Do you experience a sharp, stabbing pain in your lower back every time you cough? You’re not alone. Many people suffer from lower back pain triggered by coughing. You might wonder, “Why does my lower back hurt when I cough?” Coughing can cause or exacerbate lower back pain due to the sudden, forceful contraction of the muscles in the back. The rapid, repetitive motion puts strain on the muscles, ligaments, and other tissues in the lower back region. In this article, we’ll explore 14 possible reasons why your lower back might hurt when you cough.

Why Does My Lower Back Hurt When I Cough? 14 Potential Causes
1. Muscle Strain
One of the most common causes of lower back pain when coughing is muscle strain. When you cough, your abdominal and back muscles contract forcefully. If these muscles are weak, tight, or overworked, they may become strained or sprained during a coughing fit.
Imagine your back muscles as a team of supportive friends. When they’re strong and well-rested, they can handle the occasional challenge of a coughing fit. But if they’re already tired or strained from poor posture, lack of exercise, or overexertion, coughing can be the last straw that leads to pain and discomfort.
To prevent muscle strain, focus on:
- Maintaining good posture
- Engaging in regular exercise to strengthen your core and back muscles
- Stretching to improve flexibility
- Taking breaks and avoiding overexertion
If you do experience muscle strain, apply ice to the affected area for the first 24-48 hours, then switch to heat. Over-the-counter pain relievers and gentle stretching can also provide relief as you heal.
2. Herniated or Bulging Disc
Another potential cause of lower back pain when coughing is a herniated or bulging disc. The discs in your spine act as cushions between the vertebrae. When a disc becomes damaged or weakened, it can bulge or rupture, putting pressure on nearby nerves and causing pain.
Coughing can put extra pressure on an already compromised disc, leading to that telltale twinge in your lower back. Other symptoms of a herniated disc may include:
- Pain that radiates down your leg
- Numbness or tingling in your leg or foot
- Muscle weakness
If you suspect a herniated disc, it’s important to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis. Treatment may include rest, physical therapy, medications, or in severe cases, surgery.
3. Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a condition in which the spaces within your spine narrow. This will put pressure on the nerves that travel through them. This narrowing can be caused by age-related changes, such as osteoarthritis, or by conditions like scoliosis or spinal tumors.
When you cough, the sudden force can compress the already narrowed spaces in your spine, leading to pain in your lower back. Other symptoms of spinal stenosis may include:
- Pain, numbness, or weakness in your legs
- Difficulty walking or standing for long periods
- Loss of bladder or bowel control (in severe cases)
If you experience these symptoms, see your doctor. They may recommend imaging tests to diagnose spinal stenosis and develop a treatment plan.
4. Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a common age-related condition that causes the cartilage in your joints to break down over time. When it affects the spine, it can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Coughing can aggravate osteoarthritis pain in the lower back by putting extra pressure on the affected joints. Other signs of spinal osteoarthritis include:
- Pain that worsens with activity and improves with rest
- Stiffness in the back, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity
- A grinding sensation when moving the spine
If you suspect osteoarthritis, talk to your doctor. They may recommend lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and staying active, as well as medications.
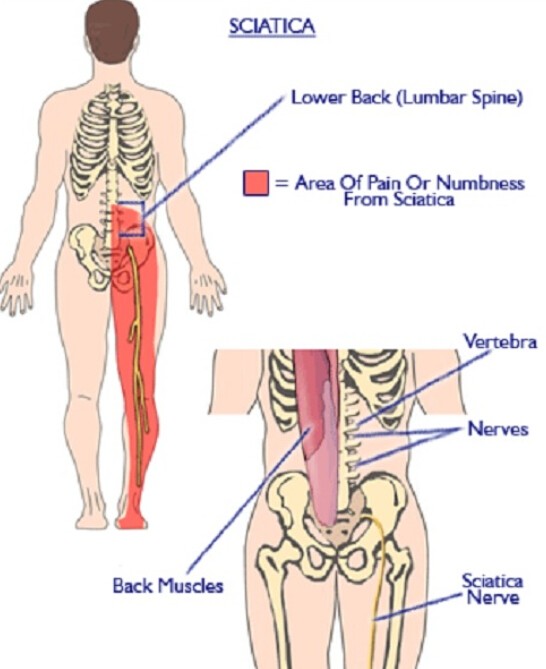
5. Sciatica
Sciatica is a condition that occurs when the sciatic nerve, which runs from your lower back down each leg, becomes compressed or irritated. This can cause pain, numbness, or weakness in your lower back, buttocks, and legs.
Coughing can exacerbate sciatica pain by putting extra pressure on the affected nerve. Other symptoms of sciatica include:
- Pain that radiates down one or both legs
- A burning or tingling sensation in the affected leg
- Weakness or numbness in the affected leg
If you experience these symptoms, see your doctor. They may recommend treatments such as physical therapy, and medications. In some cases, surgery to relieve pressure on the sciatic nerve.
6. Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition in which the spine curves abnormally to the side. It can be present from birth or develop during childhood or adolescence. In some cases, scoliosis can cause lower back pain, especially during activities that put extra stress on the spine, like coughing.
Other signs of scoliosis include:
- Uneven shoulders or hips
- One shoulder blade appears more prominent than the other
- A visible curve in the spine
If you suspect scoliosis, see your doctor for an evaluation. Treatment may include monitoring the curve, wearing a brace, or in severe cases, surgery to correct the curvature.
7. Spinal Tumors
In rare cases, lower back pain when coughing could be a sign of a spinal tumor. Tumors can grow within the spinal cord, on the membranes covering the spinal cord. As they grow, they can put pressure on the nerves and cause pain.
Other symptoms of spinal tumors may include:
- Back pain that worsens at night
- Numbness, weakness, or tingling in the arms or legs
- Difficulty walking or standing
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
If you experience these symptoms, see your doctor right away. They may order imaging tests to diagnose a spinal tumor and develop a treatment plan. This could include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
8. Spinal Infections
Spinal infections, such as osteomyelitis (infection of the vertebrae) or discitis (infection of the discs), can cause lower back pain that worsens with coughing. These infections can be caused by bacteria, fungi, or tuberculosis and may spread to the spine from other parts of the body.
Other symptoms of spinal infections include:
- Fever and chills
- Night sweats
- Unexplained weight loss
- Redness, warmth, or swelling in the affected area
If you suspect a spinal infection, seek medical attention promptly. Your doctor may order blood tests and imaging studies to diagnose the infection and prescribe antibiotics or other treatments to clear it.
9. Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine. It causes inflammation in the vertebrae and sacroiliac joints, leading to pain and stiffness in the lower back, hips, and buttocks.
Coughing can aggravate ankylosing spondylitis pain by putting extra stress on the inflamed joints. Other symptoms of this condition include:
- Pain and stiffness that worsen with inactivity and improve with movement
- Fatigue
- Eye inflammation (uveitis)
- Difficulty taking deep breaths
If you experience these symptoms, see a rheumatologist. They may recommend treatments such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), physical therapy, or biologic medications to manage inflammation and prevent joint damage.
10. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition that causes bones to become weak and brittle, increasing the risk of fractures. When it affects the spine, it can lead to compression fractures in the vertebrae, causing sudden, severe back pain that may worsen with coughing.
Other signs of osteoporosis include:
- Loss of height over time
- A stooped or hunched posture
- Back pain that improves with rest
If you suspect osteoporosis, talk to your doctor. They may recommend a bone density test to diagnose the condition and suggest treatments to strengthen your bones.
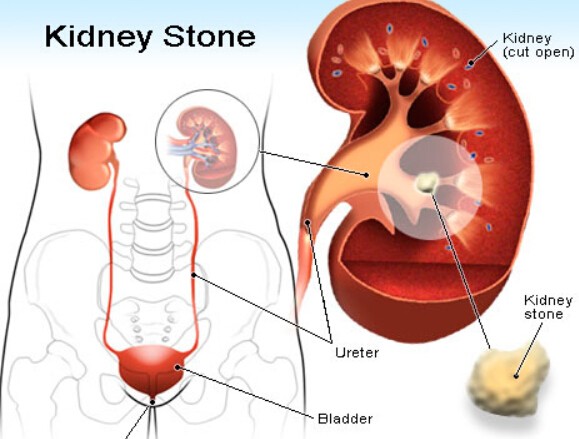
11. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that can form in the kidneys and cause severe pain as they pass through the urinary tract. While kidney stone pain is typically felt in the side and back, it can sometimes radiate to the lower back and be aggravated by coughing.
Other symptoms of kidney stones include:
- Sharp, cramping pain in the side and back
- Pain that comes in waves and varies in intensity
- Pain or burning sensation during urination
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Blood in the urine
If you suspect a kidney stone, see your doctor. They may recommend imaging tests to diagnose the stone and suggest treatments such as pain medications, drinking plenty of fluids, or in some cases, surgery to remove the stone.
12. Pleurisy
Pleurisy is an inflammation of the pleura, the thin membrane that lines the lungs and chest wall. It can cause sharp chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing. In some cases, this pain may be felt in the lower back, especially if the inflammation is near the diaphragm.
Other symptoms of pleurisy include:
- Shortness of breath
- Cough
- Fever and chills (if caused by an infection)
If you experience these symptoms, see your doctor. They may order imaging tests to diagnose pleurisy and recommend treatments such as anti-inflammatory medications, antibiotics (if caused by a bacterial infection), or procedures to remove excess fluid from the chest cavity.
13. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, causing them to fill with fluid or pus. It can cause coughing, and chest pain. In some cases, lower back pain is due to the strain on the muscles and joints from frequent coughing.
Other symptoms of pneumonia include:
- Fever and chills
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
If you suspect pneumonia, see your doctor right away. They may order chest X-rays and blood tests to diagnose the infection and prescribe antibiotics to treat it.
14. Lung Cancer
In rare cases, lower back pain when coughing could be a sign of lung cancer. Tumors in the lungs can cause persistent coughing, which may lead to back pain due to the strain on the muscles and joints. Lung cancer may also cause back pain if it spreads to the bones in the spine.
Other symptoms of lung cancer include:
- Coughing up blood
- Chest pain
- Hoarseness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Shortness of breath
If you experience these symptoms, especially if you have a history of smoking, see your doctor promptly. They may order imaging tests and biopsies to diagnose lung cancer and develop a treatment plan.

Best Home Remedies for Lower Back Hurt When Cough
1. Apply Heat or Cold Therapy
One of the simplest and most effective ways to ease back pain is by applying heat or cold to the affected area. Heat therapy helps relax tense muscles, improves blood flow, and reduces pain. You can use a heating pad, warm compress, or even take a warm bath to soothe your aching back.
On the flip side, cold therapy works by reducing inflammation and numbing pain. Try applying an ice pack or cold compress to your lower back for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. Just be sure to wrap the ice in a towel to protect your skin.
2. Practice Proper Coughing Techniques
Believe it or not, the way you cough can have a big impact on your back. When you feel a cough coming on, try to keep your back in its natural arch instead of hunching forward. This helps distribute the force of the cough more evenly and reduces strain on your lower back.
Another helpful trick is to place your hand on a stable surface like a desk or countertop when you cough. This simple action can decrease the compressive effects on your spine and minimize discomfort.
3. Take Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen can be a lifesaver when it comes to managing back pain. These medications work by reducing inflammation and providing temporary relief from discomfort. Just be sure to follow the recommended dosage and talk to your doctor if you have any concerns.
4. Try Gentle Stretches and Exercises
While it may seem counterintuitive, staying active can help alleviate back pain. Gentle stretches and low-impact exercises like walking or swimming can help reduce muscle tension, improve flexibility, and promote healing.
Just be sure to listen to your body and avoid any movements that cause pain. If you’re unsure where to start, consider working with a physical therapist who can develop a personalized exercise plan for you.
5. Get a Massage
There’s nothing quite like a soothing massage to melt away tension and ease back pain. Massaging the affected area can help relax tight muscles, improve circulation, and promote relaxation.
You can try self-massage using a foam roller or massage ball, or treat yourself to a professional massage from a licensed therapist. Just be sure to communicate any areas of discomfort and let your therapist know if the pressure is too intense.
6. Consider Acupuncture
If you’re open to alternative therapies, acupuncture may be worth a try. This ancient Chinese practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to alleviate pain and promote healing.
While more research is needed to fully understand how acupuncture works, many people find it to be an effective way to manage back pain. Just be sure to choose a licensed and experienced acupuncturist for your treatment.
When to See a Doctor?
While occasional lower back pain when coughing is usually not a cause for concern, there are times when it’s important to see a doctor. Seek medical attention if:
- Your pain is severe or persistent
- You have numbness, weakness, or tingling in your legs
- You experience loss of bladder or bowel control
- You have a fever, unexplained weight loss, or other concerning symptoms
- Your pain interferes with your daily activities or quality of life
Your doctor can help diagnose the underlying cause of your pain and recommend appropriate treatments to help you find relief and prevent further complications.