Potassium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. While it is commonly associated with its ability to regulate blood pressure, potassium also offers numerous benefits for weight loss. This article will explore the 12 ways Potassium can help you lose weight.
What is Potassium?
Potassium is an essential mineral and electrolyte that is vital for the proper functioning of the human body. It is classified as an electrolyte because it carries an electric charge when dissolved in bodily fluids, such as blood and cells.
Potassium plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions. It is also involved in regulating blood pressure, supporting heart health, and promoting proper kidney function.
Potassium and Weight Loss Connection Study
A study published in 2019 examined the relationship between changes in potassium intake and weight loss in overweight and obese adults on calorie-restricted diets. It found that participants who had greater increases in potassium intake during the diet also experienced greater reductions in BMI (body mass index).
Specifically, for every 1 gram per day increment in potassium intake, participants lost an additional 0.3 kg of body weight over the 6 month study. This suggests higher potassium consumption is associated with enhanced weight loss results on energy-restricted diets.

12 Ways Potassium Helps You Lose Weight
Below we detail the 12 major research-backed ways that ensuring optimal potassium intake promotes weight loss.
1. Potassium Reduces Water Retention and Bloating
Water retention leads to bloating, puffiness, and temporary weight gain from fluid accumulation. Potassium acts as a key electrolyte to help balance sodium levels. It works against sodium to reduce water retention in the cells and tissues.
Multiple studies confirm potassium supplementation significantly reduces water retention, especially in women prone to bloating during specific hormonal phases.
Consuming adequate potassium alleviates water retention under the skin and around the stomach, decreasing abdominal bloating. This leads to a slimmer, leaner appearance as fluid puffiness subsides.
2. Potassium Lowers Blood Pressure
Research demonstrates that obesity and excess weight put you at high risk for hypertension and elevated blood pressure. When blood vessels narrow it makes the heart pump harder to circulate blood, increasing strain on the cardiovascular system.
Potassium helps relax blood vessel walls, lowering blood pressure levels. It acts as a vasodilator to counterbalance sodium and open up constricted vessels that contribute to hypertension.
Population studies show that people with the highest dietary potassium intakes have up to a 20% reduced risk of developing high blood pressure compared to those with the lowest intakes.
Keeping blood pressure levels within a healthy range is key for heart health and sustainable weight management.
3. Potassium Improves Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin resistance is one of the leading precursors to weight gain and obesity. When cells stop responding properly to the hormone insulin, it causes chaos in the metabolism. Blood sugar and fat storage dysregulation occur, resulting in weight accumulation, particularly around the abdominal region.
Research confirms that getting higher levels of potassium markedly improves insulin sensitivity in insulin-resistant individuals. This allows cells to efficiently uptake glucose again, restoring healthy blood sugar balance.
Higher dietary potassium intakes are associated with up to a 30% lower risk of developing insulin resistance leading to type 2 diabetes.
4. Potassium Preserves Muscle Mass While Losing Fat
Losing weight without losing muscle is key to keeping your metabolism revved up. But most forms of dieting lead to some degree of muscle loss in addition to fat loss. Some diets can strip away significant muscle, drastically slowing metabolic rate.
Consuming adequate potassium helps preserve lean muscle mass as you drop excess pounds of body fat. It reduces protein breakdown in the muscles while enhancing protein synthesis, especially after exercise. Athletes supplementing with potassium experience less muscle damage and enhanced muscle repair and growth.
The more muscle you can hold onto while losing weight, the better your metabolism and fat-burning capacity will remain. Potassium supports fat loss without muscle waste.
5. Potassium Boosts Metabolism Through Multiple Mechanisms
Science confirms potassium plays many intricate roles in fueling metabolism. It helps convert carbohydrates into usable energy rather than stored body fat. Potassium also enhances the way your body utilizes stored fat as fuel through fatty acid oxidation.
Research also demonstrates that potassium helps support the adrenal glands which regulate the body’s metabolic response to stressors like dieting and exercise.
Individuals who test low in potassium see significant improvements in their resting metabolic rates when supplementing with potassium. This shows the potent effects adequate potassium status plays in stoking the metabolic fire.

6. Potassium Alleviates Stress and Anxiety While Dieting
Stress triggers the release of the hormone cortisol, which acts as a messenger signaling your body to store more abdominal and hip fat. It’s your body’s way of providing extra fuel reserves to counter the strain from high stress. However, this stress-induced fat storage tends to accumulate around the midsection, contributing to weight gain.
Potassium helps regulate electrolyte imbalances that frequently occur when you feel stressed, anxious, or overwhelmed. Consuming more potassium can help decrease both anxiety and cortisol levels. This prevents stress-triggered fat storage during weight loss attempts.
7. Potassium Supports Muscle Growth and Prevents Muscle Wasting
Building or at least maintaining muscle mass equals a faster, more robust metabolism. The more muscle you have, the more calories and fat you burn 24/7. Resistance training is excellent for building metabolically active muscle mass. But hard exercise also damages muscle tissue, allowing muscle breakdown to occur.
Consuming adequate potassium supports optimal protein synthesis, boosting the repair and growth of muscle tissue in response to exercise.
Potassium also attenuates the protein breakdown that occurs from intense training and even fasting. The more potassium you get, the more muscle you can build and the less muscle tissue you waste from dietary restrictions.
8. Potassium Improves Digestion and Nutrient Absorption
Sub-optimal digestion prevents you from fully breaking down and assimilating all the nutrients from the foods you eat. Poor digestion allows calories and macronutrients to escape absorption and be eliminated unused.
Research shows potassium activates key enzymes needed for the efficient digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, proteins, and other compounds.
Potassium ensures you adequately break down nutrients from food and draw them into the bloodstream for use. Healthy digestion supported by potassium means you fully access and utilize the calories you consume.
9. Potassium Alleviates Bloating and Water Weight Gain
Bloating makes your stomach look significantly bigger, preventing you from seeing weight loss results on the scale or in the mirror. Even minor bloat can hide fat loss success. Excess abdominal bloating also puts pressure on your internal organs.
Consuming adequate potassium balances sodium levels, reducing bloat caused by fluid retention and water weight gain. Multiple studies confirm potassium supplementation meaningfully decreases temporary water weight gain and stomach bloating episodes.

10. Potassium Prevents Cramps and Fatigue Dragging You Down
Muscle cramps and fatigue are common side effects of dietary restrictions, calorie deficits, and increased activity levels associated with losing weight. Leg, foot, and abdominal cramps can strike at night or during workouts. General fatigue, weakness, and low energy also frequently occur.
These issues can severely undermine your weight loss progress. Muscle cramps and debilitating fatigue destroy your ability to be active and exercise. Low energy sinks motivation and determination.
Research shows potassium prevents the lactic acid build-up in muscle tissue that contributes to cramping and fatigue. It also optimizes the way muscles utilize energy for contraction. This allows muscles to function at peak levels during exercise instead of tiring early.
11. Potassium Helps Regulate Fluid Balance to Prevent Puffiness
Maintaining optimal fluid balance in the body prevents puffiness, swelling, and water weight gain that hides fat loss. Fluid accumulation in the skin and abdomen leads to a puffy appearance lacking muscle definition.
But fluid imbalance also strains organs like the heart and kidneys. Consuming adequate potassium allows it to act as a key electrolyte that precisely regulates fluid balance.
12. Potassium Boosts Energy Levels to Keep You Active
Inadequate potassium frequently manifests in low energy, fatigue, weakness, and generally feeling run down. Without enough potassium, your cells simply can’t produce adequate ATP energy. This destroys motivation to exercise and be active as fatigue takes over.
Maintaining optimal potassium levels reduces fatigue. This can help energy stays higher for exercising, working, playing with kids, and all other daily activities. Keeping energy levels up prevents fatigue-induced inactivity.
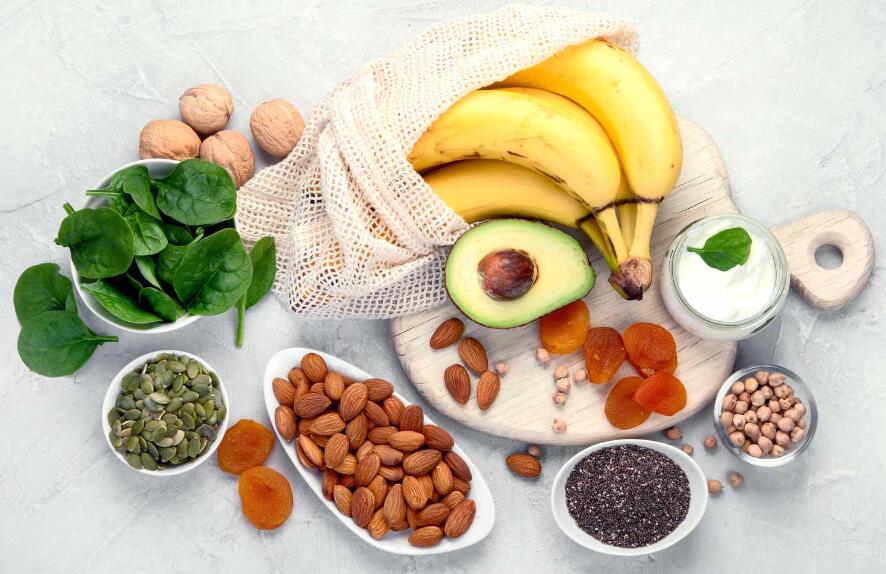

How To Use Potassium For Weight Loss?
Here are the top tips for effectively using potassium’s weight loss benefits:
1. Focus On Potassium-Rich Foods First
Aim to obtain as much of your daily potassium needs as possible from whole food sources like fruits, vegetables, beans, fish, and yogurt. Potassium-rich foods provide better nutrient balance and absorption compared to supplements alone.
Excellent dietary sources of potassium include leafy greens like spinach, nutrient-dense potatoes, bananas, avocados, salmon, beans, and lentils. Tracking intake through apps can help ensure optimal consumption.
2. Take Potassium Supplements If Deficient
Those following calorie-restricted diets for weight loss tend to lower their potassium intake along with overall calories. Chronically low dietary potassium coupled with fluid loss from workouts can lead to deficiency over time.
Mild potassium deficiency doesn’t always cause overt symptoms but can stall weight loss efforts and metabolism. Testing levels through bloodwork can reveal if supplementation is warranted.
Under medical supervision, potassium supplements ranging from 100-400mg per day may aid weight loss results if low levels are detected. This helps optimize potassium status to allow its weight loss benefits to fully manifest.
3. Stay Well Hydrated Daily
Drinking adequate water and fluid daily is especially important when increasing potassium intake for weight loss. Potassium and water balance each other in the body. Consuming more potassium can increase fluid needs.
Chronic dehydration is also detrimental to weight loss, causing fatigue, poor digestion, fluid retention, and metabolic issues. Aim for around 2-3 liters of total fluid daily from water, herbal tea, vegetables, and low-sugar fruits.
4. Combine With Exercise and Metabolic Support
While beneficial on its own, potassium works best as part of a comprehensive weight loss plan including regular exercise, calorie control, metabolism-optimizing nutrition, and stress reduction.
The multi-faceted approach maximizes potassium’s mechanisms to reduce fluid retention, build muscle, improve insulin function, and prevent fatigue for better weight loss capacity. Aim for 30-60 minutes of cardio and strength training most days along with a nutritious, balanced diet.
Top 10 Potassium-Rich Foods
Here is an expanded list of the top 10 potassium-rich foods with more details on each:
1. Swiss Chard
Swiss chard is one of the absolute best sources of dietary potassium. Just one cup of cooked Swiss chard provides a whopping 960 milligrams of potassium.
That’s about 28% of the recommended daily intake. Swiss chard also delivers fiber, vitamin K, vitamin A, vitamin C, magnesium, and more. Add some Swiss chard to soups, stews, casseroles, or sauté with olive oil and garlic.
2. Spinach
Spinach is another leafy green rockstar when it comes to potassium content. One cup of cooked spinach contains 839 milligrams of potassium. Spinach also provides vitamin A, vitamin K, folate, magnesium and more. Spinach is delicious raw in salads but also stands up well to cooking. You can add it to eggs, pasta, casseroles, or stir-fries.
3. Avocado
Avocados offer a unique blend of heart-healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants along with lots of potassium – 708 milligrams per cup! Avocados lend their creamy, rich flavor to sandwiches, salads, and salsas. Their fat content allows them to be used in smoothies or even chocolate pudding.
4. Sweet Potato
A medium-baked sweet potato with skin packs 700 milligrams of potassium. Sweet potatoes also provide fiber, vitamin A, and vitamin C. You can add sweet potato to stews or chili or turn them into a creamy, potassium-rich soup.
5. Bok Choy
One cup of cooked bok choy delivers 630 milligrams of potassium along with vitamin C, vitamin A, and calcium. Bok choy has a mild flavor that works well in stir-fries, soups, and stews. Try adding some shredded bok choy to eggs or grain bowls too.
6. Potatoes
Plain potatoes are an underrated source of potassium, with 610 milligrams per medium spud. Opt for potatoes with the skin for more fiber and nutrients. Beyond baked potatoes and mashed potatoes, also try roasted potato wedges or cubes, potato salad, or hashbrowns.
7. White Beans
Just half a cup of cooked white beans provides 600 milligrams of potassium along with protein and fiber. Cannellini and great northern beans are the highest. Beans work well in soups, stews, pasta dishes, casseroles, dips, and more. Puree them for a creamy, high-potassium spread.
8. Beets
One cup of cooked beets delivers 518 milligrams of potassium along with fiber, folate, and manganese. Beets lend their vibrant color and earthy flavor to salads, slaws, soups, and sandwiches. Roast or steam and top with lemon juice and olive oil.
9. Brussels Sprouts
A cup of cooked Brussels sprouts has 500 milligrams of potassium. It also has fiber, folate, vitamin C and vitamin K. Roast Brussels sprouts with olive oil, sea salt, and pepper or quickly stir fry with garlic.
10. Broccoli
One cup of cooked broccoli florets provides 457 milligrams of potassium. In addition, it provides vitamin C and vitamin K. Broccoli is so versatile. You can add it to pasta, pizza, casseroles, soups, and egg dishes, or eat it raw with dip.