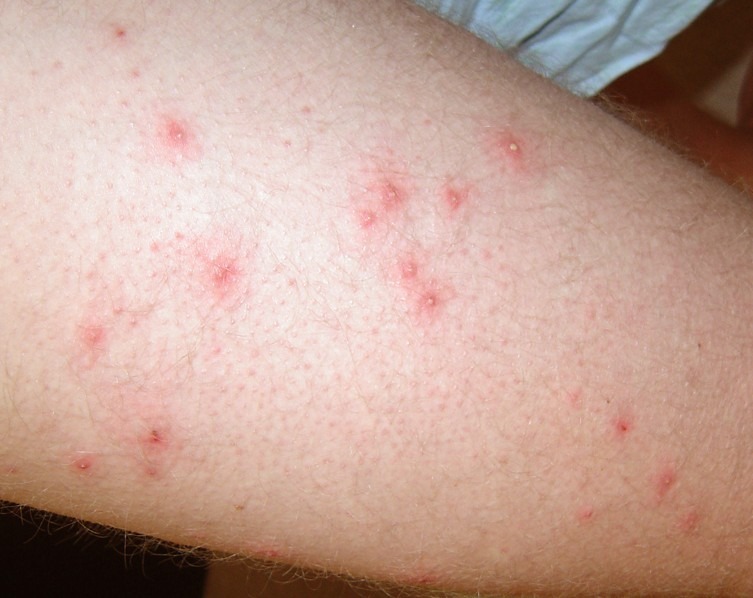
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that can cause tiny red itchy bumps—this inflammation of the hair follicle is caused by a bacterial, chemical, drug, or fungal infection.
Infection of hair follicles from Staphylococcus aureus (staph) bacteria is the most common cause of Folliculitis Folliculitis can occur everywhere on your body that has hair. But it is most common on the buttocks, legs, arms, back, and beard area.
Folliculitis can cause swelling, Pus-filled blisters, small red bumps, or white-headed pimples around the hair follicle. The infection can spread into large swollen nodes or crusty sores. You may feel Itchy, pain, tenderness, or burning skin. Sometimes, severe conditions can lead to scarring and permanent hair loss.
How to treat and prevent folliculitis You can try these tips:
- Wash your skin often with warm water and antibacterial soap.
- Before shaving, smooth the embedded hair with a towel and apply a lot of shaving lotion. Use a sharp blade and rinse with warm water; apply moisturizing lotion after shaving.
- Try to reduce the number of shavings and avoid sharing razors and towels.
- Use hair removal products to reduce skin irritation, and always shave in the direction of hair growth.
- Wear loose clothing and wash clothes with antibacterial soap after each use.
- Use a clean heated swimming pool or bathtub, clean regularly, and add chlorine as recommended.
- If folliculitis is severe, consult your doctor as soon as possible.
Home Remedies to Treat Itchy Red Bumps on Your Skin
Some itchy red bumps stay for a short time; others tend to stay longer. Some skin infections can last a lifetime.
While most rashes can be treated with over-the-counter products like antihistamines and hydrocortisone creams, simple home remedies can relieve symptoms and clear up unsightly rashes in no time.
Here are some remedies you can try for a nasty skin rash.
- Apply a cold compress on the region of the infection will help reduce the swelling and the urge to itch.
- Using a good moisturizer will prevent your skin from breaking. Apply your moisturizer twice a day immediately after you take your bath.
- Apply hydrocortisone, calamine lotion, or anti-itch cream to reduce the urge to itch. Most topical creams are readily available in drug stores or pharmacies.
- If you have sensitive skin, harsh soaps and detergents could worsen the itchy skin. Instead, use skin-sensitive soaps or unscented detergents.
- Avoid scratching. The itch can be intolerable most times. However, scratching your rash can damage your skin or spread it from one area of your body to another. When you feel itchy, you can distract yourself by exercising or playing a game.
- If your body reacts to extreme temperatures, you can take a lukewarm bath to avoid triggering a rash.
- Avoid substances that irritate your skin.